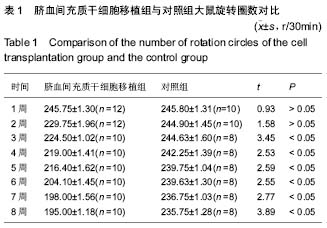
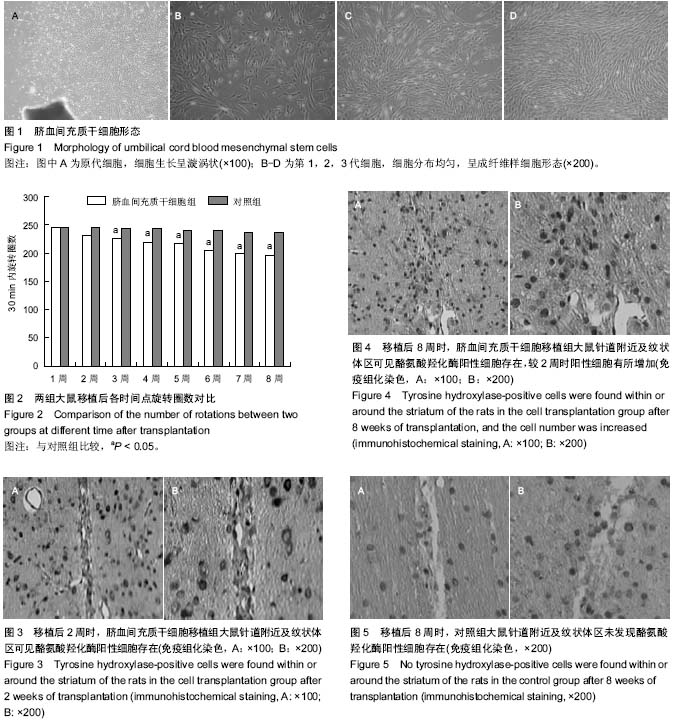
| [1] Kobari L, Giarratana MC, Gluckman JC, et al. Ex vivo expansion does not alter the capacity of umbilical cord blood CD34+ cells to generate functional T lymphocytes and dendritic cells. Stem Cells. 2006;24(9):2150-2157.
[2] Hess DA, Craft TP, Wirthlin L, et al. Widespread nonhematopoietic tissue distribution by transplanted human progenitor cells with high aldehyde dehydrogenase activity. Stem Cells. 2008;26(3):611-620.
[3] Rocha V, Gluckman E; Eurocord and European Blood and Marrow Transplant Group. Clinical use of umbilical cord blood hematopoietic stem cells. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2006; 12(1 Suppl 1):34-41.
[4] Joundi RA, Brittain JS, Green AL, et al. High-frequency stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus selectively decreases central variance of rhythmic finger tapping in Parkinson's disease. Neuropsychologia. 2012;50(10):2460-2466.
[5] Kim BG, Hwang DH, Lee SI, et al. Stem cell-based cell therapy for spinal cord injury. Cell Transplant. 2007;16(4): 355-364.
[6] Phinney DG, Prockop DJ. Concise review: mesenchymal stem/multipotent stromal cells: the state of transdifferentiation and modes of tissue repair--current views. Stem Cells. 2007; 25(11):2896-2902.
[7] Woodbury D, Schwarz EJ, Prockop DJ, et al. Adult rat and human bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neurons. J Neurosci Res. 2000;61(4):364-370.
[8] Decressac M, Mattsson B, Björklund A. Comparison of the behavioural and histological characteristics of the 6-OHDA and α-synuclein rat models of Parkinson's disease. Exp Neurol. 2012;235(1):306-315.
[9] Sanchez-Ramos J. Stem cells from umbilical cord blood. Semin Reprod Med. 2006;24(5):358-369.
[10] Prodoehl J, Burciu RG, Vaillancourt DE. Resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging in Parkinson's disease. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2014;14(6):448.
[11] Mimeault M, Hauke R, Batra SK. Stem cells: a revolution in therapeutics-recent advances in stem cell biology and their therapeutic applications in regenerative medicine and cancer therapies. lin Pharmacol Ther. 2007;82(3):252-264.
[12] 李晓文,田映红.脐血间充质干细胞体外扩增和向神经元样细胞的定向诱导[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(1): 57-60.
[13] 胡琦,康慧聪,刘晓艳,等.增强型绿色荧光蛋白标记骨髓间充质干细胞移植对帕金森病大鼠模型的治疗作用[J].华中科技大学学报:医学版,2009,38(2):181-184,189.
[14] Chen X, Katakowski M, Li Y, et al. Human bone marrow stromal cell cultures conditioned by traumatic brain tissue extracts: growth factor production. J Neurosci Res. 2002; 69(5):687-691.
[15] Crigler L, Robey RC, Asawachaicharn A, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell subpopulations express a variety of neuro-regulatory molecules and promote neuronal cell survival and neuritogenesis. Exp Neurol. 2006;198(1):54-64.
[16] Joundi RA, Brittain JS, Punt TD, et al. Stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus improves velocity of ballistic movements in Parkinson's disease. Neuroreport. 2012;23(6):390-394.
[17] Phinney DG, Isakova I. Plasticity and therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells in the nervous system. Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11(10):1255-1265.
[18] Joyce NC, Harris DL, Markov V, et al. Potential of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells to heal damaged corneal endothelium. Mol Vis. 2012;18:547-564. |