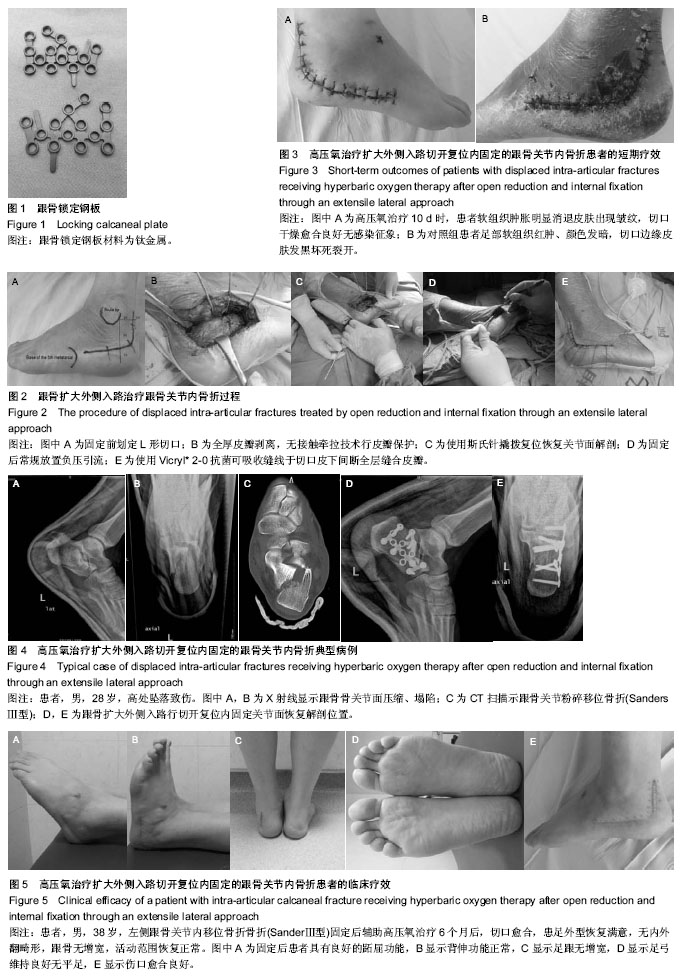
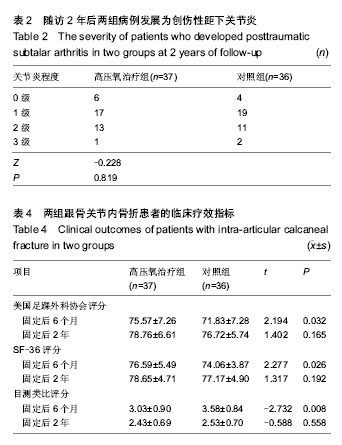
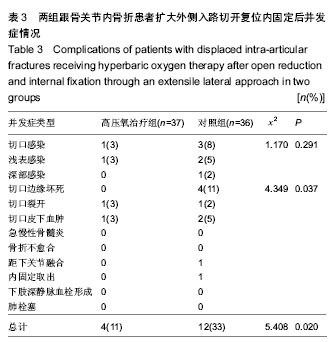
| [1] Sanders R. Displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82(2):225-250.
[2] Gupta A, Ghalambor N, Nihal A, et al. The modified Palmer lateral approach for calcaneal fractures: wound healing and postoperative computed tomographic evaluation of fracture reduction. Foot Ankle Int. 2003;24(10):744-753.
[3] Gordillo GM, Sen CK. Revisiting the essential role of oxygen in wound healing. Am J Surg. 2003;186(3):259-263.
[4] 李彬彬,李厚成,陈文,等.高压氧综合治疗跟骨骨折术后切口皮瓣愈合的临床疗效观察[J].中华航海医学与高气压医学杂志,2013, 20(6):410-411.
[5] 和艳红,李志强,栗申,等.高压氧治疗跟骨骨折局部软组织损伤的临床观察[J].中华航海医学与高气压医学杂志,2013,20(2): 101-103.
[6] Bhattacharya R, Vassan UT, Finn P, et al. Sanders classification of fractures of the os calcis. An analysis of inter- and intra-observer variability. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005; 87(2):205-208.
[7] Baumhauer JF, Nawoczenski DA, DiGiovanni BF, et al. Reliability and validity of the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society Clinical Rating Scale: a pilot study for the hallux and lesser toes. Foot Ankle Int. 2006;27(12):1014-1019.
[8] Hildebrand KA, Buckley RE, Mohtadi NG, et al. Functional outcome measures after displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996;78(1):119-123.
[9] Ware JE Jr, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care. 1992;30(6):473-483.
[10] Lim EV, Leung JP. Complications of intraarticular calcaneal fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(391):7-16.
[11] Broussard CL. Hyperbaric oxygenation and wound healing. J Vasc Nurs. 2004;22(2):42-48.
[12] Koomanachai P, Keel RA, Johnson-Arbor KK, et al. Linezolid penetration into wound tissue of two diabetic patients before and after hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Undersea Hyperb Med. 2011;38(1):11-16.
[13] Thom SR, Milovanova TN, Yang M, et al. Vasculogenic stem cell mobilization and wound recruitment in diabetic patients: increased cell number and intracellular regulatory protein content associated with hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Wound Repair Regen. 2011;19(2):149-161.
[14] Stoekenbroek RM, Santema TB, Legemate DA, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers: a systematic review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2014;47(6): 647-655.
[15] Dauwe PB, Pulikkottil BJ, Lavery L, et al. Does hyperbaric oxygen therapy work in facilitating acute wound healing: a systematic review. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014;133(2): 208e-215e.
[16] Benirschke SK, Kramer PA. Wound healing complications in closed and open calcaneal fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2004;18(1):1-6.
[17] Court-Brown CM, Schmied M, Schutte BG. Factors affecting infection after calcaneal fracture fixation. Injury. 2009;40(12): 1313-1315.
[18] Schepers T, Den Hartog D, Vogels LM, et al. Extended lateral approach for intra-articular calcaneal fractures: an inverse relationship between surgeon experience and wound complications. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2013;52(2):167-171.
[19] Huang KC, Tsai YH, Hsu RW. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy facilitates surgery on complex open elbow injuries: preliminary results. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16(4): 454-460.
[20] Löndahl M, Landin-Olsson M, Katzman P. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy improves health-related quality of life in patients with diabetes and chronic foot ulcer. Diabet Med. 2011;28(2): 186-190.
[21] Rammelt S, Zwipp H, Schneiders W, et al. Severity of injury predicts subsequent function in surgically treated displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013; 471(9):2885-2898. |