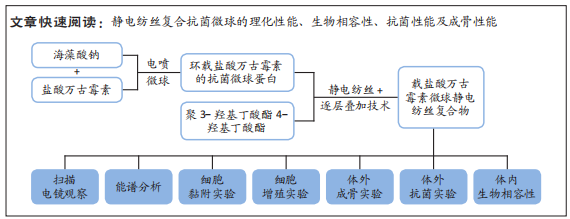
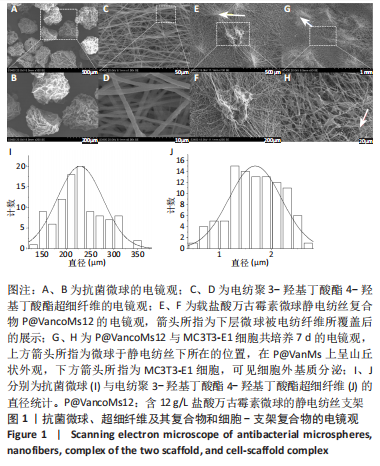
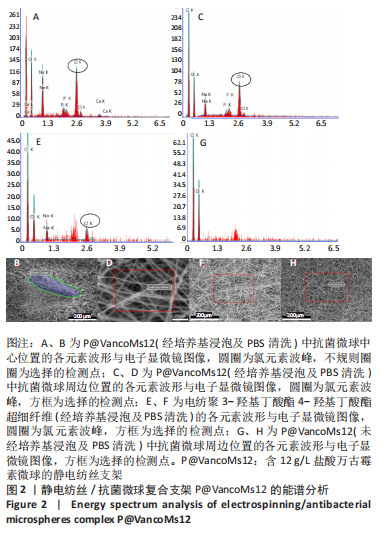
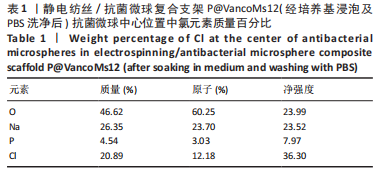
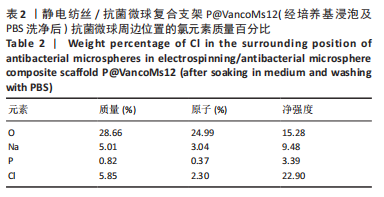
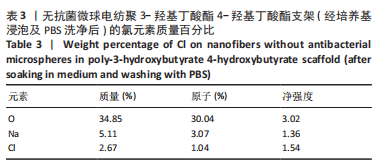
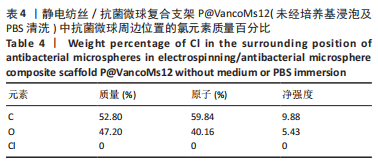
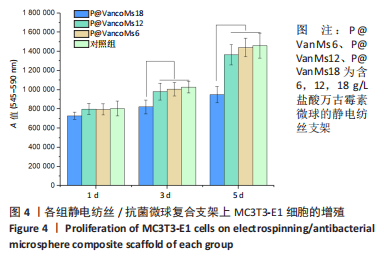
[1] HAMM CA, HAMPE O, SCHWARZ D, et al. A comprehensive diagnostic approach combining phylogenetic disease bracketing and CT imaging reveals osteomyelitis in a Tyrannosaurus rex. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):18897.
[2] WOODS CR, BRADLEY JS, CHATTERJEE A, et al. Clinical Practice Guideline by the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America: 2021 Guideline on Diagnosis and Management of Acute Hematogenous Osteomyelitis in Pediatrics. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2021;10(8):801-844.
[3] PREMKUMAR A, KOLIN DA, FARLEY KX, et al. Projected Economic Burden of Periprosthetic Joint Infection of the Hip and Knee in the United States. J Arthroplasty. 2021;36(5):1484-1489.e3.
[4] ARCIOLA CR, AN YH, CAMPOCCIA D, et al. Etiology of implant orthopedic infections: a survey on 1027 clinical isolates. Int J Artif Organs. 2005;28(11):1091-1100
[5] WALTER G, KEMMERER M, KAPPLER C, et al. Treatment algorithms for chronic osteomyelitis. Dtsch Arzteblatt Int. 2012;109(14):257-264.
[6] 苏珊,何娜,翟所迪.儿童患者万古霉素初始给药方案的分析[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2021,37(5):576-579+595.
[7] HUMPHREY C, VEVE MP, WALKER B, et al. Long-term vancomycin use had low risk of ototoxicity. PLoS One. 2019;14(11):e0224561.
[8] 吴婧,刘小兰,郭德群,等.替考拉宁和万古霉素治疗脊柱后路术后手术深部耐甲氧西林革兰阳性菌感染的临床疗效[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2020,30(18):2790-2793.
[9] GUO Y, SONG G, SUN M, et al. Prevalence and Therapies of Antibiotic-Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020; 10:107.
[10] 化昊天,王新卫,张磊,等.慢性骨髓炎的诊疗研究进展[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2022,11(2):132-136.
[11] CYPHERT EL, LU CY, MARQUES DW, et al. Combination antibiotic delivery in pmma provides sustained broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity and allows for postimplantation refilling. Biomacromolecules. 2020;21(2):854-866.
[12] 尤加省,李宏烨,刘超.载抗生素骨水泥在治疗下肢感染性创面中的疗效分析[J].中国骨伤,2021,34(7):670-673.
[13] XUE JJ, WU T, DAI YQ, et al. Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers: Methods, Materials, and Applications. Chem Rev. 2019;119:5298-5415.
[14] CHEN ZY, SONG Y, ZHANG J, et al. Laminated electrospun nHA/PHB-composite scaffolds mimicking bone extracellular matrix for bone tissue engineering. Mat Sci Eng C. 2017;72:341-351.
[15] BOCK N, DARGAVILLE TR, WOODRUFF MA. Electrospraying of polymers with therapeutic molecules: state of the art. Prog Polym Sci. 2012; 37(11):1510-1551.
[16] JAWOREK A, SOBCZYK AT. Electrospraying route to nanotechnology: an overview. J Electrostat. 2008;66(3-4):197-219
[17] 马博,顾勇,陈亮.骨修复缓释微球的应用进展[J].实用骨科杂志, 2022,28(2):142-145+149.
[18] YE C, HU P, MA M, et al. PHB/PHBHHx scaffolds and human adipose-derived stem cells for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2009; 30(7):4401-4406.
[19] MA MX, LIU Q, YE C, et al. Preparation of P3HB4HB/(gelatin+PV A) composite scaffolds by coaxial electrospinning and its bio-compatibility evaluation. BioMed Res Int. 2017;2017:9251806.
[20] 张静,林华庆,马秋燕,等.海藻酸钠及其衍生物在生物医药中的应用进展[J].中国药房,2019,30(23):3307-3312.
[21] 毛金超,隋振全,徐桂云,等.天然生物质材料的制备、性质与应用(Ⅱ)——pH敏感型功能海洋多糖:海藻酸钠[J].日用化学工业, 2022,52(2):124-133.
[22] JUNTAPRAM K, PRAPHAIRAKSIT N, SIRALEARTMUKUL K, et al. Electrosprayed polyelectrolyte complexes between mucoadhesive N,N,N,-trimethylchitosanhomocysteine thiolactone and alginate/carrageenan for camptothecin delivery. Carbohydr Polym. 2012;90(4): 1469-1479.
[23] PARK H, KIM PH, HWANG T, et al. Fabrication of cross-linked alginate beads using electrospraying for adenovirus delivery. Int J Pharm. 2012; 427(2):417-425.
[24] COCHRAN AR, ONG KL, LAU E, et al. Risk of reinfection after treatment of infected total knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2016;31:156-161.
[25] GALLIE WE. First recurrence of osteomyelitis eighty years after infection. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1951;33-B(1):110-111.
[26] LIBRATY DH, PATKAR C, TORRES B. Staphylococcus aureus reactivation osteomyelitis after 75 years. New Engl J Med. 2012;366:481-482.
[27] Hogan A, Heppert VG, Suda AJ. Osteomyelitis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(9):1183-1196.
[28] QIAN G, ZHANG L, LIU X, et al. Silver-doped bioglass modified scaffolds: A sustained antibacterial efficacy. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021; 129:112425.
[29] 管捷,程坚,谢幼专,等.含纳米银颗粒的β-磷酸三钙复合支架的抗菌性和促成骨性的研究[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2018, 15(2):9-13+82-83.
[30] 任亚明,黄晨,刘达,等.一期外固定支架、抗生素骨水泥珠链置入联合负压封闭引流治疗GustiloⅢ型胫腓骨开放性骨折的临床效果[J].中国医刊,2021,56(9):987-989.
[31] 周武,夏天,刘梦非,等.Ⅰ期清创联合抗生素骨水泥珠链填塞治疗骨折后慢性感染[J].中华创伤杂志,2018,34(11):1001-1006.
[32] 李荣俊,张萌.万古霉素骨水泥填充联合负压封闭引流治疗对慢性骨髓炎患者血清肿瘤坏死因子水平的影响[J].中国现代医生,2021, 59(26):103-106.
[33] FATHI M, AKBARI B, TAHERIAZAM A. Antibiotics drug release control-ling and osteoblast adhesion from titania nanotubes arrays using silk fibroin coating. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater. 2019;103:109743.
[34] LORA-TAMAYO J, MURILLO O. Shorter treatments for vertebral osteomyelitis. Lancet. 2015;385(9971):836-837.
[35] LI H, ROMBACH I, ZAMBELLAS R, et al. Oral versus intravenous antibiotics for bone and joint infection. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(5):
425-436.
[36] JELINKOVA P, MAZUMDAR A, SUR VP, et al. Nanoparticle-drug conjugates treating bacterial infections. J Control Release. 2019;307: 166-185.
[37] MUNITA JM, ARIAS CA. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol Spectr. 2016;4(2):10.1128/microbiolspec.VMBF-0016-2015. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.VMBF-0016-2015.
[38] CHENG CA, DENG T, LIN FC, et al. Supramolecular nanomachines as stimuli-responsive gatekeepers on mesoporous silica nanoparticles for antibiotic and cancer drug delivery. Theranostics. 2019;9(11):3341-3364
[39] DZIEMIDOWICZ K, SANG Q, WU J, et al. Electrospinning for healthcare: recent advancements. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(4):939-951.
[40] DHAMECHA D, MOVSAS R, SANO U, et al. Applications of alginate microspheres in therapeutics delivery and cell culture: Past, present and future. Int J Pharm. 2019;569:118627.
[41] WANG W, LIU Y, LIU Z, et al. Evaluation of Interleukin-4-Loaded Sodium Alginate-Chitosan Microspheres for Their Support of Microvascularization in Engineered Tissues. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021;7(10):4946-4958.
[42] ANTOCI V JR, ADAMS CS, HICKOK NJ, et al. Antibiotics for local delivery systems cause skeletal cell toxicity in vitro. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007; 462:200-206.
|