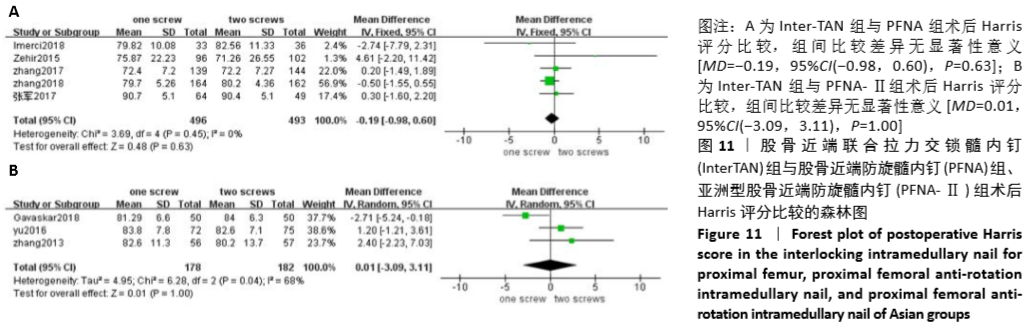
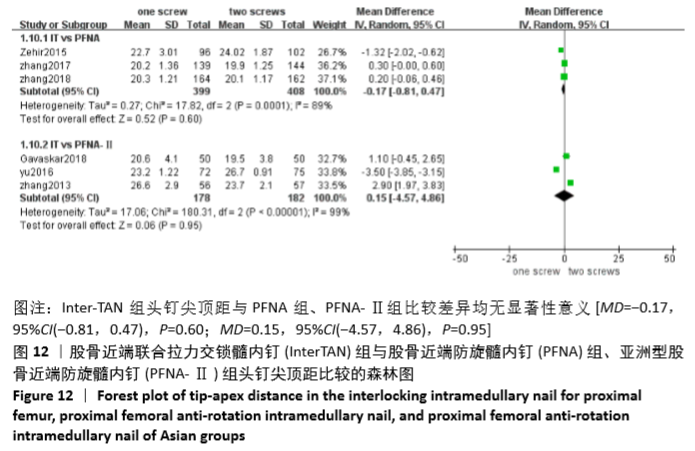
[1] 高金华,王明洋,顾文浩,等.经皮撬拨复位PFNA内固定和股骨近端解剖锁定板内固定治疗老年不稳定股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2017,32(6):619-620.
[2] 唐佩福.股骨转子间骨折的治疗进展与策略[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2017,19(2): 93-94.
[3] 袁志,毕龙.老年股骨转子间骨折的治疗趋势[J].中华骨科杂志,2017,37(17): 1057-1060.
[4] GAVASKAR AS, TUMMALA NC, SRINIVASAN P, et al.Helical blade or the integrated lag screws: a matched pair analysis of 100 patients with unstable trochanteric fractures.J Orthop Trauma.2018;32(6):274-277.
[5] İMERCI A, AYDOGAN NH, TOSUN K. A comparison of the InterTan nail and proximal femoral fail antirotation in the treatment of reverse intertrochanteric femoral fractures. Acta Orthop Belg.2018; 84(2):123-131.
[6] YU W, ZHANG X, ZHU X, et al. A retrospective analysis of the InterTan nail and proximal femoral nail anti-rotation-Asia in the treatment of unstable intertrochanteric femur fractures in the elderly.J Orthop Surg Res.2016;11:10.
[7] ZEHIR S, ŞAHIN E, ZEHIR R. Comparison of clinical outcomes with three different intramedullary nailing devices in the treatment of unstable trochanteric fractures.Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2015;21(6):469-476.
[8] ZHANG S, ZHANG K, JIA Y, et al. InterTan nail versus Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation-Asia in the treatment of unstable trochanteric fractures.Orthopedics. 2013; 36(3):e288-e294.
[9] ZHANG H, ZHU X, PEI G, et al. A retrospective analysis of the InterTan nail and proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients with osteoporosis:a minimum follow-up of 3 years.J Orthop Surg Res.2017;12(1):147.
[10] ZHANG C, XU B, LIANG G, et al. Optimizing stability in AO/OTA 31-A2 intertrochanteric fracture fixation in older patients with osteoporosis.J Int Med Res.2018;46(5):1767-1778.
[11] 张军,曹烈虎,陈晓,等.PFNA与InterTAN髓内钉治疗不稳定股骨粗隆间骨折疗效的比较[J].中国骨伤, 2017, 30(7):597-601.
[12] 张保中,邱贵兴.高龄股骨转子间骨折的手术治疗[J].中华创伤杂志,2005, 21(8):582-584.
[13] SCHIPPER IB, MARTI RK, VAN DER WERKEN C. Unstable trochanteric femoral fractures: extramedullary or intramedullary fixation.Review of literature.Injury.2004;35(2):142-151.
[14] ROBERTS KC, BROX WT, JEVSEVAR DS, et al. Management of hip fractures in the elderly. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015; 23(2):131-137.
[15] PALM H, JACOBSEN S, SONNE-HOLM S, et al. Integrity of the lateral femoral wall in intertrochanteric hip fractures: an important predictor of a reoperation.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2007;89(3):470-475.
[16] IRGIT K, RICHARD RD, BEEBE MJ, et al. Reverse Oblique and Transverse Intertrochanteric Femoral Fractures Treated With the Long Cephalomedullary Nail.J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(9):e299-e304.
[17] 俞光荣,王树青,饶志涛,等.防旋股骨近端髓内钉治疗不稳定性转子间骨折33例[J].中华创伤杂志,2007,23(2):83-86.
[18] 郝有亮,张志山,周方,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉固定治疗股骨反转子间骨折内固定失败的危险因素分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2019,21(9):771-776.
[19] 焦竞,熊元,王俊文,等.亚洲型股骨近端防旋髓内钉固定治疗股骨转子间骨折术后大腿痛的原因分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2017,19(8):685-690.
[20] HOFFMANN S, PAETZOLD R, STEPHAN D, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of interlocking lag screw design in intramedullary nailing of unstable pertrochanteric fractures.J Orthop Trauma.2013;27(9):483-490.
[21] NÜCHTERN JV, RUECKER AH, SELLENSCHLOH K, et al. Malpositioning of the lag screws by 1- or 2-screw nailing systems for pertrochanteric femoral fractures:a biomechanical comparison of gamma 3 and intertan.J Orthop Trauma. 2014;28(5):276-282.
[22] 高翔,李杰,姜勇,等.InterTAN 髓内钉治疗股骨转子间骨折术中主钉置入困难的原因分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2015,17(11):962-966.
[23] 应霁翀,刘观燚,张勇,等.三种不同内固定方式治疗股骨转子间骨折术后隐性失血及血栓形成的比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2016,18(5):442-446.
[24] 杜力,沈玉春,肖海军.股骨转子间骨折股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定术后螺旋刀片向内穿透股骨头一例[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2019,33(10):1275-1276.
[25] FREI HC, HOTZ T, CADOSCH D,et al.Central head perforation,or”cut through,” caused by the helical blade of the proximal femoral nail antirotation.J Orthop Trauma. 2012;26(8):e102-e107.
[26] GOFFIN JM, PANKAJ P, SIMPSON AH,et al. Does bone compaction around the helical blade of a proximal femoral nail anti-rotation (PFNA) decrease the risk of cut-out?:A subject-specific computational study.Bone Joint Res.2013;2(5):79-83.
[27] 余新平,刘康,何智勇,等.InterTan髓内钉治疗426例老年股骨转子间骨折的临床疗效及体会[J].创伤外科杂志,2017, 19(5):370-374.
[28] SEYHAN M, TURKMEN I, UNAY K, et al. Do PFNA devices and Intertan nails both have the same effects in the treatment of trochanteric fractures? A prospective clinical study. J Orthop Sci.2015;20(6): 1053-1061.
[29] 纪方,刘培钊,佟大可.股骨转子间骨折热点问题的探讨[J].中国骨伤,2017, 30(7):587-590.
[30] 曹立,沈惠良,雍宜民.影响双拉力螺钉股骨近端髓内钉切出股骨头的因素[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2008,23(3):177-179.
[31] 肖湘,张铁良,马宝通.“尖顶距”值与拉力螺钉切出股骨头关系的临床回顾性研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2006,8(8): 722-724.
[32] KASHIGAR A, VINCENT A, GUNTON MJ, et al. Predictors of failure for cephalomedullary nailing of proximal femoral fractures.Bone Joint J.2014;96-B(8):1029-1034.
[33] RUBIO-AVILA J, MADDEN K, SIMUNOVIC N, et al. Tip to apex distance in femoral intertrochanteric fractures:a systematic review.J Orthop Sci.2013;18(4):592-598.
[34] 杨家赵,方诗元,夏睿,等.TAD值在INTERTAN髓内钉治疗骨质疏松性股骨粗隆间骨折中的应用价值[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2012,18(12):1101-1104.
[35] LENZ M, SCHWINN J, HOFMANN-FLIRI L, et al.Influence of reduced tip-apex distance on helical blade fixation-a biomechanical study.J Orthop Res.2019;37(3):649-654.
[36] MCCONNELL T, TORNETTA P, BENSON E, et al. Gluteus medius tendon injury during reaming for gamma nail insertion.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2003;(407):199-202.
[37] PU JS, LIU L, WANG GL, et al. Results of the proximal femoral nail anti-rotation (PFNA) in elderly Chinese patients.Int Orthop.2009;33(5):1441-1444.
[38] LV C, FANG Y, LIU L, et al. The new proximal femoral nail antirotation-Asia:early results.Orthopedics.2011;34(5):351.
[39] 郑颖捷,李开南.股骨转子间骨折外侧壁的研究进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2017, 19(2):133-137.
[40] NORRIS R, BHATTACHARJEE D, PARKER MJ. Occurrence of secondary fracture around intramedullary nails used for trochanteric hip fractures: a systematic review of 13,568 patients.Injury.2012;43(6):706-711.
[41] HOU Z, BOWEN TR, IRGIT KS, et al. Treatment of pertrochanteric fractures (OTA 31-A1 and A2):long versus short cephalomedullary nailing.J Orthop Trauma. 2013;27(6):318-324.
[42] 张世民,余斌.AO/OTA-2018版股骨转子间骨折分类的解读与讨论[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2018,20(7):583-587. |