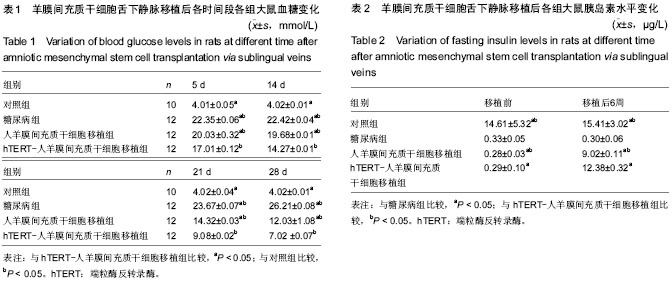
中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (36): 5827-5832.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.36.016
• 干细胞移植 stem cell transplantation • 上一篇 下一篇
端粒酶反转录酶基因电转染人羊膜间充质干细胞移植治疗糖尿病
付建茹
- 天津市津南区咸水沽医院内科,天津市 300350
Telomerase reverse transcriptase gene transfection of human amniotic electrical mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for treatment of diabetes mellitus
Fu Jian-ru
- Department of Internal Medicine, Xianshuigu Hospital of Jinnan District, Tianjin 300350, China
摘要:
背景:羊膜是胎儿出生后的废弃物,羊膜间充质干细胞具有取材方便、增殖能力强、无伦理学争议、免疫原性低等优势。
目的:通过端粒酶反转录酶(human telomerase reverse transcriptase,hTERT)基因电转染人羊膜间充质干细胞移植到大鼠糖尿病模型,探讨其对糖尿病大鼠的疗效。
方法:分离培养人羊膜间充质干细胞,经hTERT基因电转染羊膜间充质干细胞,从50只SD大鼠中随机取10只作为对照组,剩余40只按45 mg/kg的剂量注射链脲霉素,建立糖尿病模型后,将建模成功的36只SD大鼠随机分为糖尿病组、人羊膜间充质干细胞移植组和hTERT-人羊膜间充质干细胞移植组,每组各12只;人羊膜间充质干细胞移植组和hTERT-人羊膜间充质干细胞移植组分别通过大鼠舌下静脉注射移植人羊膜间充质干细胞和经hTERT基因电转染羊膜间充质干细胞。移植后各组进行动态血糖水平监测,于移植后每周检测各组大鼠血浆胰岛素的浓度,胰腺切片苏木精-伊红染色观察病理变化。
结果与结论:移植后4周,与糖尿病组比较,人羊膜间充质干细胞移植组和hTERT-人羊膜间充质干细胞移植组血糖水平明显下降(P < 0.05),尤其是hTERT-人羊膜间充质干细胞移植组的空腹血糖水平接近于对照组水平(P > 0.05),而糖尿病组空腹血糖维持在较高水平;移植后6周,与糖尿病组比较,人羊膜间充质干细胞移植组和hTERT-人羊膜间充质干细胞移植组的血浆胰岛素含量增加(P < 0.05),胰腺病损程度减轻(P < 0.05),hTERT-人羊膜间充质干细胞移植组更明显(P < 0.05)。结果证实,提示hTERT转染的羊膜间充质干细胞移植能明显降低糖尿病大鼠血糖和减轻胰岛损伤,可以有效治疗大鼠糖尿病。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: