中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (28): 4572-4575.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.28.026
• 干细胞移植 stem cell transplantation • 上一篇 下一篇
自体脐血单个核细胞回输早产儿:免疫功能及预后
杨春燕,许 平,李宝云,杨玉军,贾焕荣,周丽英,杨巧芝
- 聊城市人民医院,山东省聊城市 252000
Autologous umbilical cord blood mononuclear cell transfusion in preterm children: immune function and prognosis
Yang Chun-yan, Xu Ping, Li Bao-yun, Yang Yu-jun, Jia Huan-rong, Zhou Li-ying, Yang Qiao-zhi
- Liaocheng People’s Hospital, Liaocheng 252000, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
背景:脐血中富含造血干/祖细胞,有很强的增殖、分化及形成集落的能力,在刺激骨髓造血功能、提高血细胞活力和数量、促进免疫细胞发育成熟,维持机体免疫平衡等方面发挥重要作用。
目的:探讨自体脐血单个核细胞移植对早产儿免疫功能及预后的影响。
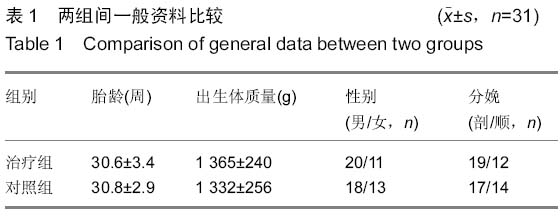
方法:选取2010年7月至2012年7月出生立即入住NICU病房,体质量≤ 1 500 g的早产儿62例,根据患儿家长自愿性原则分为治疗组和对照组;治疗组娩出后立即经脐静脉穿刺收集脐血,4 h内送中心实验室密度梯度离心后回输早产儿体内;治疗前后监测细胞免疫、体液免疫指标及相关临床指标。
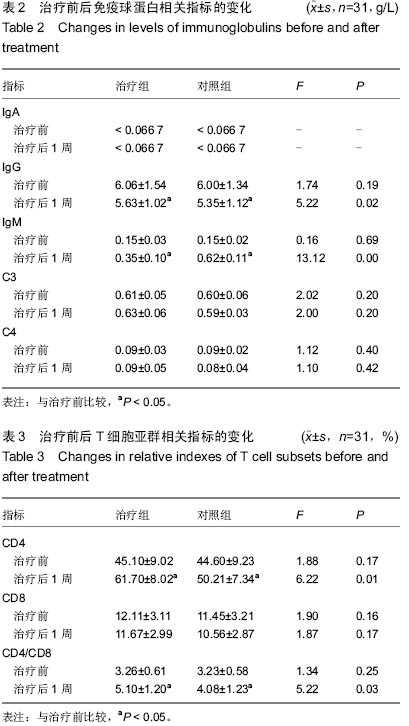
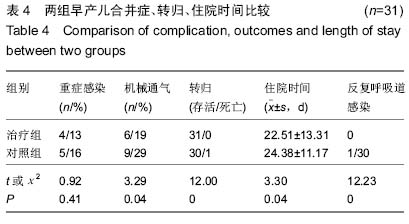
结果与结论:治疗组治疗1周复查时细胞免疫指标CD4、CD4/CD8水平较前明显升高,较对照组比较差异有显著性意义(P=0.01,0.03),而CD8变化不明显。治疗1周后两组早产儿的体液免疫指标IgM水平均较治疗前升高,但以对照组升高明显(P=0.00);IgA水平改变不明显,IgG水平下降,以对照组下降明显(P=0.02);住院期间,治疗组的重症感染发病率为13%,较对照组(16%)低,但差异无显著性意义;治疗组需机械通气患儿比例、平均住院时间与对照组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。两组早产儿均随访至12个月,治疗组中反复呼吸道感染的发病人数为0例,而对照组为1例,两者比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。结果表明自体脐血干细胞移植有利于改善机体细胞免疫功能,减慢IgG下降水平,减少呼吸机的使用率,缩短住院时间,减低小婴儿的反复呼吸道感染的发病率。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: