| [1] 黄雁翔,邓建平,张治平,等.硅胶假体隆乳术临床应用观察[J].中国美容医学,2013,22(6):624-625.
[2] 黎石峰,李俊明,张昕霞,等.假体隆乳术3种置入层次回顾性分析:450例临床报告[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2013,24(6): 355-357.
[3] 王培生,沈恒丽,王增顺.硅胶假体隆乳术临床研究[J].中国现代药物应用,2012,6(17):41-42.
[4] Mendes D,Veiga D,Veiga-Filho J,et al.Application time for postoperative wound dressing following breast augmentation with implants: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials.2015;16(1):19. [Epub ahead of print]
[5] Wazir U, Kasem A, Mokbel K.The clinical implications of poly implant prothèse breast implants: an overview.Arch Plast Surg.2015;42(1):4-10.
[6] Swanson E.Breast Reduction versus Breast Reduction Plus Implants: A Comparative Study with Measurements and Outcomes.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2015;2(12): e281.
[7] Frame JD.Commentary on: Breast Implants and the Risk of Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis on Cohort Studies.Aesthet Surg J. 2015;35(1):63-65.
[8] Ota D,Fukuuchi A,Iwahira Y,et al.Identification of complications in mastectomy with immediate reconstruction using tissue expanders and permanent implants for breast cancer patients.Breast Cancer. 2014 Dec 30. [Epub ahead of print]
[9] De Lorenzi F,Gazzola R,Sangalli C,et al.Poly implant prothèse asymmetrical anatomical breast implants: a product recall study.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;135(1): 25-33.
[10] Godwin Y, Duncan RT, Feig C, et al.Soft, Brown Rupture: Clinical Signs and Symptoms Associated with Ruptured PIP Breast Implants.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2014;2(11): e249.
[11] Chung KC.Large Cell Lymphoma (ALCL) in Women with Breast Implants: Analysis of 173 Cases World Wide Discussion by Dr. Kevin C. Chung.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014 Dec 8. [Epub ahead of print] No abstract available.
[12] Glasberg SB.Discussion: Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (ALCL) in Women with Breast Implants: Analysis of 173 Cases World Wide.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014 Dec 8. [Epub ahead of print] No abstract available.
[13] Figueres ML,Beaume J,Vuiblet V,et al.Crystalline light chain proximal tubulopathy with chronic renal failure and silicone gel breast implants: 1 case report.Hum Pathol. 2015;46(1): 165-168.
[14] Akhtari M,Nitsch PL,Bass BL,et al.Long-term outcome of accelerated partial breast irradiation using a multilumen balloon applicator in a patient with existing breast implants.Brachytherapy.2014 Nov 5. pii: S1538-4721(14) 00646-1.
[15] Bogaert P, Perrot P, Duteille F.Should we drain after pre-pectoral breast implants? Analysis of a cohort of 400 patients operated for breast augmentation with pre-pectoral silicone implants.Ann Chir Plast Esthet.2014 Nov 6.pii: S0294-1260(14)00141-1. 10.1016/j.anplas.2014.08.014.[Epub ahead of print] French.
[16] 金莉.化疗对患者口腔黏膜细胞凋亡和增殖的影响及中药的干预作用[J].浙江中医药大学学报,2012,36(2):162-163.
[17] 邹游,李小兰,肖徽,等.肠外瘘对患者口腔黏膜细胞凋亡和增殖的影响[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2011,27(3):131-133.
[18] 高纯,魏欣,朱真闯,等.口腔黏膜细胞凋亡和增殖率与化疗患者营养状况的关系[J].华中科技大学学报:医学版,2009,38(1):56-58.
[19] 中华医学会整形外科学分会乳房专业学组.硅胶乳房假体隆乳术临床技术指南[J].中华整形外科杂志,2013,29(1):1-4.
[20] Almeida AI,Correia M,Camilo M,et al.Length of stay in surgical patients: nutritional predictive parameters revisited.Br J Nutr.2013;109(2):322-328.
[21] Botha D.The next step: optimizing preoperative functional fitness and nutritional intervention.Can J Anaesth.2013;60(2): 208-208.
[22] Valente da Silva HG, Santos SO, et al.Nutritional assessment associated with length of inpatients' hospital stay.Nutr Hosp. 2012;27(2):542-547.
[23] Planas M,Audivert S,Pérez-Portabella C,et al.utritional status among adult patients admitted to an university-affiliated hospital in Spain at the time of genoma.Clin Nutr.2004;23(5): 1016-1024.
[24] Ordoñez AM, Madalozzo Schieferdecker ME, et al.Nutritional status influences the length of stay and clinical outcomes in patients hospitalized in internal medicine wards.Nutr Hosp. 2013;28(4):1313-1320.
[25] Ferreira C, Lavinhas C, Fernandes L,et al.Nutritional risk and status of surgical patients; the relevance of nutrition training of medical students.Nutr Hosp. 2012;27(4):1086-1091.
[26] Carli F,Brown R,Kennepohl S.Prehabilitation to enhance postoperative recovery for an octogenarian following robotic-assisted hysterectomy with endometrial cancer.Can J Anaesth.2012;59(8):779-784.
[27] Gaia G,Holloway RW,Santoro L,et al.Robotic-assisted hysterectomy for endometrial cancer compared with traditional laparoscopic and laparotomy approaches: a systematic review.Obstet Gynecol.2010;116(6):1422-1431.
[28] 王璐,刘林嶓,陈旻静,等.硅胶假体隆乳6个月~8年并发症19例[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(47):8765-8768.
[29] 冯煜,黄建平,胡俊波,等.不同营养状态下大鼠口腔与肠道黏膜细胞凋亡率的关系研究[J]. 中国医药指南,2012,10(11):1-3.
[30] 高纯,魏欣,朱真闯,等.口腔黏膜细胞凋亡和增殖率与化疗患者营养状况的关系[J]. 华中科技大学学报:医学版,2009,38(1): 56-58.
[31] 李绮雯,李桂超,王亚农,等.胃癌辅助放化疗患者的营养状态与放化疗不良反应及治疗耐受性的关系[J].中华胃肠外科杂志,2013, 16(6):529-533.
[32] 谢小亮,夏羽菡,李海,等.120例结直肠癌患者术前营养状态评估[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2013,35(10):1139-1141.
[33] DeSouzaMenezesF,LeiteHP,KochNogueiraPC,et al. Malnutrition as an independent predictor of clinical outcome in critically ill children.Nutrition.2012;28(3):267-270.
[34] Mehta NM, Bechard LJ, Cahill N, et al.Nutritional practices and their relationship to clinical outcomes in critically ill children--an international multicenter cohort study*.Crit Care Med. 2012;40(7):2204-2211.
[35] Leite HP,de Lima LF,de Oliveira Iglesias SB,et al.Malnutrition may worsen the prognosis of critically ill children with hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr.2013;37(3):335-341.
[36] Mekitarian Filho E, Carvalho WB, Troster EJ.Hyperglycemia, morbidity and mortality in critically ill children: critical analysis based on a systematic review.Rev Assoc Med Bras.2009; 55(4):475-483.
[37] 魏欣,高纯,朱真闯,等.化疗对患者口腔黏膜细胞生长状态的影响[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2009,25(4):199-201.
[38] BaganP,BernaP,DeDominicisF,et al.Nutritional status and postoperative outcome after pneumonectomy for lung cancer. AnnThorac Surg.2013;95(2):392-396.
[39] 尹小平,龚建平.手术创伤对口腔黏膜细胞凋亡和增殖的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志,2011,28(11):1927-1929. |
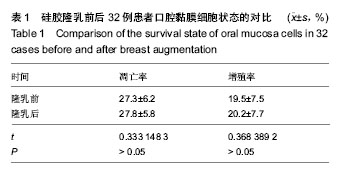
.jpg)
.jpg)