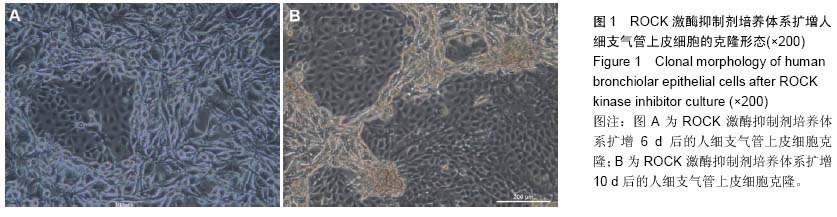
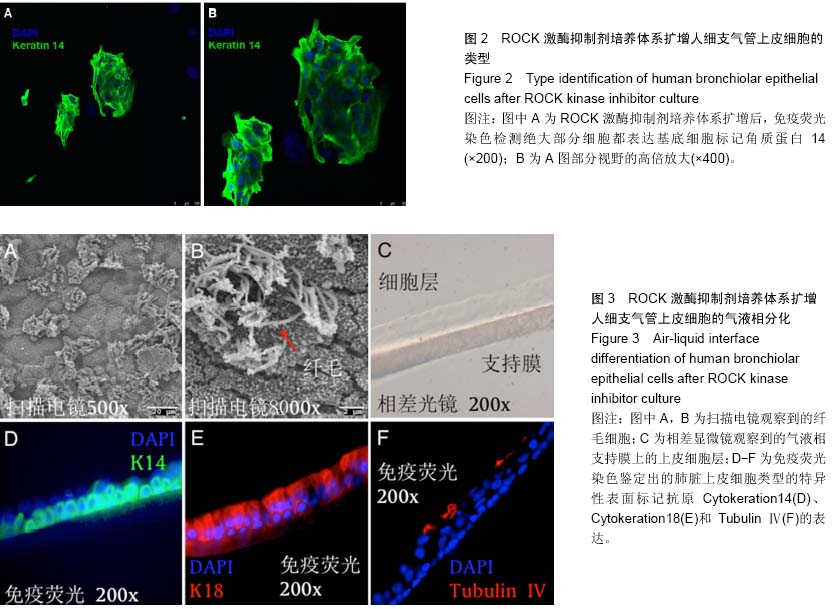
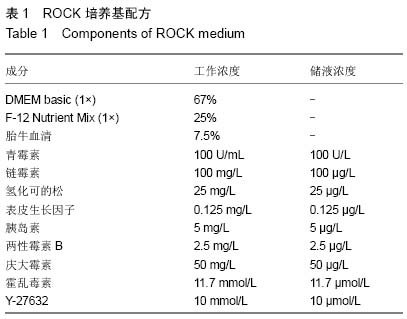
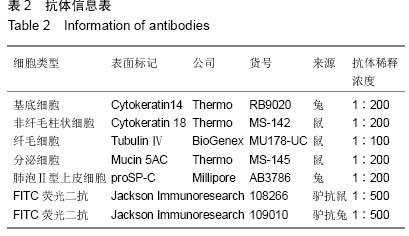
| [1] Yamamoto K, Ahyi AN, Pepper-Cunningham ZA, et al. Roles of lung epithelium in neutrophil recruitment during pneumococcal pneumonia. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2014; 50(2):253-262.
[2] Li Y, Wang Y, Liu X. The role of airway epithelial cells in response to mycobacteria infection. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012; 2012:791392.
[3] Kourembanas S. Stem cell-based therapy for newborn lung and brain injury: feasible, safe, and the next therapeutic breakthrough. J Pediatr. 2014;164(5):954-956.
[4] Weiss DJ, Bates JH, Gilbert T, et al. Stem cells and cell therapies in lung biology and diseases: conference report. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2013;10(5):S25-44.
[5] Chellapandian D, Lehrnbecher T, Phillips B, et al. Bronchoalveolar lavage and lung biopsy in patients with cancer and hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation recipients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2015; 33(5):501-509.
[6] Vogl UM, Nagayama K, Bojic M, et al. Lung transplantation for bronchiolitis obliterans after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a single-center experience. Transplantation. 2013;95(4):623-628.
[7] Zhou YM, Lan X, Guo HB, et al. Rho/ROCK signal cascade mediates asymmetric dimethylarginine-induced vascular smooth muscle cells migration and phenotype change. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:683707.
[8] Ji H, Tang H, Lin H, et al. Rho/Rock cross-talks with transforming growth factor-β/Smad pathway participates in lung fibroblast-myofibroblast differentiation. Biomed Rep. 2014;2(6):787-792..
[9] Ji H, Tang H, Lin H, et al. Rho/Rock cross-talks with transforming growth factor-β/Smad pathway participates in lung fibroblast-myofibroblast differentiation. Biomed Rep. 2014;2(6):787-792.
[10] Whitcutt MJ, Adler KB, Wu R. A biphasic chamber system for maintaining polarity of differentiation of cultured respiratory tract epithelial cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1988;24(5): 420-428.
[11] Rach J, Budde J, Möhle N, et al. Direct exposure at the air-liquid interface: evaluation of an in vitro approach for simulating inhalation of airborne substances. J Appl Toxicol. 2014;34(5):506-515.
[12] Xu W, Janocha AJ, Leahy RA, et al. A novel method for pulmonary research: assessment of bioenergetic function at the air-liquid interface. Redox Biol. 2014;2:513-519.
[13] Hirst RA, Jackson CL, Coles JL, et al. Culture of primary ciliary dyskinesia epithelial cells at air-liquid interface can alter ciliary phenotype but remains a robust and informative diagnostic aid. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e89675.
[14] Liu X, Luo M, Trygg C, et al. Biological Differences in rAAV Transduction of Airway Epithelia in Humans and in Old World Non-human Primates. Mol Ther. 2007;15(12):2114-2123.
[15] Liu X, Yan F, Yao H, et al. Involvement of RhoA/ROCK in insulin secretion of pancreatic β-cells in 3D culture. Cell Tissue Res. 2014;358(2):359-369.
[16] Liu X, Luo M, Zhang L, et al. Bioelectric properties of chloride channels in human, pig, ferret, and mouse airway epithelia. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2007;36(3):313-323.
[17] Frankart A, Malaisse J, De Vuyst E, et al. Epidermal morphogenesis during progressive in vitro 3D reconstruction at the air-liquid interface. Exp Dermatol. 2012;21(11):871-875.
[18] Hill DB, Button B. Establishment of respiratory air-liquid interface cultures and their use in studying mucin production, secretion, and function. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;842:245-258.
[19] Xie Y, Williams NG, Tolic A, et al. Aerosolized ZnO nanoparticles induce toxicity in alveolar type II epithelial cells at the air-liquid interface. Toxicol Sci. 2012;125(2):450-461.
[20] Abraham G, Zizzadoro C, Kacza J, et al. Growth and differentiation of primary and passaged equine bronchial epithelial cells under conventional and air-liquid-interface culture conditions. BMC Vet Res. 2011;7:26.
[21] Bae CH, Kim JS, Song SY, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 induces MUC8 and MUC5B expression via ERK1 and p38 MAPK in human airway epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;430(2):683-688.
[22] McQualter JL, Bertoncello I. Clonal culture of adult mouse lung epithelial stem/progenitor cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2015; 1235:231-241.
[23] Green MD, Huang SX, Snoeck HW. Stem cells of the respiratory system: from identification to differentiation into functional epithelium. Bioessays. 2013;35(3):261-270.
[24] Rock JR, Onaitis MW, Rawlins EL, et al. Basal cells as stem cells of the mouse trachea and human airway epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(31):12771-12775.
[25] Zuo W, Zhang T, Wu DZ, et al. p63(+)Krt5(+) distal airway stem cells are essential for lung regeneration. Nature. 2015; 517(7536):616-620.
[26] Christie J, Keshavjee S, Orens J, et al. Potential refinements of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation primary graft dysfunction grading system. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2008;27(1):138.
[27] Zaglool SS, Zickri MB, Abd El Aziz DH, et al. Effect of stem cell therapy on amiodarone induced fibrosing interstitial lung disease in albino rat. Int J Stem Cells. 2011;4(2):133-142.
[28] Agostini C. Stem cell therapy for chronic lung diseases: hope and reality. Respir Med. 2010;104 Suppl 1:S86-91.
[29] Siniscalco D, Sullo N, Maione S, et al. Stem cell therapy: the great promise in lung disease. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2008; 2(3):173-177.
[30] Plumb DA, Ferrara L, Torbica T, et al. Collagen XXVII organises the pericellular matrix in the growth plate. PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e29422. |