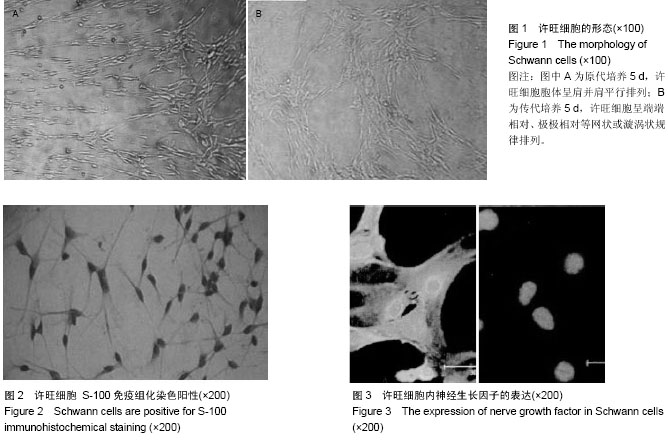
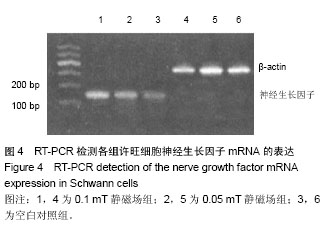
| [1] Ban DX, Ning GZ, Feng SQ, et al. Combination of activated Schwann cells with bone mesenchymal stem cells: the best cell strategy for repair after spinal cord injury in rats. Regen Med. 2011;6(6):707-720.
[2] Lunn ER, Scourfield J, Keynes RJ, et al. The neural tube origin of ventral root sheath cells in the chick embryo. Development. 1987;101(2):247-254.
[3] 孙晓红,窦文波,佟晓杰,等.许旺细胞与脱细胞神经移植物共培养在周围神经损伤修复中的作用[J].中国临床康复, 2006, 10(29):19-21.
[4] 顾丹丹,张沛云.许旺细胞对周围神经再生的促进效应[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008, 12(25): 4921-4926.
[5] Gambarotta G, Fregnan F, Gnavi S, et al. Neuregulin 1 role in Schwann cell regulation and potential applications to promote peripheral nerve regeneration. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2013;108:223-256.
[6] Koelsch B, van den Berg L, Grabellus F, et al. Chemically induced rat Schwann cell neoplasia as a model for early-stage human peripheral nerve sheath tumors: phenotypic characteristics and dysregulated gene expression. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2013;72(5):404-415.
[7] Suganuma S, Tada K, Hayashi K, et al. Uncultured adipose-derived regenerative cells promote peripheral nerve regeneration. J Orthop Sci. 2013;18(1):145-151.
[8] Godinho MJ, Teh L, Pollett MA, et al. Immunohistochemical, ultrastructural and functional analysis of axonal regeneration through peripheral nerve grafts containing Schwann cells expressing BDNF, CNTF or NT3. PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e69987.
[9] 巴越洋,王辉,宁昕杰,等.人胶质细胞源性神经营养因子基因修饰猴雪旺细胞的构建与鉴定[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2013, 27(11):1363-1367.
[10] Yu B, Qian T, Wang Y, et al. miR-182 inhibits Schwann cell proliferation and migration by targeting FGF9 and NTM, respectively at an early stage following sciatic nerve injury. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(20):10356-10365.
[11] 周江文, 谢青松,许信龙,等.新型超顺磁性氧化铁在雪旺细胞移植后活体示踪中的应用研究[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2013, 18(12):1338-1343.
[12] Sango K, Kawakami E, Yanagisawa H, et al. Myelination in coculture of established neuronal and Schwann cell lines. Histochem Cell Biol. 2012;137(6):829-839.
[13] Ammoun S, Schmid MC, Zhou L, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) regulates human schwannoma proliferation, adhesion and survival. Oncogene. 2012;31(13):1710-1722.
[14] Yazdani SO, Golestaneh AF, Shafiee A, et al. Effects of low level laser therapy on proliferation and neurotrophic factor gene expression of human schwann cells in vitro. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2012;107:9-13.
[15] Liu F,Zhang HW,Zhang KM,et al.Rapamycin promotes Schwann cell migration and nerve growth factor secretion . Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(6): 602-609.
[16] Ma SZ,Peng CL,Wu SQ,et al.Sciatic nerve regeneration using a nerve growth factor-containing fibrin glue membrane.Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(36):3416-3422.
[17] Pereira Lopes FR, Lisboa BC, Frattini F, et al. Enhancement of sciatic nerve regeneration after vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) gene therapy. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2011; 37(6):600-612.
[18] 赵煜,李冰雁,巢永烈,等.磁性附着体模拟静磁场对成骨细胞增殖活性和周期分布及凋亡率的影响[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2007, 25(5):437-440.
[19] 丁冲,陈晓虎,李迪杰,等.骨组织生物磁性及磁场生物学效应研究[J].常州大学学报:自然科学版,2013,25(1):20-24.
[20] Azanchi R, Bernal G, Gupta R, et al. Combined demyelination plus Schwann cell transplantation therapy increases spread of cells and axonal regeneration following contusion injury. J Neurotrauma. 2004;21(6):775-788.
[21] Zhou LN, Zhang JW, Wang JC, et al. Bone marrow stromal and Schwann cells from adult rats can interact synergistically to aid in peripheral nerve repair even without intercellular contact in vitro. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2012;6(7):579-588.
[22] Provenzano MJ, Minner SA, Zander K, et al. p75(NTR) expression and nuclear localization of p75(NTR) intracellular domain in spiral ganglion Schwann cells following deafness correlate with cell proliferation. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2011; 47(4):306-315.
[23] 曹建平,骞爱荣,张维,等.0.2-0.4T静磁场对肿瘤细胞生长和黏附功能的影响[J].世界华人消化杂志,2000,18(13):1337-1343.
[24] 仇丽鸿,张凌,汤旭娜,等. 静磁场对成骨细胞骨形成蛋白2和Ⅰ型胶原的影响[J].上海口腔医学,2007,16(1):33-35.
[25] Fan CG, Zhang QJ, Zhou JR. Therapeutic potentials of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human umbilical cord. Stem Cell Rev. 2011;7(1):195-207.
[26] Ceccarelli G, Bloise N, Mantelli M, et al. A comparative analysis of the in vitro effects of pulsed electromagnetic field treatment on osteogenic differentiation of two different mesenchymal cell lineages. Biores Open Access. 2013; 2(4):283-294.
[27] Feng SW, Lo YJ, Chang WJ, et al. Static magnetic field exposure promotes differentiation of osteoblastic cells grown on the surface of a poly-L-lactide substrate. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2010;48(8):793-798.
[28] 杨凌,巢永烈,杜莉.磁性附着体模拟静磁场对人牙周膜成纤维细胞的生物学效应研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2007,25(4): 316-319.
[29] László JF, Szilvási J, Fényi A, et al. Daily exposure to inhomogeneous static magnetic field significantly reduces blood glucose level in diabetic mice. Int J Radiat Biol. 2011; 87(1):36-45.
[30] Kim IS, Song YM, Cho TH, et al. Biphasic electrical targeting plays a significant role in schwann cell activation. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(9-10):1327-1340.
[31] 李亮,张鑫鑫,姜晓锐,等.雪旺细胞促进组织工程骨修复大鼠股骨缺损的实验研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2013, 15(2):148-152.
[32] Dourado DM, Fávero S, et al. Low-level laser therapy promotes vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 expression in endothelial and nonendothelial cells of mice gastrocnemius exposed to snake venom. Photochem Photobiol. 2011;87(2):418-426. |