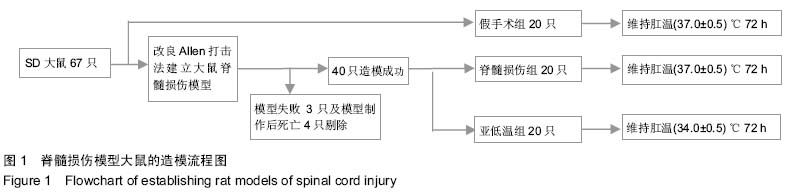
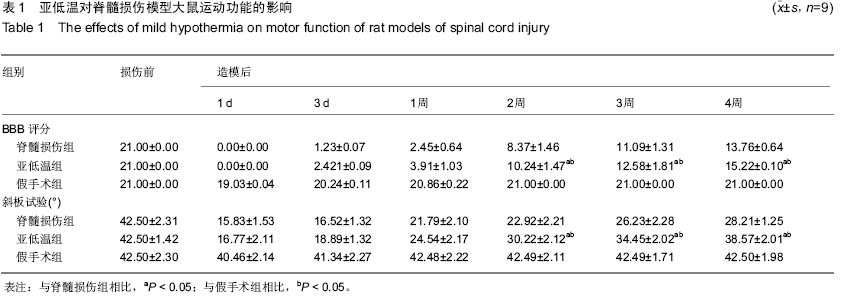
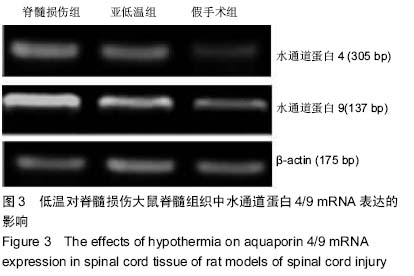
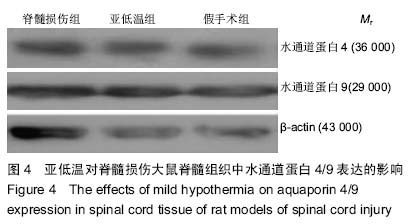
| [1] Nishimura Y, Isa T. Compensatory changes at the cerebral cortical level after spinal cord injury. Neuroscientist. 2009; 15(5): 436-444.
[2] Park WB, Kim SY, Lee SH, et al. The effect of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on the recovery of bladder and hindlimb function after spinal cord contusion in rats. BMC Neurosci. 2010;11:119.
[3] Koelsch A, Feng Y, Fink DJ, et al. Transgene-mediated GDNF expression enhances synaptic connectivity and GABA transmission to improve functional outcome after spinal cord contusion. J Neurochem. 2010;113(1):143-152.
[4] 陶晓峰,刘畅,华正宇,等.亚低温对大鼠局灶性脑缺血再灌注后HIF-1α及凋亡相关蛋白变化的影响[J].中风与神经疾病杂志, 2010,27(10):902-905.
[5] Bethea CL, Reddy AP, Pedersen D, et al. Expression profile of differentiating serotonin neurons derived from rhesus embryonic stem cells and comparison to adult serotonin neurons. Gene Expr Patterns. 2009;9(2):94-108.
[6] Waterhouse EG, Xu B. New insights into the role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in synaptic plasticity. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2009;42(2):81-89.
[7] Han X, Yang N, Xu Y, et al. Simvastatin treatment improves functional recovery after experimental spinal cord injury by upregulating the expression of BDNF and GDNF. Neurosci Lett. 2011;487(3):255-259.
[8] Huang HH, Fetters L, Hale J, et al. Bound for success: a systematic review of constraint-induced movement therapy in children with cerebral palsy supports improved arm and hand use. Phys Ther. 2009;89(11):1126-1141.
[9] Darian-Smith C. Synaptic plasticity, neurogenesis, and functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Neuroscientist. 2009;15(2):149-165.
[10] 杨惠林,孟斌.脊髓损伤模型的评价标准[J].国外医学:骨科学分册, 2003,24(2):74-76.
[11] Nielsen J, Gotfryd K, Li S, et al. Role of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF)-neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) interactions in induction of neurite outgrowth and identification of a binding site for NCAM in the heel region of GDNF. J Neurosci. 2009; 29(36):11360-11376.
[12] Donn SM, Chiswick ML, Fanaroff JM. Medico-legal implications of hypoxic-ischemic birth injury. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014;19(5):317-321.
[13] Dietrich WD, Bramlett HM. The evidence for hypothermia as a neuroprotectant in traumatic brain injury. Neurotherapeutics. 2010;7(1):43-50.
[14] Auer M, Schweigreiter R, Hausott B, et al. Rho-independent stimulation of axon outgrowth and activation of the ERK and Akt signaling pathways by C3 transferase in sensory neurons. Front Cell Neurosci. 2012;6:43.
[15] 郭亚乐,李瑞林,李占魁,等.缺氧缺血性脑损害亚低温干预持续时间的选择[J].陕西医学杂志,2003,32(1):92.
[16] Kobbe P, Lichte P, Wellmann M, et al. Impact of hypothermia on the severely injured patient. Unfallchirurg. 2009;112(12): 1055-1061.
[17] Pallini R, Vitiani LR, Bez A, et al. Homologous transplantation of neural stem cells to the injured spinal cord of mice. Neurosurgery. 2005;57(5):1014-1025; discussion 1014-1025.
[18] Huang T, Solano J, He D, et al. Traumatic injury activates MAP kinases in astrocytes: mechanisms of hypothermia and hyperthermia. J Neurotrauma. 2009;26(9):1535-1545.
[19] Falchetti ML, Pallini R, D'Ambrosio E, et al. In situ detection of telomerase catalytic subunit mRNA in glioblastoma multiforme. Int J Cancer. 2000;88(6):895-901.
[20] 孙振刚,文益民,毛庆花,等.三磷酸腺苷通过激活mTOR/STAT3信号通路促进大鼠脊髓损伤修复[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2010,24(2):165-171.
[21] Theus MH, Wei L, Cui L, et al. In vitro hypoxic preconditioning of embryonic stem cells as a strategy of promoting cell survival and functional benefits after transplantation into the ischemic rat brain. Exp Neurol. 2008;210(2):656-670.
[22] Deng H, Han HS, Cheng D, et al. Mild hypothermia inhibits inflammation after experimental stroke and brain inflammation. Stroke. 2003;34(10):2495-2501.
[23] Shen LH, Li Y, Gao Q, et al. Down-regulation of neurocan expression in reactive astrocytes promotes axonal regeneration and facilitates the neurorestorative effects of bone marrow stromal cells in the ischemic rat brain. Glia. 2008;56(16):1747-1754.
[24] Mothe AJ, Kulbatski I, Parr A, et al. Adult spinal cord stem/progenitor cells transplanted as neurospheres preferentially differentiate into oligodendrocytes in the adult rat spinal cord. Cell Transplant. 2008;17(7):735-751.
[25] Kan EM, Ling EA, Lu J. Microenvironment changes in mild traumatic brain injury. Brain Res Bull. 2012;87(4-5): 359-372.
[26] 陈翀,涂悦,孙洪涛,等.干细胞联合亚低温抵抗颅脑创伤后缺氧微环境[J].中华神经外科杂志,2012,28(10):1070-1075.
[27] Schwab ME. Functions of Nogo proteins and their receptors in the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2010;11(12):799-811.
[28] Saito T, Saito S, Yamamoto H, et al. Neuroprotection following mild hypothermia after spinal cord ischemia in rats. J Vasc Surg. 2013;57(1):173-181.
[29] Bhang SH, Lee YE, Cho SW, et al. Basic fibroblast growth factor promotes bone marrow stromal cell transplantation-mediated neural regeneration in traumatic brain injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;359(1): 40-45.
[30] Carvalho KA, Vialle EN, Moreira GH, et al. Functional outcome of bone marrow stem cells (CD45(+)/CD34(-)) after cell therapy in chronic spinal cord injury in Wistar rats. Transplant Proc. 2008;40(3):845-846.
[31] Fagan-Solis KD, Schneider SS, Pentecost BT, et al. The RhoA pathway mediates MMP-2 and MMP-9-independent invasive behavior in a triple-negative breast cancer cell line. J Cell Biochem. 2013;114(6):1385-1394.
[32] Wang HM, Wang Y, Liu M, et al. Fluoxetine inhibits monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial remodeling involved in inhibition of RhoA-Rho kinase and Akt signalling pathways in rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012;90(11): 1506-1515.
[33] Alon G, Levitt AF, McCarthy PA. Functional electrical stimulation enhancement of upper extremity functional recovery during stroke rehabilitation: a pilot study. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2007;21(3):207-215.
[34] 穆宏伟.应用血泵对中枢性高热患者亚低温治疗效果的观察及护理[J].吉林医学,2013,34(12):2360.
[35] Zausinger S, Westermaier T, Plesnila N, et al. Neuroprotection in transient focal cerebral ischemia by combination drug therapy and mild hypothermia: comparison with customary therapeutic regimen. Stroke. 2003;34(6): 1526-1532.
[36] 王剑刃,傅西安,吴建东,等.亚低温对创伤性脑损伤患者脑脊液髓鞘基本蛋白的影响[J].中国综合临床,2012,28(2):152-154.
[37] Halstead LS, Seager SW. The effects of rectal probe electrostimulation on spinal cord injury spasticity. Paraplegia. 1991;29(1):43-47.
[38] Bayir H, Clark RS, Kochanek PM. Promising strategies to minimize secondary brain injury after head trauma. Crit Care Med. 2003;31(1 Suppl):S112-117.
[39] Yilmaz ER, Kertmen H, Dolgun H, et al. Effects of darbepoetin-α in spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury in the rabbit. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2012;154(6):1037-1043; discussion 1043-1044.
[40] Lu PG, Hu SL, Hu R, et al. Functional recovery in rat spinal cord injury induced by hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning. Neurol Res. 2012;34(10):944-951.
[41] 李方明,聂青.适量X线照射促进脊髓损伤神经再生和运动功能恢复的研究进展[J].中华放射肿瘤学杂志,2009,18(4):333-336.
[42] Blasi J, Chapman ER, Link E, et al. Botulinum neurotoxin A selectively cleaves the synaptic protein SNAP-25. Nature. 1993;365(6442):160-163.
[43] Bregy A, Nixon R, Lotocki G, et al. Posttraumatic hypothermia increases doublecortin expressing neurons in the dentate gyrus after traumatic brain injury in the rat. Exp Neurol. 2012; 233(2):821-828.
[44] 马长城.脊髓损伤的基础研究现状与展望[J].中华神经医学杂志,2011,10(10):976-978.
[45] Hasnan N, Ektas N, Tanhoffer AI, et al. Exercise responses during functional electrical stimulation cycling in individuals with spinal cord injury. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2013;45(6): 1131-1138.
[46] 蒋晓蓉,唐四元.颅脑损伤患者亚低温治疗的护理进展[J].现代护理,2007,13(31):3068-3070.
[47] Shields CB, Zhang YP, Shields LB, et al. The therapeutic window for spinal cord decompression in a rat spinal cord injury model. J Neurosurg Spine. 2005;3(4):302-307.
[48] Wu D, Xiong W, Jia X, et al. Short- and long-latency somatosensory neuronal responses reveal selective brain injury and effect of hypothermia in global hypoxic ischemia. J Neurophysiol. 2012;107(4):1164-1171.
[49] Bialek P, Morris C, Parkington J, et al. Distinct protein degradation profiles are induced by different disuse models of skeletal muscle atrophy. Physiol Genomics. 2011;43(19): 1075-1086.
[50] Robert AA, Al Jadid MS, Bin Afif S, et al. The effects of different rehabilitation strategies on the functional recovery of spinal cord injured rats: an experimental study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010 ;35(23):E1273-1277.
[51] 王维,马雪,赵晓晨,等.功能电刺激对脊髓损伤大鼠运动功能恢复和神经再生的影响[J].中华神经医学杂志,2014,13(1):17-21.
[52] Seo TB, Chang IA, Lee JH, et al. Beneficial function of cell division cycle 2 activity in astrocytes on axonal regeneration after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2013;30(12):1053-1061.
[53] Straus D, Prasad V, Munoz L. Selective therapeutic hypothermia: a review of invasive and noninvasive techniques. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2011;69(6):981-987. |