|
[1] Kou YH,Yin XF,Zhang PX,et al.Small-gap bridging technology for peripheral nerve injury repair and the new sleeve material. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao. 2011;43(5):647-651.
[2] Zhang PX,Kou YH,Han N,et al.Clinical effect observation of biodegradable conduit small gap tublization repairing peripheral nerve injury. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao.2012; 44(6):842-846.
[3] Zhang PX,An S,Wang GQ,et al.Pain assessment of biological conduit small gap tubulization in rat sciatic nerve multilation model. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao.2013;45(5): 675-678.
[4] 朱国臣,肖大江,娄卫华.去细胞异体神经桥接面神经缺损的实验研究[J].中华创伤杂志,2005,21(11):54-56.
[5] 衷鸿宾,卢世璧,侯树勋,等.去细胞神经同种异体移植的运动功能恢复.中华创伤杂志,2002,18(9):20-222.
[6] 衷鸿宾,卢世璧,侯树勋,等.犬化学去细胞神经同种异体移植的神经电生理研究[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,2003,18(1):30-32.
[7] 梁安霖.复合gdnf和vegf质粒的异体脱细胞神经支架对大鼠坐骨神经缺损的修复作用[D].重庆医科大学,2006.
[8] 张旭,才艳红,贾桦,等.异种神经脱细胞移植物修复周围神经缺损的实验研究[J].解剖科学进展,2007,13(1):46-48,98.
[9] 何红云,邓仪昊,朱建华,等.异种脱细胞神经移植物修复坐骨神经缺损的实验研究[J].实用医学杂志,2011,27(24):4392-4395.
[10] 谢会斌.异种生物型神经导管修复周围神经缺损的实验研究[D]. 广州中医药大学,2009.
[11] Cullen DK,Tang-Schomer MD,Struzyna LA,et al.Microtissue engineered constructs with living axons for targeted nervous system reconstruction. Tissue Eng Part A.2012;18(21-22): 2280-2289.
[12] Liu T,Houle JD,Xu J,et al.Nanofibrous collagen nerve conduits for spinal cord repair.Tissue Eng Part A.2012;18(9-10): 1057-1066.
[13] Zaminy A,Shokrgozar MA,Sadeghi Y,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells as an alternative for Schwann cells in rat spinal cord injury.Iran Biomed J.2013;17(3):113-122.
[14] East E,de Oliveira DB,Golding JP,et al.Alignment of astrocytes increases neuronal growth in three-dimensional collagen gels and is maintained following plastic compression to form a spinal cord repair conduit.Tissue Eng Part A.2010; 16(10):3173-3184.
[15] Han Q,Sun W,Lin H,et al.Linear ordered collagen scaffolds loaded with collagen-binding brain-derived neurotrophic factor improve the recovery of spinal cord injury in rats.Tissue Eng Part A.2009;15(10):2927-2935.
[16] Ghaznavi AM,Kokai LE,Lovett ML,et al.Silk fibroin conduits: a cellular and functional assessment of peripheral nerve repair. Ann Plast Surg.2011;66(3):273-279.
[17] Mottaghitalab F,Farokhi M,Zaminy A,et al.A biosynthetic nerve guide conduit based on silk/SWNT/fibronectin nanocomposite for peripheral nerve regeneration. PloS One.2013;8(9): e74417.
[18] Sharp KG,Dickson AR,Marchenko SA,et al.Salmon fibrin treatment of spinal cord injury promotes functional recovery and density of serotonergic innervation.Exp Neurol.2012; 235(1):345-356.
[19] Johnson PJ,Parker SR,Sakiyama-Elbert SE.Controlled release of neurotrophin-3 from fibrin-based tissue engineering scaffolds enhances neural fiber sprouting following subacute spinal cord injury.Biotechnol Bioeng.2009;104(6):1207-1214.
[20] Gao M,Lu P,Bednark B,et al.Templated agarose scaffolds for the support of motor axon regeneration into sites of complete spinal cord transection.Biomaterials.2013;34(5): 1529-1536.
[21] do Nascimento-Elias AH,Fresnesdas BC,Schiavoni MC,et al.Identification of adequate vehicles to carry nerve regeneration inducers using tubulisation.BMC Neurosci.2012; 13:100.
[22] Ezra M,Bushman J,Shreiber D,et al.Enhanced femoral nerve regeneration after tubulization with a tyrosine-derived polycarbonate terpolymer: effects of protein adsorption and independence of conduit porosity.Tissue Eng Part A.2014; 20(3-4):518-528.
[23] Sharma AK,Bury MI,Fuller NJ,et al.Cotransplantation with specific populations of spina bifida bone marrow stem/progenitor cells enhances urinary bladder regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2013;110(10):4003-4008.
[24] Wang Y,Zhao Z,Zhao B,et al.Biocompatibility evaluation of electrospun aligned poly (propylene carbonate) nanofibrous scaffolds with peripheral nerve tissues and cells in vitro. Chin Med J (Engl).2011;124(15):2361-2366.
[25] 朱惠光,计剑,高长有,等.聚乳酸组织工程支架材料[J].功能高分子学报,2001,14(4):488-492.
[26] Thomas AM,Kubilius MB,Holland SJ,et al.Channel density and porosity of degradable bridging scaffolds on axon growth after spinal injury.Biomaterials.2013;34(9): 2213-2220.
[27] Tuinstra HM,Aviles MO,Shin S,et al.Multifunctional, multichannel bridges that deliver neurotrophin encoding lentivirus for regeneration following spinal cord injury. Biomaterials.2012;33(5):1618-1626.
[28] Rui J,Dadsetan M,Runge MB,et al.Controlled release of vascular endothelial growth factor using poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid microspheres: in vitro characterization and application in polycaprolactone fumarate nerve conduits. Acta Biomaterialia. 2012;8(2): 511-518.
[29] Reid AJ,de Luca AC,Faroni A,et al.Long term peripheral nerve regeneration using a novel PCL nerve conduit.Neurosci Lett. 2013;544:125-130.
[30] Chen BK,Knight AM,Madigan NN,et al.Comparison of polymer scaffolds in rat spinal cord: a step toward quantitative assessment of combinatorial approaches to spinal cord repair. Biomaterials.2011;32(32):8077-86.
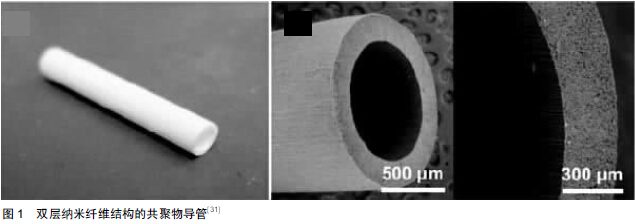
[31] Zhu Y,Wang A,Patel S,et al.Engineering bi-layer nanofibrous conduits for peripheral nerve regeneration.Tissue Eng Part C Methods.2011;17(7):705-715.
[32] Wang A,Tang Z,Park IH,et al.Induced pluripotent stem cells for neural tissue engineering.Biomaterials.2011;32(22): 5023-5032.
[33] 杜江华,杨青芳,张楠楠,等.聚羟基丁酸酯支架在组织工程中的应用[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(37):114-116.
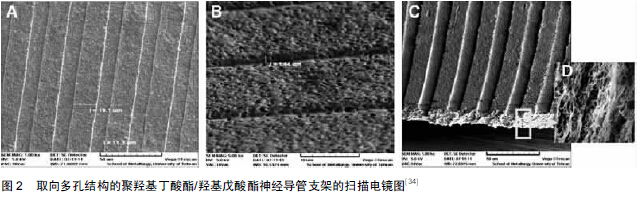
[34] Karimi M,Biazar E,Keshel SH,et al.Rat sciatic nerve reconstruction across a 30 mm defect bridged by an oriented porous PHBV tube with Schwann cell as artificial nerve graft. ASAIO J.2014;60(2):224-233.
[35] Zhang YG,Huang JH,Hu XY,et al.Omentum-wrapped scaffold with longitudinally oriented micro-channels promotes axonal regeneration and motor functional recovery in rats. PloS One. 2011;6(12):e29184.
[36] Yu W,Zhao W,Zhu C,et al.Sciatic nerve regeneration in rats by a promising electrospun collagen/poly(epsilon-caprolactone) nerve conduit with tailored degradation rate. BMC Neurosci. 2011;12:68.
[37] Radtke C,Allmeling C,Waldmann KH,et al.Spider silk constructs enhance axonal regeneration and remyelination in long nerve defects in sheep.PloS One.2011;6(2): e16990.
[38] Hronik-Tupaj M,Raja WK,Tang-Schomer M,et al.Neural responses to electrical stimulation on patterned silk films.J Biomed Mater Res A.2013;101(9):2559-2572.
[39] Purcell EK,Naim Y,Yang A,et al.Combining topographical and genetic cues to promote neuronal fate specification in stem cells. Biomacromolecules.2012;13(11): 3427-3438. |