中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (40): 6460-6464.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.40.012
• 器官移植动物模型 organ transplantation and animal model • 上一篇 下一篇
高压氧治疗促进脑梗死模型大鼠神经再生微环境及神经功能的恢复
孙晶晶1,宋乃光2,张耀龙2,高淑焕1,孙彩悦1,薛 建1,贺永贵3,习瑾琨3,张国彬3
- 唐山市协和医院,1神经内一科,2急诊科,河北省唐山市 063000;3河北联合大学培养办公室,河北省唐山市 063000
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy improves nerve regeneration microenvironment and promotes rat nerve function recovery after cerebral infarction
Sun Jing-jing1, Song Nai-guang2, Zhang Yao-long2, Gao Shu-huan1, Sun Cai-yue1, Xue Jian1, He Yong-gui3, Xi Jin-kun3, Zhang Guo-bin3
- 1First Department of Neurology, 2Department of Emergency, Tangshan Union Medical College Hospital, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China; 3Training Office, Hebei United University, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
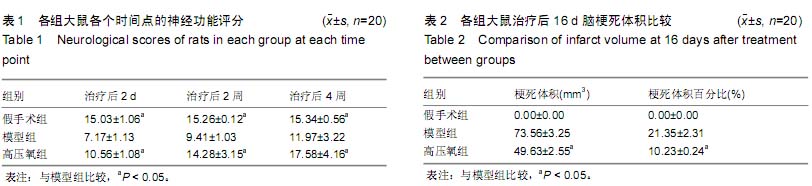
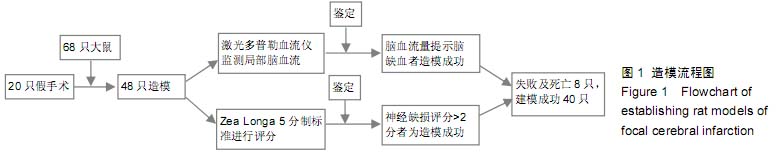
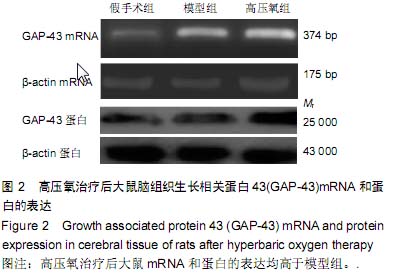
背景:大量临床研究证实,脊髓损伤区域的微环境通过高压氧可获得显著改善,但高压氧对脑损伤微环境有何影响呢? 目的:观察高压氧治疗对大鼠脑梗死区神经再生微环境及神经功能恢复的影响。 方法:构建大脑中动脉阻断制作局灶性脑梗死模型大鼠,并进行高压氧治疗,设假手术组和模型组作对照,假手术组不结扎颈内动脉不干预,模型组造模后模拟除压力和氧浓度以外的其他高压氧治疗过程及环境条件。 结果与结论:与模型组相比,治疗后第16天高压氧组的大鼠肢体功能评分、术后14 d 脑梗死区组织生长相关蛋白43表达均升高(P < 0.05),术后24 h梗死灶体积均降低(P < 0.05)。结果证实,高压氧治疗促进脑梗死模型大鼠神经再生微环境及神经功能的恢复。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:肾移植;肝移植;移植;心脏移植;组织移植;皮肤移植;皮瓣移植;血管移植;器官移植;组织工程
中图分类号: