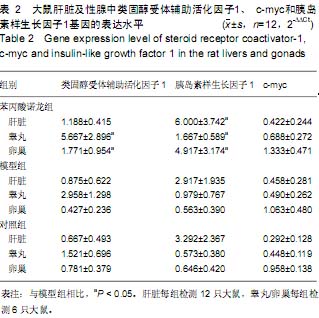
| [1] Jahoor F, Desai M, Herndon DN, et al. Dynamics of the protein metabolic response to burn injury. Metabolism. 1988; 37(4):330-337.
[2] Cerra FB. Hypermetabolism, organ failure, and metabolic support. Surgery. 1987;101(1):1-14.
[3] Mendenhall CL, Moritz TE, Roselle GA, et al. A study of oral nutritional support with oxandrolone in malnourished patients with alcoholic hepatitis: results of a Department of Veterans Affairs cooperative study. Hepatology. 1993;17(4):564-576.
[4] Demling RH. Comparison of the anabolic effects and complications of human growth hormone and the testosterone analog, oxandrolone, after severe burn injury. Burns. 1999; 25(3):215-221.
[5] 罗旭松,岑瑛,刘晓雪,等.苯丙酸诺龙治疗严重烧伤患者的临床观察[J].中华烧伤杂志,2001,17(3):188.
[6] 李凯,岑瑛,刘晓雪,等.苯丙酸诺龙对烧伤大鼠肝脏和性腺雄激素受体表达的影响[J].四川大学学报:医学版,2003,34(4):708-710.
[7] 岑瑛,李凯,刘晓雪,等.苯丙酸诺龙对烧伤大鼠肝细胞白蛋白mRNA和雄激素受体表达的影响[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2003,17(6):439-441.
[8] 岑瑛,李凯,刘宁,等.苯丙酸诺龙对烧伤大鼠肝脏白蛋白与创面前胶原蛋白mRNA表达的影响[J].四川大学学报:医学版, 2004, 35(1):77-79.
[9] 岑瑛,刘宁,李凯,等.苯丙酸诺龙对烧伤大鼠创面成纤维细胞的影响[J].四川大学学报:医学版,2004,35(4):508-511.
[10] 刘宁,岑瑛,李凯,等.苯丙酸诺龙对大鼠成纤维细胞增殖作用的研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2005,19(1):42-44.
[11] 达明绪,马克娴,段体武.烧伤对垂体-睾丸轴影响的临床研究[J].中华整形烧伤外科杂志,1999,15(5):373-375.
[12] Basaria S, Wahlstrom JT, Dobs AS. Clinical review 138: Anabolic-androgenic steroid therapy in the treatment of chronic diseases. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86(11): 5108-5417.
[13] Dickerman RD, Pertusi RM, Zachariah NY, et al. Anabolic steroid-induced hepatotoxicity: is it overstated? Clin J Sport Med. 1999;9(1):34-39.
[14] Demling RH. Oxandrolone, an anabolic steroid, enhances the healing of a cutaneous wound in the rat. Wound Repair Regen. 2000;8(2):97-102.
[15] Whitney AC, Clark AS. Effects of acute stanozolol treatment on puberty in female rats. Biol Reprod. 2001;64(5):1460-1465.
[16] 霍涌玮,邱曙东,程健,等.雄激素受体在大鼠睾丸发育过程中表达及雄激素对其表达的调节作用[J].西安医科大学学报, 2001, 22(3):193-196.
[17] Takala J, Ruokonen E, Webster NR, et al. Increased mortality associated with growth hormone treatment in critically ill adults. N Engl J Med. 1999;341(11):785-792.
[18] Dumelow NW, Sinnett-Smith PA, Pearson JT, et al. Effect of nandrolone phenylpropionate on protein metabolism in rats. Horm Metab Res. 1985;17(8):431.
[19] 顾军,黎介寿,李维勤,等.重组生长激素对严重感染后蛋白质代谢影响的实验研究[J].中华外科杂志,1997,35(2):104-107.
[20] Sheffield-Moore M. Androgens and the control of skeletal muscle protein synthesis. Ann Med. 2000;32(3):181-186.
[21] Menard CS, Harlan RE. Up-regulation of androgen receptor immunoreactivity in the rat brain by androgenic-anabolic steroids. Brain Res. 1993;622(1-2):226-236.
[22] Lynch CS, Story AJ. Dihydrotestosterone and estrogen regulation of rat brain androgen-receptor immunoreactivity. Physiol Behav. 2000;69(4-5):445-453.
[23] Abu-Shakra SR, Nachtman FC. Anabolic steroids induce skeletal muscle injury and immediate early gene expression through a receptor-independent mechanism. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995;761:395-399.
[24] Demling RH, DeSanti L. Oxandrolone, an anabolic steroid, significantly increases the rate of weight gain in the recovery phase after major burns. J Trauma. 1997;43(1):47-51.
[25] Boada LD, Fernández L, Zumbado M, et al. Identification of a specific binding site for the anabolic steroid stanozolol in male rat liver microsomes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996;279(3): 1123-1129.
[26] 穆小民,刘以训.核受体及其转录活化机制研究的新突破-辅活化子和辅阻遏子[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,1998,25(3): 222-226.
[27] 杜国光,李平风,顾文霞.辅调节因子在核受体基因表达调控中的作用[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2000,16(5):565-568.
[28] 黎鳌,杨宗诚.烧伤治疗学[M].2版.北京:人民卫生出版社,1995: 650-657.
[29] Schmittgen TD. Real-time quantitative PCR. Methods. 2001; 25(4):383-385.
[30] Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402-408.
[31] Klein D. Quantification using real-time PCR technology: applications and limitations. Trends Mol Med. 2002;8(6): 257-260.
[32] Wong IH, Leung T, Ho S, et al. Semiquantification of circulating hepatocellular carcinoma cells by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. Br J Cancer. 1997; 76(5):628-633.
[33] Mahajan MA, Das S, Zhu H, et al. The nuclear hormone receptor coactivator NRC is a pleiotropic modulator affecting growth, development, apoptosis, reproduction, and wound repair. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24(11):4994-5004.
[34] Misiti S, Koibuchi N, Bei M, et al. Expression of steroid receptor coactivator-1 mRNA in the developing mouse embryo: a possible role in olfactory epithelium development. Endocrinology. 1999;140(4):1957-1960.
[35] Wong CW, Komm B, Cheskis BJ. Structure-function evaluation of ER alpha and beta interplay with SRC family coactivators. ER selective ligands. Biochemistry. 2001; 40(23): 6756-6765.
[36] Nishikawa J, Saito K, Goto J, et al. New screening methods for chemicals with hormonal activities using interaction of nuclear hormone receptor with coactivator. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1999;154(1):76-83.
[37] Martinez de Arrieta C, Koibuchi N, Chin WW. Coactivator and corepressor gene expression in rat cerebellum during postnatal development and the effect of altered thyroid status. Endocrinology. 2000;141(5):1693-1698.
[38] Carson-Jurica MA, Schrader WT, O'Malley BW. Steroid receptor family: structure and functions. Endocr Rev. 1990; 11(2): 201-220.
[39] Fujimoto N, Mizokami A, Harada S, et al. Different expression of androgen receptor coactivators in human prostate. Urology. 2001;58(2):289-294.
[40] Ravaglia G, Forti P, Maioli F, et al. Body composition, sex steroids, IGF-1, and bone mineral status in aging men. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2000;55(9):M516-521.
[41] Youl Kang H, Hwan Kim S, Jun Lee W, et al. Effects of ginseng ingestion on growth hormone, testosterone, cortisol, and insulin-like growth factor 1 responses to acute resistance exercise. J Strength Cond Res. 2002;16(2):179-183.
[42] Navarro JF, Mora C, Macía M, et al. Randomized prospective comparison between erythropoietin and androgens in CAPD patients. Kidney Int. 2002;61(4):1537-1544.
[43] Fouque D, Peng SC, Shamir E, et al. Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-1 induces an anabolic response in malnourished CAPD patients. Kidney Int. 2000;57(2): 646-654.
[44] Nahrendorf M, Frantz S, Hu K, et al. Effect of testosterone on post-myocardial infarction remodeling and function. Cardiovasc Res. 2003;57(2):370-378.
[45] Hochberg Z. Mechanisms of steroid impairment of growth. Horm Res. 2002;58 Suppl 1:33-38.
[46] Bonnefoy M, Patricot MC, Lacour JR, et al. Relation between physical activity, muscle function and IGF-1, testosterone and DHEAS concentrations in the elderly. Rev Med Interne. 2002; 23(10):819-827.
[47] Fernández-Rodriguez CM1, Prada I, Andrade A, et al. Disturbed synthesis of insulinlike growth factor I and its binding proteins may influence renal function changes in liver cirrhosis. Dig Dis Sci. 2001;46(6):1313-1320.
[48] Lee CH, Edwards AM. Structural specificity of steroids in stimulating DNA synthesis and protooncogene expression in primary rat hepatocyte cultures. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2002;81(1):25-36.
[49] 黄行许,朴英杰,霍霞. c-myc和细胞凋亡[J].细胞生物学杂志, 1998,20(1):9-12.
[50] Wang Y, Toury R, Hauchecorne M, et al. Expression and subcellular localization of the Myc superfamily proteins: c-Myc, Max, Mad1 and Mxi1 in the epiphyseal plate cartilage chondrocytes of growing rats. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 1997;43(2):175-188.
[51] Waikel RL, Kawachi Y, Waikel PA, et al. Deregulated expression of c-Myc depletes epidermal stem cells. Nat Genet. 2001;28(2):165-168.
[52] Frye M, Gardner C, Li ER, et al. Evidence that Myc activation depletes the epidermal stem cell compartment by modulating adhesive interactions with the local microenvironment. Development. 2003;130(12):2793-2808. |