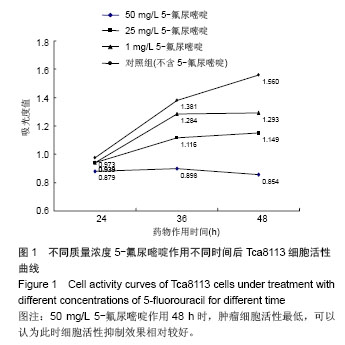
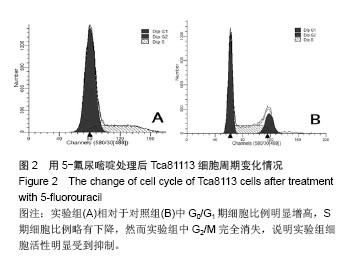
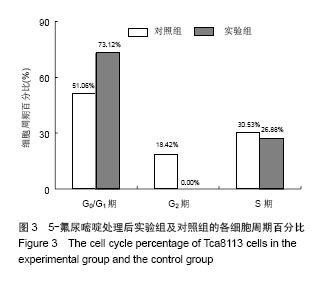
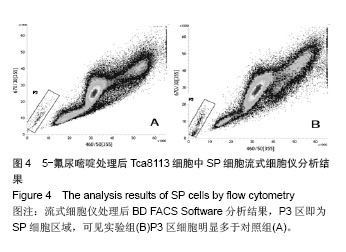
| [1]Chen YJ, Chang JT, Liao CT, et al. Head and neck cancer in the betel quid chewing area: recent advances in molecular carcinogenesis.Cancer Sci. 2008;99(8):1507-1514.
[2]韩文遒. 结肠癌干细胞的筛选及其耐药性研究[J].医学美学美容:中旬刊,2014,22(3):141-142.
[3]Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF,et al.Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells.Nature. 2001;414(6859):105-111.
[4]Lapidot T, Sirard C, Vormoor J,et al.A cell initiating human acute myeloid leukaemia after transplantation into SCID mice. Nature. 1994;367(6464):645-648.
[5]Dalerba P, Cho RW, Clarke MF.Cancer stem cells: models and concepts.Annu Rev Med. 2007;58:267-284.
[6]Wei XD, Zhou L, Cheng L,et al. In vivo investigation of CD133 as a putative marker of cancer stem cells in Hep-2 cell line. Head Neck. 2009;31(1):94-101.
[7]Clay MR, Tabor M, Owen JH,et al.Single-marker identification of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cancer stem cells with aldehyde dehydrogenase.Head Neck. 2010;32(9):1195-1201.
[8]Tabor MH, Clay MR, Owen JH,et al.Head and neck cancer stem cells: the side population.Laryngoscope. 2011;121(3): 527-533.
[9]孙守娟,季平,邹波,等.无血清悬浮培养舌鳞癌Tca8113细胞系及肿瘤干细胞样亚群筛选[J].重庆医科大学学报,2011,36(12): 1416-1419.
[10]袁吉,倪孟祥.5-氟尿嘧啶及其衍生物的研究进展[J].药物生物技术,2012,19(5):462-465.
[11]Hodgson GS, Bradley TR.Properties of haematopoietic stem cells surviving 5-fluorouracil treatment: evidence for a pre-CFU-S cell?Nature. 1979;281(5730):381-382.
[12]邱蔚六.口腔颌面外科学[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社,2008: 467-487.
[13]Hong NJ, Wright FC, Gagliardi AR,et al. Examining the potential relationship between multidisciplinary cancer care and patient survival: an international literature review.J Surg Oncol. 2010;102(2):125-134.
[14]Wong RJ, Shah JP.The role of the head and neck surgeon in contemporary multidisciplinary treatment programs for advanced head and neck cancer.Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010;18(2):79-82.
[15]Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M,et al.Identification of a cancer stem cell in human brain tumors.Cancer Res. 2003; 63(18):5821-5828.
[16]王景涛,季平,邓诚,等.无血清培养法分选舌癌侧群细胞及其特性的鉴定[J].第三军医大学学报,2011,33(8):818-821.
[17]Li R, Wu X, Wei H,et al.Characterization of side population cells isolated from the gastric cancer cell line SGC-7901. Oncol Lett. 2013;5(3):877-883.
[18]Wang S, Xu ZY, Wang LF,et al.CD133+ cancer stem cells in lung cancer.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2013;18:447-453.
[19]Shigeishi H, Biddle A, Gammon L,et al.Maintenance of stem cell self-renewal in head and neck cancers requires actions of GSK3β influenced by CD44 and RHAMM.Stem Cells. 2013; 31(10):2073-2083.
[20]Canis M, Lechner A, Mack B,et al.CD133 is a predictor of poor survival in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Biomark. 2012;12(2):97-105.
[21]Chen YC, Chang CJ, Hsu HS,et al. Inhibition of tumorigenicity and enhancement of radiochemosensitivity in head and neck squamous cell cancer-derived ALDH1-positive cells by knockdown of Bmi-1.Oral Oncol. 2010;46(3):158-165.
[22]Yu CC, Lo WL, Chen YW,et al. Bmi-1 Regulates Snail Expression and Promotes Metastasis Ability in Head and Neck Squamous Cancer-Derived ALDH1 Positive Cells.J Oncol. 2011;2011. pii: 609259.
[23]Wu CP, Zhou L, Xie M,et al. Identification of cancer stem-like side population cells in purified primary cultured human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma epithelia.PLoS One. 2013; 8(6):e65750.
[24]He K, Xu T, Xu Y,et al.Cancer cells acquire a drug resistant, highly tumorigenic, cancer stem-like phenotype through modulation of the PI3K/Akt/β-catenin/CBP pathway.Int J Cancer. 2014;134(1):43-54.
[25]Teshima K, Nara M, Watanabe A,et al.Dysregulation of BMI1 and microRNA-16 collaborate to enhance an anti-apoptotic potential in the side population of refractory mantle cell lymphoma.Oncogene. 2014;33(17):2191-2203.
[26]Song J, Chang I, Chen Z,et al.Characterization of side populations in HNSCC: highly invasive, chemoresistant and abnormal Wnt signaling.PLoS One. 2010;5(7):e11456.
[27]Yanamoto S, Kawasaki G, Yamada S,et al.Isolation and characterization of cancer stem-like side population cells in human oral cancer cells.Oral Oncol. 2011;47(9):855-860.
[28]Tsai LL, Yu CC, Chang YC,et al.Markedly increased Oct4 and Nanog expression correlates with cisplatin resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma.J Oral Pathol Med. 2011;40(8): 621-628.
[29]Grimm M, Krimmel M, Polligkeit J,et al.ABCB5 expression and cancer stem cell hypothesis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 2012;48(17):3186-3197. |