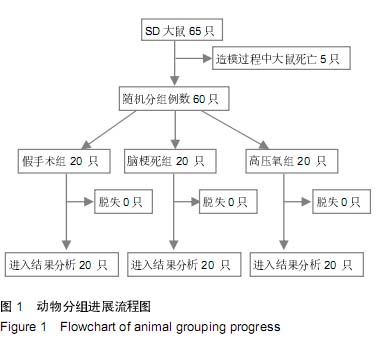
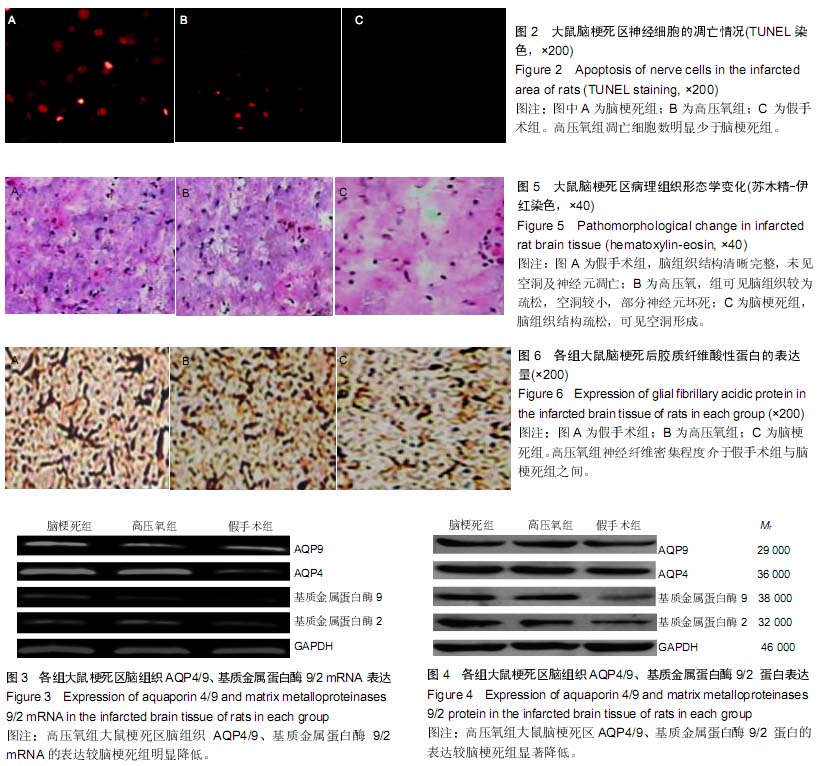
| [1] Green AR,Shuaib A. Therapeutic strategies for the treatment of stroke. Drug Discov Today.2006;11:681-693.
[2] Donnan GA, Fisher M, Macleod M, et al. Stroke. Lancet.2008; 371 (9624):1612-1623.
[3] Haku T, Okuda S, Kanematsu F, Oda T,et al. Repair of cervical esophageal perforation using longus colli muscle flap: a case report of a patient with cervical spinal cord injury. Spine J. 2008 Sep-Oct;8(5):831-835.
[4] 张海明,张映.神经生长因子对神经元作用的研究进展动物医学进展[J].动物医学进展, 2006, 27(9):39-41.
[5] Young W.Spinal cord contusion models.Prog Brain Res.2002; 137:231-255.
[6] Mutlu O, Ulak G, Celikyurt IK, et al.Effects of olanzapine, sertindole and clozapine on learning and memory in the Morris water maze test in naive and MK-801-treated mice. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior.2011;98 (3): 398-404.
[7] 周国庆,金怡,张鹏.沉默RhoA基因对骨髓间充质干细胞静脉移植治疗脑梗死大鼠的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(45):8416-8420.
[8] 郭艳芹,何冬梅,王彤.银杏达莫对脑梗死的疗效观察[J].中国血液流变学杂志,2006,16(2):213-262.
[9] Pimentel-Coelho PM,Magalhães ES, Lopes LM, et al.Human cord blood transplantation in a neonatal rat model of hypoxic-ischemic brain damage: functional outcome related to neuroprotection in the striatum. Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19(3): 351-358.
[10] 颜晓华,黄瑞滨.黄芩苷体外诱导脐血间充质干细胞向神经元样细胞分化的实验研究[J]. 中华儿科杂志,2006,44:214-219. .
[11] Amar AP, Levy M L. Pathogenesis and phar macol ogical strategies formitigating secondary damage in acute s pinal cord injury.Neur osurgery.1999;44 (5):1027-1040.
[12] Albin RL,Mink JW.Recent advances in Tourette syndrome research.Trends Neurosci.2006;29:175-182.
[13] 陈雪扉,莫万斌.注射用七叶皂苷钠联合脐带间充质干细胞移植改善脑梗死大鼠神经功能[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(27):5080-5084.
[14] Li L, Ding J, Marshall C,.et al.Pretraining affects Morris water maze performance with different patterns between control and ovariectomized plus d-galactose-injected mice. Behav Brain Res. 2011 Feb 2;217(1):244-247.
[15] Leonardo CC, Hall AA, Collier LA, et al. Human umbilical cord blood cell therapy blocks the morphological change and recruitment of CD11b-expressing, isolectin-binding proinflammatory cells after middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Neurosci Res.2010;88(6):1213-1222.
[16] Björklund E, Lindberg E, Rundgren M, et al.Ischaemic brain damage after cardiac arrest and induced hypothermia–a systematic description of selective eosinophilic neuronal death[J].A neuropathologic study of 23 patients. Resuscitation. 2014 Apr;85(4):527-532.
[17] 丁进京. 高压氧治疗对急性期脑梗死患者血清ACA水平的影响[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志, 2012,15(03):34-36.
[18] Audrius Jasaitis,Hugues Ouellet,Jean-Christophe Lambry,et al.JUltrafast hemeligand recombination in truncated hemoglobin HbO from Mycobacterium tuberculosis: A ligand cageOriginal.Chemical Physics.2012;396(2):10-16.
[19] Lee HJ, Lee JK, Lee H, et al. The therapeutic potential of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells in Alzheimer's disease.Neurosci Lett.2010;481(1):30-35.
[20] Phuc PV, Nhung TH, Loan DT, et al. Differentiating of banked human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells into insulin-secreting cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2011; 47(1): 4-63.
[21] Lim R,Barker G,Wall CA, et a1.D iet ary phytophenol s reduce infect ion- i n du ced inf lam m at ory p at hw ays in hum an gest at ional t issues.Mol Hum Reprod.2013;19(7):451- 462.
[22] 樊留博,马利,中章,等.强制性运动联合高压氧对脑缺血大鼠神经功能及GAP-43 表达的影响[J].中国中医急症,2014,23 (6): 1022-1049.
[23] Sun L, Strelow H, Mies G, et al. O xygen therapy i m proves eoerg y m etabolism in foeal cerebral isch emia. Brain Res. 2011;1415:103-108.
[24] Küppers-Tiedt L, Manaenko A, Michalski D, et al. Combined systemic thrombolysis with alteplase and early hyperbaric oxygen therapy in experimental embolic stroke in rats: relationship to functional outcome and reduction of structural damage. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2011;111:167-172.
[25] 薛松,朱成全,陈华东,等.加电针治疗脑梗死疗效观察[J].广东医学,2006, 27(11):1751-1752.
[26] 华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组缺血I生脑卒中二级预防指南撰写组.中国缺血性脑卒中和短暂陛脑缺血发作二级预防指南22010[J].中华神经科杂志, 2010, 43(2):154 -160.
[27] 张琰,电针联合高压氧对脑梗死后痴呆患者认知能力和血浆同型半胱氨酸的影响[j],中国基层医药,2013,21(1):3223-3225.
[28] Chuang SK.Limited Evidence to Demonstrate that the Use of Hyperbaric Oxygen (HBO) Therapy Reduces the Incidence of Osteoradionecrosis in Irradiated Patients Requiring Tooth Extraction. J Evid Based Dent Pract. 2011 Sep;11(3):129-131.
[29] 柳太云,熊符,林军,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞移植促进脑梗死大鼠神经细胞再生和神经功能恢复[J]. 黑龙江医学,2011,35(9):663-664.
[30] Tanaka S, Tabuchi K, Hoshino T, et al.Protective effects of exogenous GM-1 ganglioside on acoustic injury of the mouse cochlea. Neurosci Lett.2010; 473(3):237-241.
[31] Ariake K, Ohtsuka H, Motoi F, et al.GCF2/LRRFIP1 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis and liver invasion through integrin-dependent RhoA activation.Cancer Letters. 2012; 325(1):99-107.
[32] 王溯.丹红治疗对急性脑梗死大鼠运动功能改善的影响[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志,2010,16(9):1204-1205.
[33] 张婷勇.骨髓间充质干细胞移植并用单唾液酸神经节苷脂治疗大鼠脑梗死[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(14): 2557-256.
[34] 王晓楠,王亮,刘丽,等. rhG-CSF对颅脑损伤大鼠神经和认知功能的影响[J]. 山东医药,2010, 50(6):34-35.
[35] R. Fuentes-Raspall,G. Oliu-lsem,J.M. Inoriza-Belzunce, et al.Efficacy of hyperbaric oxygen therapy (Hbo) for late pelvic radiation toxicity. Results of a prospective study.Radiotherapy and Oncology. 2011;98(2):23.
[36] 仲爱芳,何益民,陈升东,等.高压氧对脑梗死患者同型半胱氨酸、高敏C反应蛋白和D一二聚体的影响[J].中华航海医学与高压氧医学杂志,2014,21(2):89-91.
[37] 刘青芳,王爱民.早期康复联合高压氧治疗急性脑梗死患者的疗效分析[J].医学临床研究,2012,29(9):1663-1664.
[38] 边尧鑫,张春燕,赵飞. 同型半胱氨酸和叶酸及维生素B12与非痴呆型血管性认知障碍患者的关系[J]. 河北医药,2012, 34(22): 3417-3418.
[39] 李金庚.老年期痴呆的血浆半胱氨酸浓度检测的临床意义[J].中国临床神经科学,2012,20(3):316-319,321. |