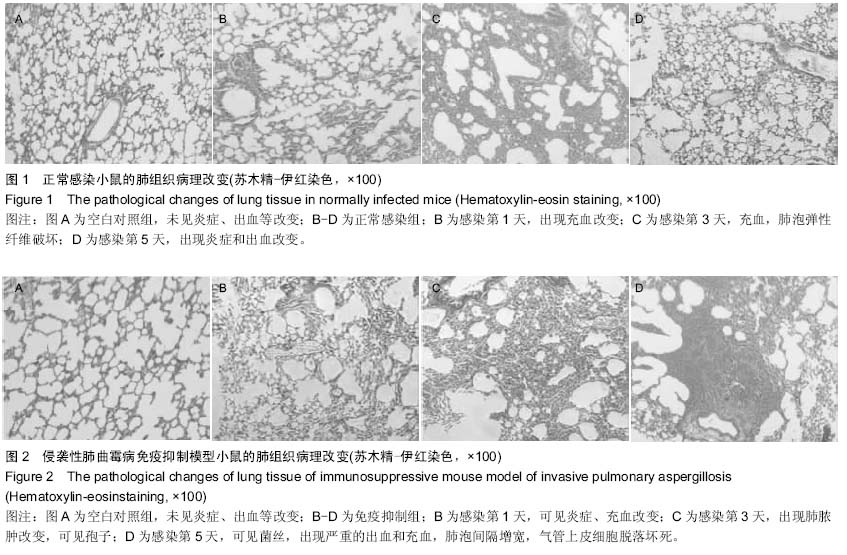
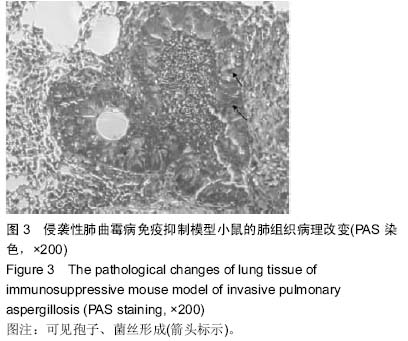
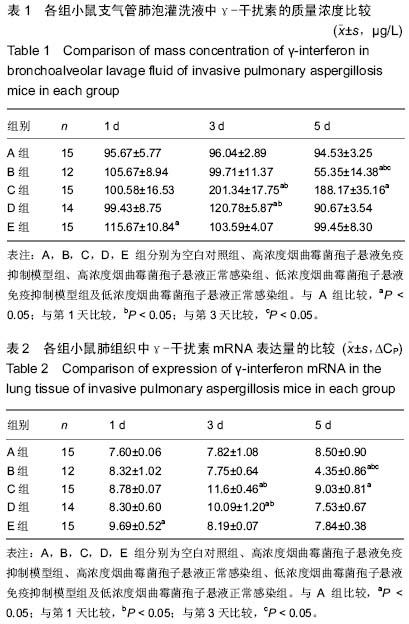
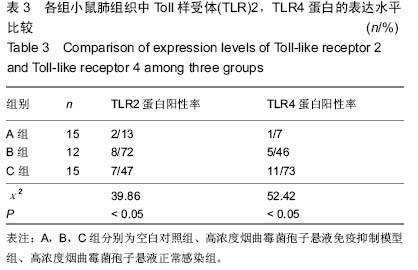
中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (27): 4309-4315.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.27.009
• 骨髓干细胞 bone marrow stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
侵袭性肺曲霉病小鼠模型构建及γ-干扰素、Toll样受体2,4的表达
高晓天1,2,王 正1,宋泽庆2,张冬梅2,张亚楠2
- 1暨南大学,广东省广州市 510632;
2广东医学院附属医院,广东省湛江市 524001
Construction of mouse models of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis and the expression of γ-interferon, Toll-like receptor 2 and Toll-like receptor 4
Gao Xiao-tian1, 2, Wang Zheng1, Song Ze-qing2, Zhang Dong-mei2, Zhang Ya-nan2
- 1Ji’nan University, Guangzhou 510632, Guangdong Province, China;
2Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524001, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
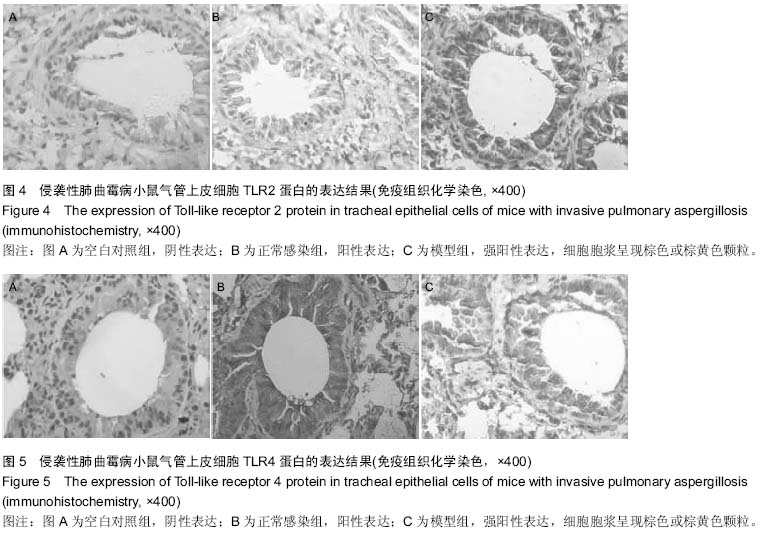
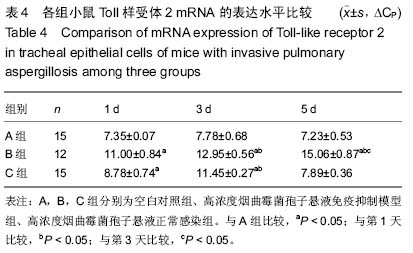
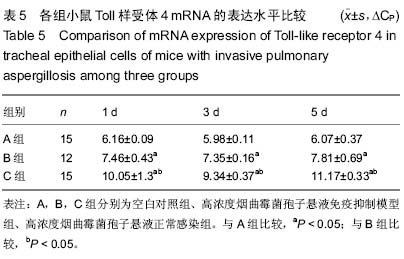
背景:曲霉菌病现已成为主要的肺部真菌感染性疾病,其临床症状、体征和影像学改变缺乏特异性,并且难以获得组织和细菌学的证实,因此临床常常延误诊断和治疗。因此构建侵袭性肺曲霉病动物模型,研究其发病机制和新的治疗手段十分必要。 目的:构建侵袭性肺曲霉病小鼠模型,检测γ-干扰素、Toll样受体2,4的表达,探讨其在侵袭性肺曲霉病中的作用机制。 方法:75只清洁级6-8周龄雌性BALB/c小鼠随机分成5组,分别为空白对照组(A组)、高浓度烟曲霉菌孢子悬液免疫抑制模型组(B组)、高浓度烟曲霉菌孢子悬液正常感染组(C组)、低浓度烟曲霉菌孢子悬液免疫抑制模型组(D组)、低浓度烟曲霉菌孢子悬液正常感染组(E组),每组15只。首先对B、D组腹腔注射环磷酰胺复制免疫抑制模型。D、E组和B、C组分别用雾化器雾化108 cfu/mL、109 cfu/mL的孢子悬液12 mL,A组以灭菌PBS代替孢子悬液。感染第1,3,5天,观察各组小鼠肺组织病理形态学改变;检测肺泡灌洗液中γ-干扰素的质量浓度及肺组织中γ-干扰素mRNA的表达;检测肺组织中Toll样受体2,4 mRNA和Toll样受体2,4蛋白的表达。 结果与结论:B组小鼠肺组织可见肺脓肿,可见到孢子以及较严重的出血和充血,肺泡间隔增宽,气管上皮细胞脱落坏死。与A组对比,B组支气管肺泡灌洗液中的γ-干扰素质量浓度与肺组织中γ-干扰素mRNA在第5天的表达量显著降低(P < 0.05)。B组Toll样受体2呈强阳性表达,C组Toll样受体2阳性表达率低于B组(P < 0.05);B、C组Toll样受体4均呈阳性表达,C组阳性表达率高于B组(P < 0.05)。B组在1,3,5 d时肺组织中Toll样受体2,4 mRNA表达均显著增加(P < 0.05)。提示对免疫抑制小鼠雾化高浓度烟曲霉菌孢子悬液能建立具有典型病理特征的稳定的侵袭性肺曲霉病模型。烟曲霉菌的感染可以同时激活Toll样受体2,4,其致病机制与机体的免疫防御功能密切相关。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:肾移植;肝移植;移植;心脏移植;组织移植;皮肤移植;皮瓣移植;血管移植;器官移植;组织工程
中图分类号: