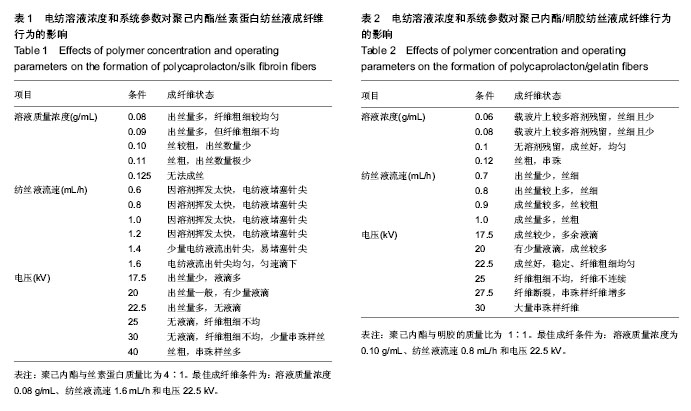
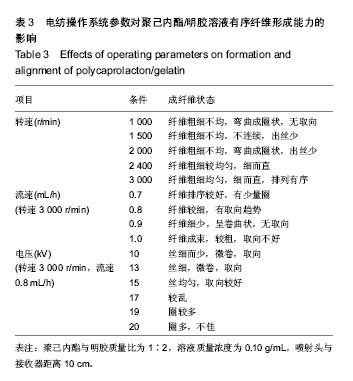
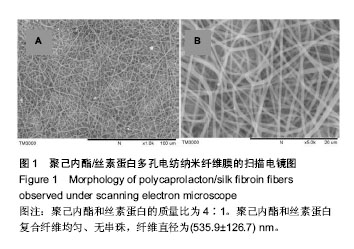
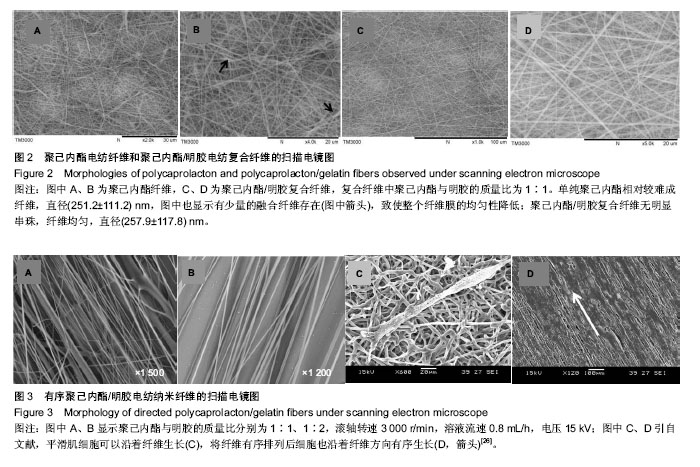
| [1] D'Journo XB,Martin J,Fermro P,et al.The esophageal remnant after gastric interposition.Dis Esophagus.2008;1:377-388.
[2] Ferahkose Z,Bedirli A,Kerem M,et al.Comparison of free jejunal graft with gastric pull-up reconstruction after resection of hypopharyngeal and cervical esophageal carcinoma.Dis Esophagus.2008;21:340-345.
[3] Doki Y, Okada K, Miyata H,et al.Long-term and short-term evaluation of esophageal reconstruction using the colon or the jejunum in esophageal cancer patients after gastrectomy. Dis Esophagus.2008;21(2):132-138.
[4] Londono R,Jobe BA,Hoppo T,et al.Esophagus and regenerative medicine.World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18(47): 6894-6899.
[5] 谢远财,张本固,彭品贤,等.应用钛镍合金-硅橡胶组合式人工食管重建食管缺损[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009, 13(34):6675-6679.
[6] Takimoto Y,Nakamura T,Yamamoto Y,et al.The experimental replacement of a cervical esophageal segment with an artificial prosthesis with the use of collagen matrix and a silicone stent.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.1998;116:98-106.
[7] 谭波,魏人前,杨志明,等.口腔黏膜上皮细胞与猪小肠黏膜下层体外复合培养的实验研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2010,28(1): 76-80.
[8] Barnes CA,Brison J,Michel R,et al.The surface molecular functionality of decellularized extracellular matrices. Biomaterials.2011;32(1):137-143.
[9] Wolf MT, Daly KA,Brennan-Pierce EP,et al.A hydrogel derived from decellularized dermal extracellular matrix. Biomaterials. 2012;33(29):7028-7038.
[10] Badylak SF,Weiss DJ,Caplan A,et al.Engineered whole organs and complex tissues.Lancet.2012;379(9819):943-952.
[11] Nieponice A,Ciotola F,NachmanF,et al.Patch Esophagoplasty: Esophageal Reconstruction Using Biologic Scaffolds.Ann Thorac Surg.2014;97(1):283-288.
[12] Urita Y,Komuro H,Chen G. Regeneration of the esophagus using gastric acellular matrix: An experimental study in a rat mode1. Pediatr Surg Int. 2007;23:21-26.
[13] 谭波,魏人前,杨志明,等.食管黏膜上皮细胞与SIS复合培养及生物学特性研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2008,22(6):742-746.
[14] Saxena AK,Komann C,Ainoedhofer H,et al.Esophagus tissue engineering: hybrid approach with esophageal epithelium and unidirectional smooth muscle tissue component generation in vitro. J Gastrointest Surg.2009;13:1037-1043.
[15] 谭波解慧琪.组织工程在食管修复重建外科中的应用[J].生物物理学报,2011,27(6):475-482.
[16] Lei YN,Zhu YB,Gong CF,et al.Synthesis, characterization and cytocompatibility of a degradable polymer using ferric catalyst for esophageal tissue engineering.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014;25(2):273-282.
[17] Zhu Y,Leong MF,Ong WF,etal.Esophageal epithelium regeneration on fibronectin grafted poly (L-lactide-co-caprolactone) (PLLC) nanofiber scaffold. Biomaterials. 2007;28(5):861-868.
[18] Gong CF,Hou L,Zhu YB,et al.In vitro constitution of esophageal muscle tissue with endocyclic and exo- longitudinal patterns.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2013;5(14): 6549-6555.
[19] Tan JY,Chua CK,Leong KF,et al.Esophageal tissue engineering: an in-depth review on scaffold design.Biotech Bioeng.2011;109:1-15.
[20] Li YY,Zhu YB,Yu HW,et al.Topographic characterization and protein quantification of esophageal basement membrane for scaffold design reference in tissue engineering.J Biomed Mater Res Part B: Appl Biomater.2012;100B:265-273.
[21] Zhu YB,Cao Y,Pan J,et al.Macro-alignment of electrospun fibers for vascular tissue engineering.J Biomed Mater Res. 2010;92B:508-516.
[22] 陈玲,竺亚斌,李媛媛,等.丝素蛋白在电纺丝法构建组织工程支架中的应用进展[J].生物工程学报,2011,27(6):831−837.
[23] Pham QP,Sharma U,Mikos AG.Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for tissue engineering applications: a review. Tissue Eng.2006;12:1197-1211.
[24] Lannuttia J,Renekerb D,Mac T,et al.Electrospinning for tissue engineering scaffolds. Mater SciEngC. 2007;27(3):504-509.
[25] Shao ZZ, Vollrath F, et al. Materials: Surprising strength of silkworm silk. Nature. 2002;418:741.
[26] Altman GH,Diaz F,Jakuba C,et al.Silk-based biomaterials. Biomaterials.2003;24(3):401-416.
[27] Park SY,Ki CS,Park YH,et al.Electrospun Silk Fibroin Scaffolds with Macropores for Bone Regeneration: An In Vitro and In Vivo Study.Tissue Eng A.2010;16(4):1271-1279.
[28] 陈玲,吕静静,於学婵,等.静电纺丝法构建食道上皮组织[J].生物工程学报, 2013, 29(12): 1796-1807.
[29] Zhu YB,Gao CY,Shen JC.Surface modification of polycaprolactone with poly(methacrylic acid) and gelatin covalent immobilization for promoting its cytocompatibility. Biomaterials.2002;23 (24):4889-4895.
[30] Zhu YB,Gao CY,He T,et al.Endothelium regeneration on luminal surface of polyurethane vascular scaffold modified with diamine and covalently grafted with gelatin. Biomaterials. 2004;25(3):423-430.
[31] Shen QX,Shi PN,Gao MN,et al.Progress on materials and scaffold fabrications applied to esophageal tissue engineering. MaterSci Eng C.2013;33(4):1860-1866.
[32] LvJ,ChenL,ZhuY, et al.Promoting Epithelium Regeneration for Esophageal Tissue Engineering through Basement Membrane Reconstitution.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014; 6(7):4954-4964.
[33] Shen ZS,KangC,Chen JJ,et al.Surface modification of polyurethane towards promoting the ex vivo cytocompatibility and in vivo biocompatibility for hypopharyngeal tissue engineering. J Biomater Appl.2013;28(4):607-616. |