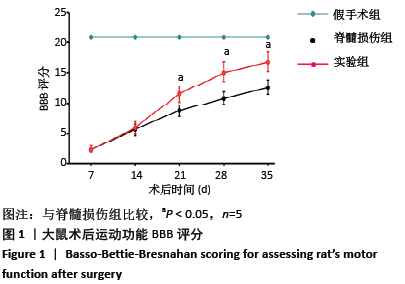
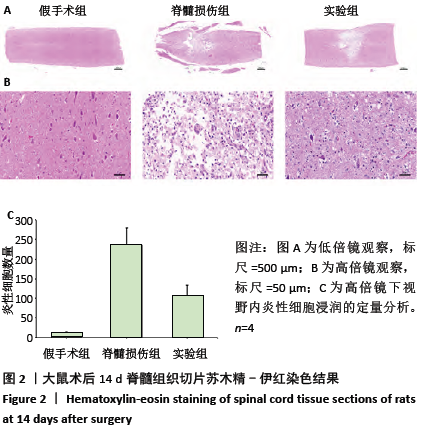
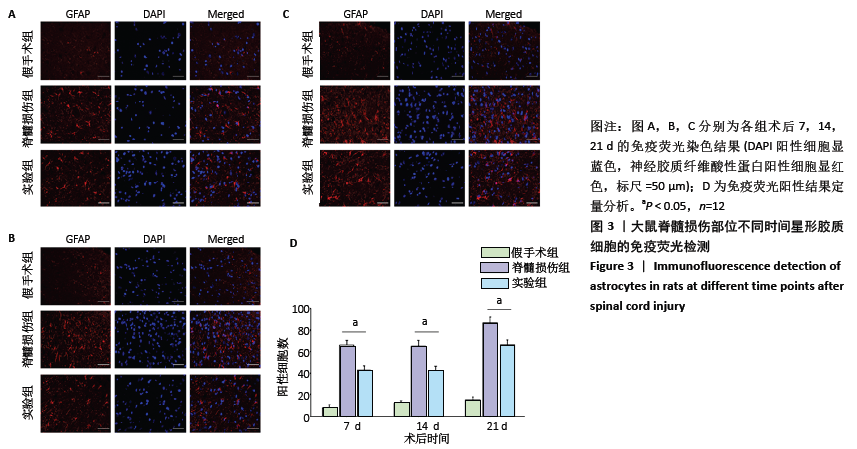
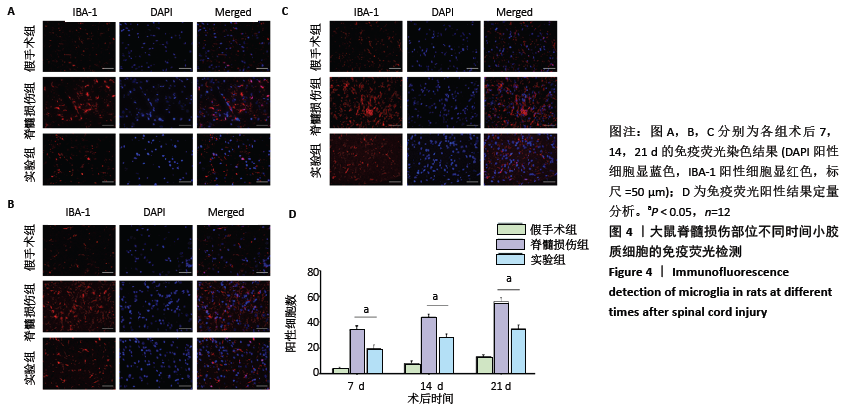
[1] Wang L, Shi Q, Dai J, et al. Increased vascularization promotes functional recovery in the transected spinal cord rats by implanted vascular endothelial growth factor-targeting collagen scaffold.J Orthop Res. 2018;36(3):1024-1034.
[2] Cho N, Squair JW, Bloch J, et al. Neurorestorative interventions involving bioelectronic implants after spinal cord injury.Bioelectron Med. 2019;5:10.
[3] Jing JH, Qian J, Zhu N, et al. Improved differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells and neurological function after spinal cord injury in rats by oscillating field stimulation. Neuroscience.2015; 303:346-351.
[4] Bacova M, Bimbova K, Fedorova J, et al. Epidural oscillating field stimulation as an effective therapeutic approach in combination therapy for spinal cord injury.J Neurosci Methods. 2019;311:102-110.
[5] Zhang C, Zhang G, Rong W, et al. Oscillating field stimulation promotes spinal cord remyelination by inducing differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells after spinal cord injury. Biomed Mater Eng. 2014;24(6):3629-3636.
[6] 黄先甲,钱军,张坤坤,等.振荡电场对大鼠损伤脊髓组织中Wnt-3a表达及运动能力的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(18): 2648-2654.
[7] Zhang YD, Zhu ZS, Zhang D, et al. Lentivirus-mediated silencing of the PTC1 and PTC2 genes promotes recovery from spinal cord injury by activating the Hedgehog signaling pathway in a rat model. Exp Mol Med. 2017;49(12):e412.
[8] Duan HQ, Wu QL, Yao X, et al. Nafamostat mesilate attenuates inflammation and apoptosis and promotes locomotor recovery after spinal cord injury. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2018;24(5):429-438.
[9] Han Q, Xie Y, Ordaz JD, et al. Restoring Cellular Energetics Promotes Axonal Regeneration and Functional Recovery after Spinal Cord Injury.Cell Metab. 2020;31(3):623-641.
[10] Hurlbert RJ, Hadley MN, Walters BC, et al. Pharmacological therapy for acute spinal cord injury. Neurosurgery. 2015;1:S71-83.
[11] van Den Hauwe L, Sundgren PC, Flanders AE. Spinal Trauma and Spinal Cord Injury (SCI). Springer. 2020;2020–2023.DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-38490-6_19
[12] Ramer LM, Ramer MS, Bradbury EJ. Restoring function after spinal cord injury: towards clinical translation of experimental strategies.Lancet Neurol. 2014;13(12):1241-1256.
[13] Wan G, An Y, Tao J, et al. MicroRNA-129-5p alleviates spinal cord injury in mice via suppressing the apoptosis and inflammatory response through HMGB1//TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Biosci Rep. 2020;BSR20193315.
[14] Fitch MT, Silver J. CNS injury, glial scars, and inflammation: Inhibitory extracellular matrices and regeneration failure. Exp Neurol. 2008; 209(2):294-301.
[15] Huynh V, Rosner J, Curt A, et al. Disentangling the Effects of Spinal Cord Injury and Related Neuropathic Pain on Supraspinal Neuroplasticity: A Systematic Review on Neuroimaging. Front Neurol. 2020;10:1413.
[16] Barbeau H, Rossignol S. Recovery of locomotion after chronic spinalization in the adult cat. Brain Res. 1987;412(1):84-95.
[17] Kadoya K, Tsukada S, Lu P, et al. Combined intrinsic and extrinsic neuronal mechanisms facilitate bridging axonal regeneration one year after spinal cord injury. Neuron. 2009;64(2):165-172.
[18] Tran AP, Silver J. Neuroscience. Systemically treating spinal cord injury.Science. 2015;348(6232):285-286.
[19] Fitzharris M, Cripps RA, Lee BB. Estimating the global incidence of traumatic spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2014;52(2):117-122.
[20] Wallace MC, Tator CH, Piper I. Recovery of spinal cord function induced by direct current stimulation of the injured rat spinal cord. Neurosurgery. 1987;20(6):878-884.
[21] Borgens RB, Toombs JP, Breur G, et al. An imposed oscillating electrical field improves the recovery of function in neurologically complete paraplegic dogs.J Neurotrauma. 1999;16(7):639-657.
[22] Borgens RB, Liu-Snyder P. Understanding second injury. Q Rev Biol. 2012;87:89-127.
[23] Li X, Liu R, Yu Z, et al. Microglial Hv1 exacerbates secondary damage after spinal cord injury in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020; (20)30272-30272.
[24] Okada S, Hara M, Kobayakawa K, et al. Astrocyte reactivity and astrogliosis after spinal cord injury. Neurosci Res. 2018;126:39-43.
[25] Park KS, Kim JB, Keung M, et al. Chronic hyperglycemia before spinal cord injury increases inflammatory reaction and astrogliosis after injury: human and rat studies. J Neurotrauma. 2020;37(9):1165-1181.
[26] Keilhoff G, Titze M, Rathert H, et al. Normoxic post-ROSC ventilation delays hippocampal CA1 neurodegeneration in a rat cardiac arrest model, but does not prevent it.Exp Brain Res. 2020; s00221-020-05746-6.
[27] Li XH, Fu NS, Xing ZM. MiR-100 suppresses inflammatory activation of microglia and neuronal apoptosis following spinal cord injury via TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(20): 8713-8720.
[28] Jian YP, Dong SJ, Xu SS, et al. MicroRNA-34a suppresses neuronal apoptosis and alleviates microglia inflammation by negatively targeting the Notch pathway in spinal cord injury.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(3):1420-1427.
[29] Choi JI, Kang HY, Han C, et al. Milk Fat Globule-Epidermal Growth Factor VIII Ameliorates Brain Injury in the Subacute Phase of Cerebral Ischemia in an Animal Model.J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2020;63(2): 163-170.
|
 文题释义:
文题释义: