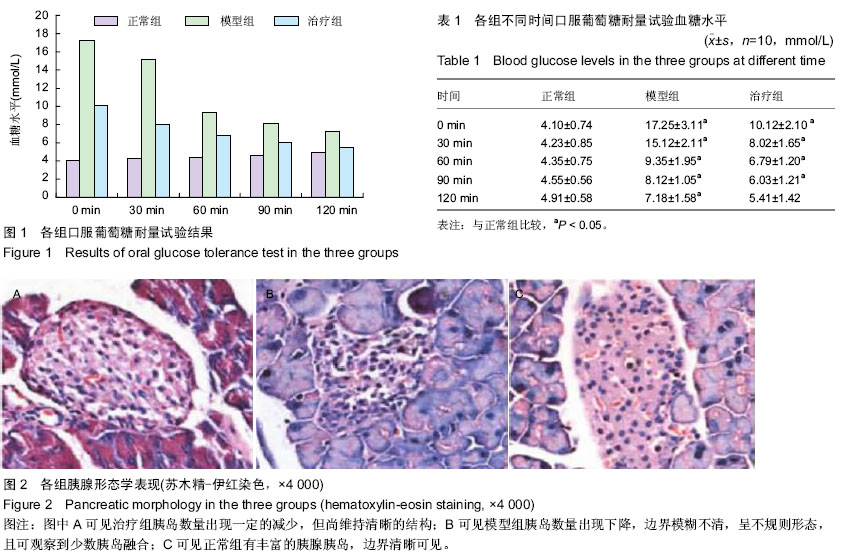
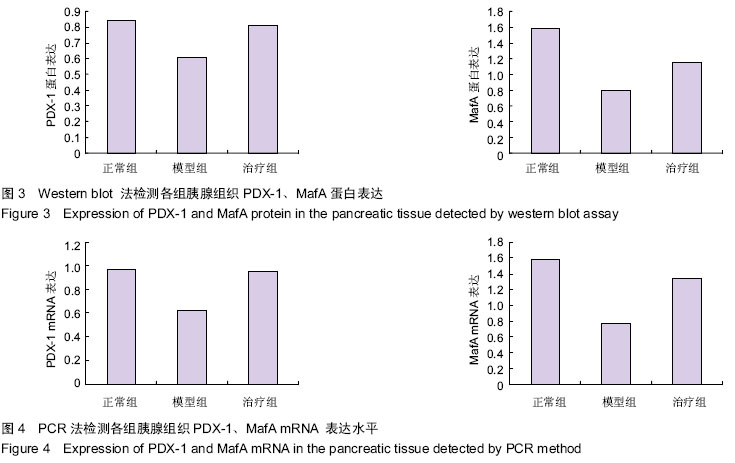
| [1] 张丽欣,孙丽芳,邢利和.脐血干细胞移植治疗1型糖尿病的研究进展[J].中国全科医学,2010,13(6):681-684.
[2] 陈舒,马威,江其生.脐血干细胞经微创介入下胰腺血管插管移植治疗Ⅱ型糖尿病1例[J].临床消化病杂志,2010,22(2):87.
[3] 李孔龙,段志胜,徐勉,等.脐血干细胞治疗1型糖尿病3例[J].中国医药指南,2013,11(26):1-3.
[4] Yamaguchi M, Ebina S, Kashiwakura I. Involvement of placental/umbilical cord blood acid-base status and gas values on the radiosensitivity of human fetal/neonatal hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. J Radiat Res. 2013; 54(2):277-284.
[5] Roszek K, Bomastek K, Dro?d?al M, et al. Dramatic differences in activity of purines metabolizing ecto-enzymes between mesenchymal stem cells isolated from human umbilical cord blood and umbilical cord tissue. Biochem Cell Biol. 2013c;91(6):519-525.
[6] 张立新,潘兴瑜.链脲佐菌素诱导1型糖尿病小鼠模型的研究[J].中国基层医药,2008,15(8):1324-1325.
[7] 张维娜,刘尚全,袁媛,等.脐血干细胞对1型糖尿病小鼠的治疗效应及作用机制[J].安徽医科大学学报,2014,49(1):27-31,32.
[8] 张丽欣,孙丽芳,邢利和.脐血干细胞移植治疗1型糖尿病的研究进展[J].临床合理用药杂志,2011,4(12):125-128.
[9] Yu X, Miao J, Xia W, et al. Preferential expansion of umbilical cord blood-derived CD34-positive cells on human leukemia inhibitory factor transgenic feeder cells cultured on regenerated silk fibroin film. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2013;101(6):964-971.
[10] 杨耀国.人脐带血干细胞移植治疗糖尿病鼠下肢缺血的研究[D]. 北京:北京协和医学院,2009.
[11] 孙念政.胎盘间充质干细胞诱导分化为胰岛素分泌细胞及其对糖尿病鼠降糖作用的研究[D].济南:山东大学,2009.
[12] 石凌峰,王清莲.不同来源的间充质干细胞治疗1型糖尿病进展[J].糖尿病新世界,2015,(3):72-73,75.
[13] 郝晓娟,朱旅云.缺氧预处理脐带间充质干细胞诱导分化为内皮样细胞[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(45):7869-7876.
[14] 范烨,王学浩,张峰,等.HGF质粒体内表达诱导脐血干细胞向肝系细胞分化[J].世界华人消化杂志,2006,14(8):767-771.
[15] 李翠芳,姚远.脐血干细胞移植2型糖尿病下肢血管病变患者内皮依赖性血管舒张的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(50): 8098-8102.
[16] 张弛,肖日军,张娜,等.脐血干细胞移植治疗糖尿病大鼠下肢缺血的实验研究[J].中华损伤与修复杂志:电子版,2012,7(1):18-23.
[17] 张亚萍,陶松桔,宋卫红,等.脐血干细胞移植治疗糖尿病足的临床观察[J].中国临床研究,2012,25(3):218-220.
[18] 刘宏娟.干细胞及干细胞治疗糖尿病:中国临床试验注册信息分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(6):975-979.
[19] 赵勇,周智广.脐血多能干细胞的免疫教育与1型糖尿病的治疗[J].中华糖尿病杂志,2014,6(2):69-72.
[20] 周飞,张小芬.脐血干细胞移植的研究及临床应用[J].医学综述, 2006, 12(19):1183-1185.
[21] 陈频,邵珠林,徐向进.利拉鲁肽联合骨髓间充质干细胞介导胃肠激素对链脲佐菌素诱导的1型糖尿病大鼠模型糖代谢的影响[J].中华内分泌代谢杂志,2015,31(3):277-281.
[22] 杨华强,李东升,杜玲,等. 脐血干细胞移植在糖尿病足治疗中的应用:附二例报告[J].中国全科医学,2010,13(23):2551-2553.
[23] 黄晓萍.脐血间充质干细胞的研究发展与应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(21):4159-4162.
[24] 毛平,段华新,王彩霞,等.人脐血造血干/祖细胞的生物反应器大规模扩增及移植实验[J].中华器官移植杂志,2009,30(3): 152-155.
[25] 秦琳,李红.脐血细胞治疗糖尿病的研究进展[J].中国医药导报, 2009,6(10):7-8,43.
[26] 赖颖晖,赖永榕,王明月,等.人骨髓及脐血单个核细胞移植构建人源化非肥胖糖尿病/重症联合免疫缺陷小鼠模型:可以提高其人源化水平吗[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(32): 6249-6254.
[27] 费小明,吴雨洁,常在,等.人骨髓基质细胞促进脐血CD34+细胞的体外扩增和对NOD/SCID小鼠的植入[J].中华血液学杂志, 2008,29(2):97-100.
[28] 贾新涛,穆媛媛,贾潇潇,等. 人脐血CD34+细胞在NOD/SCID小鼠上有效重建造血系统[J].第三军医大学学报,2011,33(11): 1136-1140.
[29] Kedong S, Xiubo F, Tianqing L, et al. Simultaneous expansion and harvest of hematopoietic stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord blood. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010;21(12):3183-3193.
[30] Murphy MB, Blashki D, Buchanan RM, et al. Adult and umbilical cord blood-derived platelet-rich plasma for mesenchymal stem cell proliferation, chemotaxis, and cryo-preservation. Biomaterials. 2012;33(21):5308-5316.
[31] Kim YS, Park IK, Kim WJ, et al. SPION nanoparticles as an efficient probe and carrier of DNA to umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2011;11(2):1507-1510.
[32] 金慧丽,蔡海波,杨施,等. 由脐血单个核细胞和富集的CD34+细胞扩增的造血干/祖细胞的生理功能比较[J].中华器官移植杂志, 2008,29(3):155-158.
[33] 肖日军,张弛,李华珠,等.人脐血干细胞移植治疗糖尿病大鼠下肢缺血的实验研究[C]//中华医学会第九次全国内分泌学学术会议论文集,2010:544.
[34] Anderson DG, Markova D, An HS, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the cultured rabbit intervertebral disc: a novel cell source for disc repair. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2013;92(5):420-429.
[35] 肖娜.脐带间充质干细胞联合脐血干细胞治疗Ⅰ型糖尿病的初步研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2009.
[36] 孙晓晖,王颜刚.干细胞移植定向分化为胰岛β细胞治疗糖尿病[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(1):165-168.
[37] 赵冬阳,李剑平.干细胞诱导分化为胰腺β细胞的研究现状[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(37):7443-7447.
[38] 谢婷,欧阳建.干细胞诱导分化为胰岛素分泌细胞的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(25):4931-4935.
[39] 郑曦,肖日军,张弛,等.静脉输注人脐血干细胞移植治疗糖尿病大鼠下肢缺血的实验研究[C]//中华医学会第九次全国内分泌学学术会议论文集,2010:278.
[40] 张芳婷,万汇涓,叶静,等.人脐血细胞移植对高血糖模型小鼠的治疗作用[J].中国全科医学,2009,12(16):1492-1494.
|