| [1] Zhu T, Tang Q, Gao H, et al. Current status of cell-mediated regenerative therapies for human spinal cord injury. Neurosci Bull. 2014;30(4):671-682.
[2] Bonfield W. Designing porous scaffolds for tissue engineering. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2006;364(1838):227-232.
[3] Evans N R, Davies E M, Dare C J, et al. Tissue engineering strategies in spinal arthrodesis: the clinical imperative and challenges to clinical translation. Regen Med. 2013;8(1):49-64.
[4] Houle J D, Tessler A. Repair of chronic spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 2003;182(2):247-260.
[5] Ji W, Hu S, Zhou J, et al. Tissue engineering is a promising method for the repair of spinal cord injuries (Review). Exp Ther Med. 2014;7(3):523-528.
[6] Lai BQ, Wang JM, Ling EA, et al. Graft of a tissue-engineered neural scaffold serves as a promising strategy to restore myelination after rat spinal cord transection. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23(8):910-921.
[7] Luo J, Borgens R, Shi R. Polyethylene glycol improves function and reduces oxidative stress in synaptosomal preparations following spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2004; 21(8):994-1007.
[8] 李森,史晓远,林卫,等.静电纺丝聚乳酸聚乙醇酸共聚物-丝素-胶原神经导管修复大鼠周围神经缺损[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(38):7087-7091.
[9] Chen SJ, Lin CC, Tuan WC, et al. Effect of recombinant galectin-1 on the growth of immortal rat chondrocyte on chitosan-coated PLGA scaffold. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010; 93(4):1482-1492.
[10] Lu JM, Wang X, Marin-Muller C, et al. Current advances in research and clinical applications of PLGA-based nanotechnology. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2009;9(4):325-341.
[11] Park BH, Zhou L, Jang KY, et al. Enhancement of tibial regeneration in a rat model by adipose-derived stromal cells in a PLGA scaffold. Bone. 2012;51(3):313-323.
[12] Wattendorf U, Merkle HP. PEGylation as a tool for the biomedical engineering of surface modified microparticles. J Pharm Sci. 2008;97(11):4655-4669.
[13] 李晓然,袁晓燕.聚乙二醇-聚乳酸共聚物药物载体[J].化学进展, 2007,19(6):973-981.
[14] 路娟,刘清飞,罗国安,等.药物的聚乙二醇修饰研究进展[J].有机化学,2009,29(8):1167-1174.
[15] Sharma H S. Post-traumatic application of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and glia-derived neurotrophic factor on the rat spinal cord enhances neuroprotection and improves motor function. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2006;96:329-334.
[16] 叶川,马敏先,张弢,等.Ⅰ型胶原修饰纯钛片促进人脂肪间充质干细胞增殖[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(25):4032-4037.
[17] 倪石磊,齐宏旭,鲍圣德,等.组织工程支架在犬急性脊髓损伤修复中应用的初步研究[J].中国微侵袭神经外科杂志,2005,10(9): 404-407.
[18] 王北岳,赵建宁.组织工程支架材料在脊髓损伤中的应用[J].医学研究生学报,2008,21(5):547-552.
[19] Mikami Y, Okano H, Sakaguchi M, et al. Implantation of dendritic cells in injured adult spinal cord results in activation of endogenous neural stem/progenitor cells leading to de novo neurogenesis and functional recovery. J Neurosci Res. 2004;76(4):453-465.
[20] Tavares I. Human neural stem cell transplantation in spinal cord injury models: how far from clinical application. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;4(3):61.
[21] Ogawa Y, Sawamoto K, Miyata T, et al. Transplantation of in vitro-expanded fetal neural progenitor cells results in neurogenesis and functional recovery after spinal cord contusion injury in adult rats. J Neurosci Res. 2002;69(6): 925-933.
[22] 庞丽云,王海,陈永霞,等.载紫杉醇聚乳酸聚乙醇酸共聚物纳米粒抑制人肝癌细胞HepG2的作用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(3):412-418.
[23] Ghasemi-Mobarakeh L, Prabhakaran M P, Morshed M, et al. Electrospun poly(epsilon-caprolactone)/gelatin nanofibrous scaffolds for nerve tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2008; 29(34):4532-4539.
[24] Lim SH, Mao HQ. Electrospun scaffolds for stem cell engineering. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2009;61(12):1084-1096.
[25] Liu J, Bauer AJ, Li B. Solvent vapor annealing: an efficient approach for inscribing secondary nanostructures onto electrospun fibers. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2014;35(17): 1503-1508.
[26] Xu L, Sheybani N, Ren S, et al. Semi-Interpenetrating Network (sIPN) Co-Electrospun Gelatin/Insulin Fiber Formulation for Transbuccal Insulin Delivery. Pharm Res. 2014 [Epub ahead of print].
[27] 谭迎赟,白石,廖运茂.双相钙磷生物陶瓷/硫酸钙骨水泥多孔三维支架的生物性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(8):1161-1164.
[28] 李卫东,崔志明,徐冠华,等.壳聚糖增强型左旋聚乳酸与嗅鞘细胞的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(29):5316-5322. |
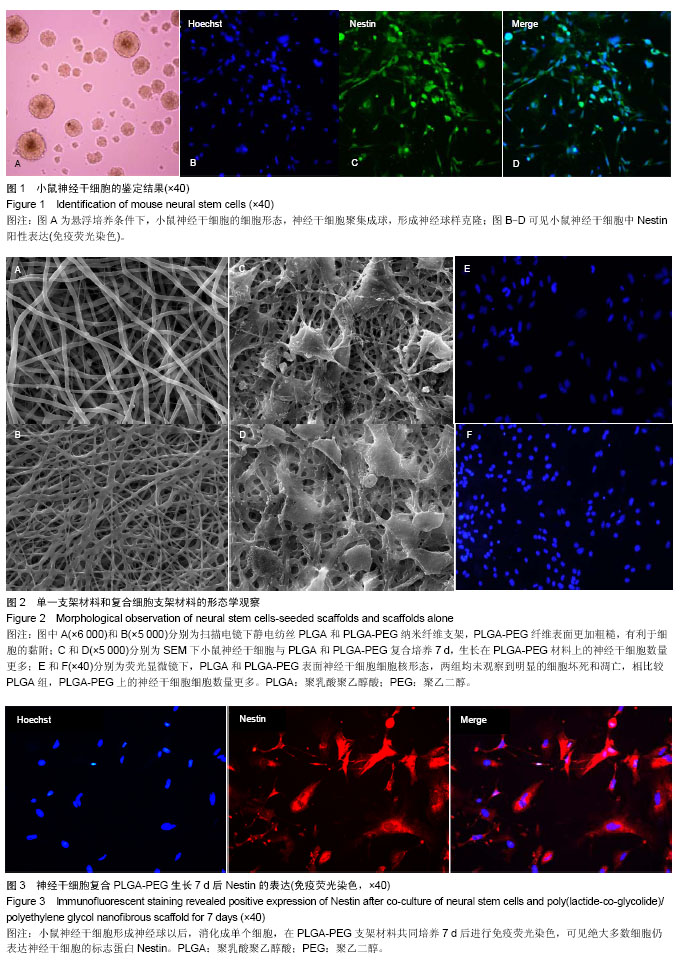
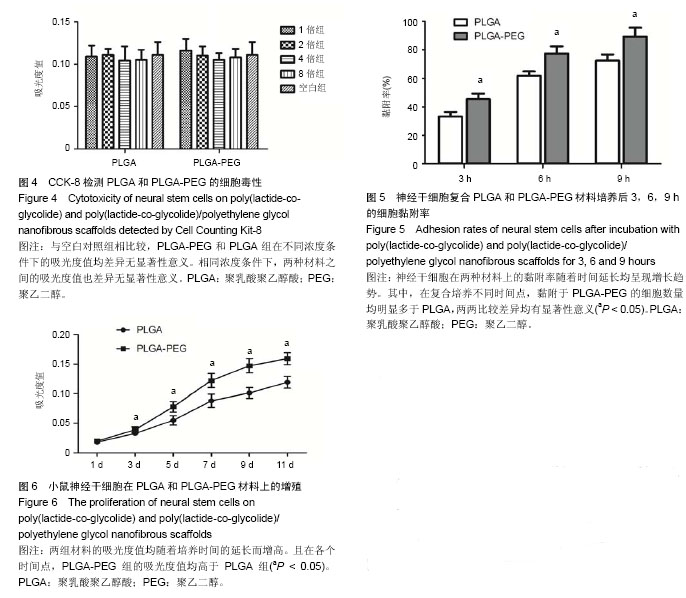
.jpg)