中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (6): 901-905.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2395
• 骨科植入物Orthopedic implants • 上一篇 下一篇
单纯HyProCure跗骨螺钉治疗青少年柔韧性平足合并痛性副舟骨
吴 刚1,2,陈建文1,2,王世隆1,2,段笑然1,2,刘海军3,董建峰3
- 1国家康复辅具研究中心附属康复医院微创足踝外科,北京市 110115;2北京市老年功能障碍康复辅助技术重点实验室,民政部人体运动分析与康复技术重点实验室,北京市 110115;3山西医科大学第二医院骨科,山西省太原市 030024
Simple HyProCure subtalar stabilization in treatment of adolescent flexible flatfoot combined with painful accessory navicular bone
Wu Gang1, 2, Chen Jianwen1, 2, Wang Shilong1, 2, Duan Xiaoran1, 2, Liu Haijun3, Dong Jianfeng3
- 1Department of Minimal Invasive Foot & Ankle, Rehabilitation Hospital, National Research Center for Rehabilitation Technical Aids, Beijing 110115, China; 2Beijing Key Laboratory of Rehabilitation Technical Aids for Old-Age Disability, Key Laboratory of Human Motion Analysis and Rehabilitation Technology of the Ministry of Civil Affairs, Beijing 110115, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030024, Shanxi Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
平足症:又称扁平足,指足弓低平或消失,患足外翻,站立、行走时足弓塌陷,引起足部疼痛的一种畸形。很多平足者特别是儿童平足没有症状,也不需要治疗,只有少部分儿童平足可能会逐渐引起整个身体体态的变化,有一部分平足可能合并足部骨结构异常,如垂直距骨、跗骨联合等。
距下关节制动:涉及放置一个植入物于跗骨窦,代表着最小的侵入性手术干预。植入物可以防止不正常的踝关节旋转,这样能够保证在动态下维持其正常的解剖结构。此技术操作简单,患儿术后恢复快,而其他替代的选择方案则需要更大的手术操作,增加了手术危险性及术后恢复难度。
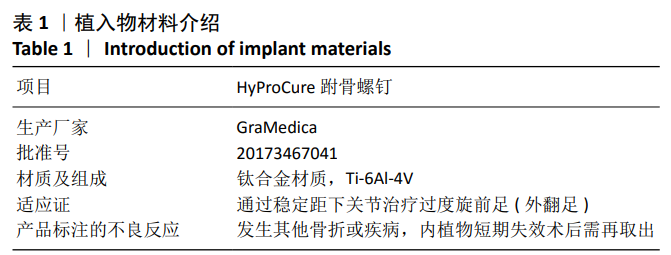
背景:HyProCure跗骨螺钉已被广泛应用于柔韧性平足症的治疗,但针对合并痛性副舟骨的青少年柔韧性平足症尚无统一的治疗方式。
目的:探讨单纯应用HyProCure跗骨螺钉治疗青少年柔韧性平足合并痛性副舟骨的临床疗效。
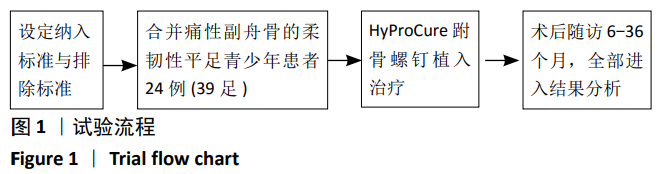
方法:选择2015年1月至2019年9月国家康复医院收治的合并痛性副舟骨的柔韧性平足青少年患者24例(39足),其中男13例(22足),女11例(17足),年龄5-15岁,均接受HyProCure跗骨螺钉植入治疗。术后随访目测类比评分和美国足踝外科协会(AOFAS)踝与后足功能评分,拍摄X射线片,测量距骨-第1跖骨角(Meary’s角)、距骨-第2跖骨角、跟骨倾斜角(Pitch角)、距骨倾斜角、跟骨外翻角、距舟覆盖角及距骨跟骨角。研究获得国家康复医院伦理委员会批准。
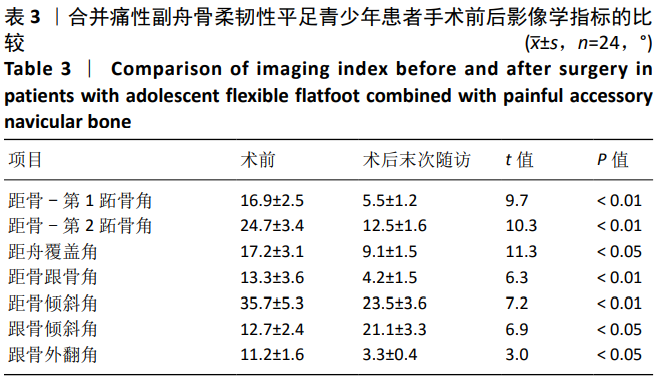
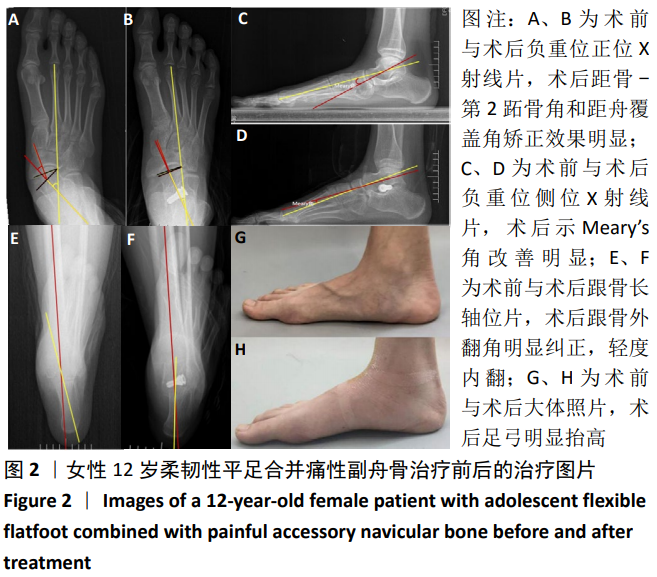
结果与结论:①术后24例患者切口均Ⅰ期愈合,其中2例(2足)出现跗骨窦区疼痛,1例(1足)术后出现跟骨轻度内翻及第1跖骨头下负重不足,1例(1足)术后残留副舟骨轻度疼痛;②24例患者获得6-36个月随访,未出现螺钉退出及二次手术取出螺钉等情况;③24例患者末次随访时的目测类比评分明显低于术前(P < 0.01),AOFAS踝与后足功能评分明显高于术前(P < 0.01);④24例患者末次随访的Meary’s角、距骨-第2跖骨角、Pitch角、距骨倾斜角、跟骨外翻角、距舟覆盖角及距骨跟骨角均较术前明显改善(P < 0.01或P < 0.05);⑤结果表明,应用HyProCure跗骨螺钉治疗青少年合并痛性副舟骨的柔韧性平足具有良好的短期疗效。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3628-9259 (吴刚)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: