| [1] 中华医学会呼吸病学分会.医院获得性肺炎诊断和治疗指南(草案)[J].中华结核和呼吸杂志.1999; 22 (4):201-208.
[2] 吴安华,任南,文细毛,等. 全国医院感染监控网1998~1999年监测资料分析[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2000,10(6): 32-35.
[3] Mandell LA, Wunderink RG, Anzueto A,et al.Infectious Diseases Society of America/American Thoracic Society consensus guidelines on the management of community-acquired pneumonia in adults.Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44 Suppl 2:S27-S72.
[4] 胡必杰,何礼贤.重症医院内肺炎病原治疗及预后相关因素分析[J]..中华流行病学杂志.1993;14:18.
[5] 林果为, 沈福民. 现代临床流行病学[M].上海:上海医科大学出版社. 2000:236-242.
[6] Ross PD.Osteoporosis. Frequency, consequences, and risk factors.Arch Intern Med. 1996;156(13):1399-1411.
[7] 蒋电明, 陈增刚.老年骨折的特点与围手术期处理.重庆医学. 2008;37(7):1145-1149.
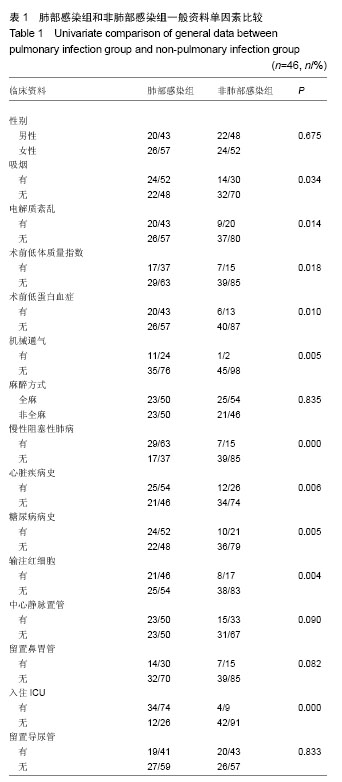
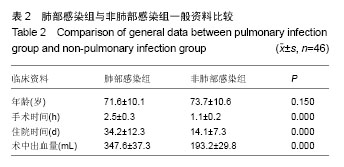
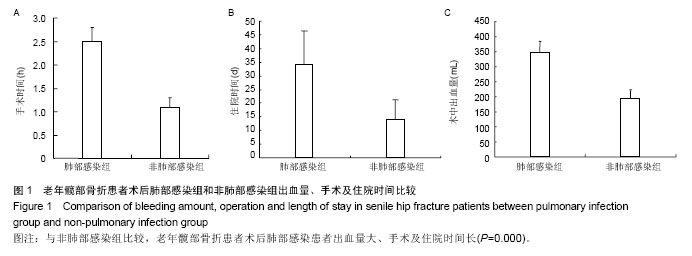
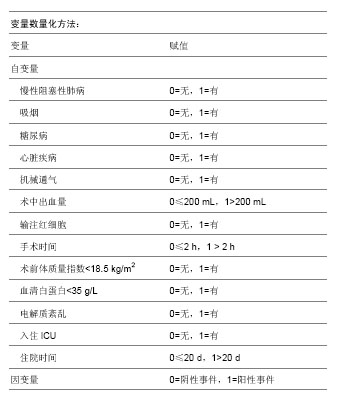
[8] 叶枫,郑移兵,金立昆.老年髋部骨折围术期肺部感染的高危因素分析[J].疑难病杂志,2012,11(8):602-604.
[9] American Thoracic Society; Infectious Diseases Society of America.Guidelines for the management of adults with hospital-acquired, ventilator-associated, and healthcare- associated pneumonia.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005; 171(4):388-416.
[10] 邱贵兴,陈宾,翁习生,等.老年骨质疏松性骨折主要部位的骨折阈值测定研究[J].中华医学杂 志,2005,85(16)1113-1116.
[11] 郑春晨,佘晖. 髋部骨折合并肺部感染134例临床特点[J].福建医药杂志,2013,35(1):33-35.
[12] 范显美.高龄髋部骨折院内肺部感染危险因素的预防控制[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2009,19 (9):1055-1057.
[13] Wahl MJ. Antibiotic prophylaxis in artificial joint patients. J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2010;68(4):949.
[14] 邱贵兴,戴尅戎.骨科手术学[M]. 3版.北京:人民卫生出版社.2006: 100-314.
[15] 韩文冬,张强.60岁以上老年人髋部骨折治疗方法选择与安全性因素分析[J].颈腰痛杂志,2007,28(2):144-146.
[16] hoda N, Yasunaga H, Horiguchi H,et al.Risk factors affecting inhospital mortality after hip fracture: retrospective analysis using the Japanese Diagnosis Procedure Combination Database.BMJ Open. 2012;2(3). pii: e000416.
[17] 万敏聪. 老年髋部骨折并发肺部感染的预防与治疗的探讨[J]内蒙古中医药,2010,29(15):51-52.
[18] 乔景泉,张向阳.老年髋部骨折患者的围手术期处理[J].甘肃医药,2011,30(12):765-766.
[19] 姜源涛,姜源波.老年髋部骨折患者围手术期肺部感染危险因素分析[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2013,23(21):5185-5187.
[20] Smetana GW, Lawrence VA, Cornell JE,et al.Preoperative pulmonary risk stratification for noncardiothoracic surgery: systematic review for the American College of Physicians.Ann Intern Med. 2006;144(8):581-595.
[21] 侯德凤,姜友珍,刘海燕.ICU 医院获得性肺炎病原菌分布及耐药性分析[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2013,23(1):27-29.
[22] Foss NB, Palm H, Krasheninnikoff M, et al. Impact of surgical complications on length of stay after hip fracture surgery. Injury.2007;38(7):780-784.
[23] Ma Rs, Zhang Y, Huang Y, et al. Causes of death after hip fracture in senile patients. Clin J Traumatol.2012;15(1):42-49.
[24] 古正涛,邓小玲,郑国栋,等. 颈脊髓损伤患者医院获得性肺炎及其病原菌分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21(1):33-37.
[25] Ramirez P, Bassi GL, Torres A. Measures to prevent nosocomial infections during mechanicalventilation.Curr Opin Crit Care.2012;18(1):86-92.
[26] 李海,英金红,张春鸣. 高龄髋部骨折病人术后肺部感染的危险因素分析及护理对策[J]. 护理研究,2013.27(5):1345-1346.
[27] 华小琴.65例肺癌全肺切除术后机械通气病人的护理[J].全科护理,2013,11(3B):717.
[28] 余珍华,魏彩虹,黄灵灵,等.循证护理在机械通气病人吸痰中的应用[J].全科护理,2012,10(11A): 2938-2939.
[29] 谷素洁,曾明,石晓磊,等. 老年脑卒中患者医院获得性肺炎特点及危险因素分析[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2011,21(23): 4944-4946.
[30] Neuman MD, Archan S, Karlawish JH,et al.The relationship between short-term mortality and quality of care for hip fracture: a meta-analysis of clinical pathways for hip fracture.J Am Geriatr Soc. 2009;57(11):2046-2054. |