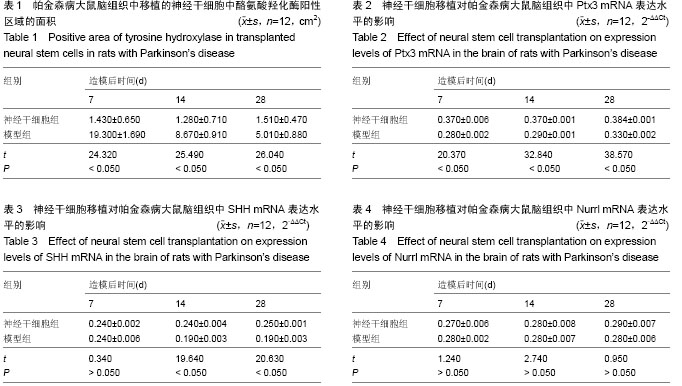
| [1] 汪锡金,张煜,陈生弟.帕金森病发病机制与治疗研究十年进展[J].中国现代神经疾病杂志,2010,11(1):36-42.
[2] 王国祥,刘殿玉.等速运动中肌氧含量及其表面肌电图中位频率的变化特点[J].广州体育学院学报,2004,24(2):38-40.
[3] 袁惠莉,汪璇,张丽娟,等.中药在防治帕金森病中的作用及研究进展[J].中国药理学通报,2010,26(7):850-854.
[4] 刘振国.医学影像学在帕金森病临床诊断中的应用[J].中国神经免疫学和神经病学杂志,2010,17(3):163-166.
[5] 刘妍梅,冼文彪,周鸿雁,等.普拉克索治疗帕金森病的疗效观察[J].内科理论与实践,2010,5(5):425-426.
[6] 吴桂英,师聪红.普拉克索治疗帕金森病的疗效分析[J].中国医药导报,2011,8(7):73-74.
[7] 苏维海.帕金森病综合治疗的研究进展[J].实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2010,18(11):1728.
[8] 赵静华.普拉克索治疗帕金森病疗效分析[J].临床医学,2010, 30(4): 60-62.
[9] 苏闻,陈海波,张振馨,等.丙炔苯丙胺治疗帕金森病多中心、随机、对照开放临床研究[J].中华神经科杂志,2010,37(5):413.
[10] 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-09-30.
[11] 李永新,高振同,左艳芳.治疗帕金森病药物的合理应用[J].中国药房,2009,10(3):130-131.
[12] 李伟仕,黄志勇,吴修信,等.帕金森病患者抑郁和焦虑状况与生存质量关系的研究[J].当代医学,2011,17(7):4-5.
[13] Drechsel DA, Patel M. Role of reactive oxygen species in the neurotoxicity of environmental agents implicated in Parkinson's disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 2008;44(11): 1873-1886.
[14] 李秋霞,陈淅泠,王欣东,等.丁苯酞注射液对血管性痴呆大鼠海马区生长相关蛋白-43及突触素P38表达的影响[J].实用医学杂志, 2012,28(7):1067-1069.
[15] 庄燕.40例立体定向下自体骨髓干细胞脑内移植治疗帕金森病患者的围手术期护理[J].中外医学研究,2011,9(3):71-72.
[16] Pfeiffer HC, Løkkegaard A, Zoetmulder M, et al. Cognitive impairment in early-stage non-demented Parkinson's disease patients. Acta Neurol Scand. 2014;129(5):307-318.
[17] Fernández de Bobadilla R, Pagonabarraga J, Martínez-Horta S, et al. Parkinson's disease-cognitive rating scale: psychometrics for mild cognitive impairment. Mov Disord. 2013;28(10):1376-1383.
[18] Smith LA, Jackson MJ, Al-Barghouthy G, et al. Multiple small doses of levodopa plus entacapone produce continuous dopaminergic stimulation and reduce dyskinesia induction in MPTP-treated drug-naive primates. Mov Disord. 2005;20(3): 306-314.
[19] Mizuno Y, Kanazawa I, Kuno S, et al. Placebo-controlled, double-blind dose-finding study of entacapone in fluctuating parkinsonian patients. Mov Disord. 2007;22(1):75-80.
[20] Poewe WH, Deuschl G, Gordin A, et al. Efficacy and safety of entacapone in Parkinson's disease patients with suboptimal levodopa response: a 6-month randomized placebo-controlled double-blind study in Germany and Austria (Celomen study). Acta Neurol Scand. 2002;105(4):245-255.
[21] 张厚亮,丁正同,王坚,等.恩他卡朋对帕金森病大鼠的疗效[J]. 中国临床神经科学,2007,15(6):620-624.
[22] 陈生弟,中华医学会神经病学分会帕金森病及运动障碍学组.中国帕金森病治疗指南(第二版)[J].中华神经科杂志,2009, 42(5): 352.
[23] Rascol O, Brooks DJ, Melamed E, et al. Rasagiline as an adjunct to levodopa in patients with Parkinson's disease and motor fluctuations (LARGO, Lasting effect in Adjunct therapy with Rasagiline Given Once daily, study): a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group trial. Lancet. 2005;365(9463): 947-954.
[24] 刘春风,尹伟华,罗蔚峰.帕金森病患者运动障碍和症状波动的影响因素[J].中华神经科杂志,2003,36(6):411-413.
[25] 冯涛,王拥军.持续性多巴胺能刺激治疗帕金森病的研究进展[J].临床神经病学,2008,21(4):315-317.
[26] 冯涛,张漩,刘萍,等.持续性多巴胺能刺激对帕金森病非运动症状作用的前瞻性研究[J].中国康复理论与实践,2009,15(10): 918-920.
[27] Westin JE, Andersson M, Lundblad M, et al. Persistent changes in striatal gene expression induced by long-term L-DOPA treatment in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. Eur J Neurosci. 2001;14(7):1171-1176.
[28] Myllylä VV, Kultalahti ER, Haapaniemi H, et al. Twelve-month safety of entacapone in patients with Parkinson's disease. Eur J Neurol. 2001;8(1):53-60.
[29] Silveira P, Vaz-da-Silva M, Almeida L, et al. Pharmacokinetic- pharmacodynamic interaction between BIA 3-202, a novel COMT inhibitor, and levodopa/benserazide. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2003;59(8-9):603-609.
[30] Brooks DJ, Agid Y, Eggert K, et al. Treatment of end-of-dose wearing-off in parkinson's disease: stalevo (levodopa/ carbidopa/entacapone) and levodopa/DDCI given in combination with Comtess/Comtan (entacapone) provide equivalent improvements in symptom control superior to that of traditional levodopa/DDCI treatment. Eur Neurol. 2005; 53(4):197-202.
[31] Myllylä V, Haapaniemi T, Kaakkola S, et al. Patient satisfaction with switching to Stalevo: an open-label evaluation in PD patients experiencing wearing-off (Simcom Study). Acta Neurol Scand. 2006;114(3):181-186. |