中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (21): 3398-3406.doi: 10.12307/2023.467
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
镁合金生物材料降解对内皮化细胞的影响
董士武1,周岚曦1,邵 路1,喻正文1,2
- 1遵义医科大学口腔医学院,贵州省遵义市 563099;2贵州省普通高等学校口腔疾病研究特色重点实验室,贵州省遵义市 563099
-
收稿日期:2022-06-16接受日期:2022-08-08出版日期:2023-07-28发布日期:2022-11-24 -
通讯作者:喻正文,副教授,硕士生导师,遵义医科大学口腔医学院,贵州省遵义市 563099;贵州省普通高等学校口腔疾病研究特色重点实验室,贵州省遵义市 563099 -
作者简介:董士武,男,1997年生,山东省泰安市人,汉族,遵义医科大学在读硕士,主要从事口腔材料与牙列缺损缺失修复研究。 -
基金资助:贵州省科技计划项目(黔科合平台人才[2017]5733-057),项目负责人:喻正文;贵州省医用生物材料研发人才基地(黔人领发[2018]3号),项目参与者:喻正文
Effect of magnesium alloy biomaterial degradation on endothelialized cells
Dong Shiwu1, Zhou Lanxi1, Shao Lu1, Yu Zhengwen1, 2
- 1School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563099, Guizhou Province, China; 2Key Laboratory of Oral Disease Research of Department of Guizhou Education, Zunyi 563099, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2022-06-16Accepted:2022-08-08Online:2023-07-28Published:2022-11-24 -
Contact:Yu Zhengwen, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563099, Guizhou Province, China; Key Laboratory of Oral Disease Research of Department of Guizhou Education, Zunyi 563099, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Dong Shiwu, Master candidate, School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563099, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Science and Technology Project of Guizhou Province, No. [2017]5733-057 (to YZW); Guizhou Province Medical Biomaterials Research & Development Talent Base, No. [2018]3 (to YZW)
摘要:
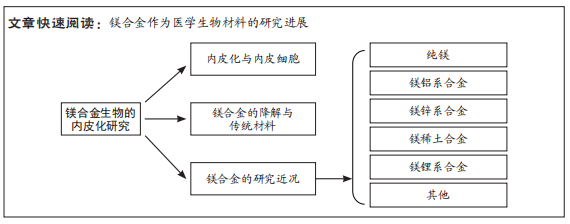
文题释义:
镁合金生物材料:在纯镁中加入Al、Zn、Ca、Mn、RE等无细胞毒性的合金元素可改善镁合金材料的力学性能、生物相容性、组织相容性,同时能在受植区为细胞黏附和骨的成长提供环境和支持。内皮化:血管受病理性或生理性刺激时内皮细胞被招募,迁移至受损区并增殖或内皮祖细胞通过归巢于内皮损伤部位,诱导血管生成,以修复损伤形成新血管。
背景:镁合金材料依靠其优良的生物相容性和可降解性被誉为“革命性的金属材料”,其降解对内皮化的影响具有重大研究意义。
目的:综述镁合金材料的研究进展。
方法:利用计算机检索PubMed、中国知网数据库、Web of Science和Elsevier等数据库中的相关文献,以“金属生物材料,镁合金材料,血管支架,内皮化,动物实验,体外实验”为中文主题检索词,以“Metallic biomaterials,Magnesium alloys, Vascular stents,Endothelialization,Animal experiments,In vitro”为英文检索词进行检索,检索时限为2015-2022年,通过阅读文题和摘要进行初步筛选,最终纳入 116 篇文献进行结果分析。
结果与结论:镁合金材料降解形成的含一定浓度镁离子的微环境有利于内皮细胞及平滑肌细胞的增殖,镁离子对内皮化的作用基本被认可。但降解速率过快是镁合金的最大问题,镁离子浓度过高会出现细胞毒性,因此目前的研究多集中于改善其降解,提高生物相容性。目前常见的改善镁合金降解的方法有纯化、合金化、表面改性,均可提高其耐腐蚀性,并且不同元素的合金化对镁合金的改善是不同方面,未来可能针对不同需求来选择不同合金化的镁合金以适应临床患者的情况,除引入其他元素外,改进镁合金的制作工艺改善降解问题也可能是一种值得尝试的方法。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7145-7361(董士武)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
董士武, 周岚曦, 邵 路, 喻正文. 镁合金生物材料降解对内皮化细胞的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(21): 3398-3406.
Dong Shiwu, Zhou Lanxi, Shao Lu, Yu Zhengwen. Effect of magnesium alloy biomaterial degradation on endothelialized cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(21): 3398-3406.
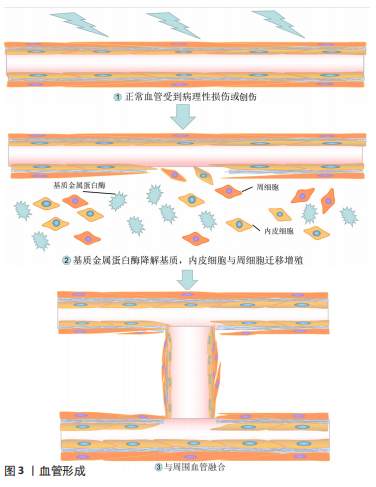
血管形成的过程与周围环境有关。在常氧条件下NF-kB信号通路稳定缺氧诱导因子[7],以使得血管内皮生长因子持续高表达,当血管内皮生长因子与内皮细胞表面受体结合后,通过RAF/ERK/MAPK信号通路刺激内皮细胞增殖并释放基质金属蛋白酶,内皮细胞失去粘连并暴露在间质中激活血管出芽[8]。血管内皮生长因子与血管内皮细胞生长因子受体2结合,诱导内皮细胞沿血管内皮生长因子的浓度梯度生长,邻近细胞形成血管性管腔 [9],当管腔融合时内皮细胞转为静息状态,最后周细胞稳定剩余血管并成熟为毛细血管[6]。在血管形成过程中,内皮细胞表达Delta-like 4(Dll4)稳定血管的发育[6]。血管内皮生长因子诱导的转录因子可以控制靶细胞来调控血管生成,在无刺激存在时中和促血管反应,防止胞外基质的过度降解和血管的过度形成。有关血管形成过程见图3。
内皮细胞与溶质、液体、大分子、血小板等重要分子的分泌有关[6],炎症时还可以刺激平滑肌细胞形成血管[10],内皮细胞在动脉与静脉中的血管发芽能力不同[11],可能与血流速度有关。内皮细胞对凝血的调控是双向的,损伤时内皮细胞暴露特定配体招募血小板,通过凝血反应止血[12],愈合过程中的血栓可被蛋白酶再次降解[7],防止堵塞;相反,内皮细胞血栓调节蛋白受体也可以与凝血酶结合,激活蛋白C,蛋白C可以对抗相关辅助因子产生抗凝血的作用,因此内皮细胞可以促进凝血也可以抗凝,这与血栓形成息息相关。内皮细胞比平滑肌细胞更能耐受缺氧环境[13],但对再灌注损伤和低温敏感,其功能障碍与动脉粥样硬化、脑卒中、胰岛素抵抗等诸多疾病息息相关。
内皮细胞源性的收缩因子和舒张因子一般保持平衡,这有助于血管的舒张。内皮细胞释放内皮素原,通过内皮素转化酶成熟为内皮素,对血管有收缩作用,在血压和血流改变时内皮细胞合成分泌一氧化氮(NO)稳定正常的血管张力[14],受炎症影响的细胞或坏死细胞会促进内皮细胞迁移并提高NO的水平,增加血管通透性,同时使内皮细胞进入促凝状态。除此之外,前列环素通过影响平滑肌细胞以及NO、前列环素协同抗凝[15],当缺乏NO和前列环素时,内皮细胞中的超极化因子EDHF成为血管主要的依赖性舒张因子,由此可见,正常功能的内皮细胞对维持血管稳态起重大作用。
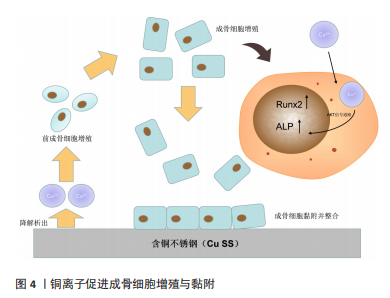
2.2 传统材料与镁合金 不锈钢支架耐腐蚀机械强度高,但材料惰性会影响骨整合的时间。有研究表明,含铜不锈钢(Cu SS)可以促进相关成骨基因的表达并抑制肿瘤坏死因子α通路产生抗炎作用[16]。YUAN等[17]进一步研究制备了含铜316L不锈钢,结果显示加入铜之后加速了成骨细胞的黏附(图4),并刺激AKT通路上调Runx2、Ⅰ型胶原表达促进成骨,加入铜元素可以改善不锈钢合金的材料惰性,缩短骨整合时间。镍钛合金具有超弹性,与人骨的弹性模量相近,易于制备成复杂形状而被应用于临床,但诱导骨整合能力弱,降解产生的镍离子具有毒性。石墨烯可以改善镍钛合金的生物相容性和耐腐蚀能力[18-19]。ION等[20]在镍钛合金表面进行表面氮化,引起内皮型一氧化氮合酶的活性增加,增强内皮细胞的黏附增殖,加速了血管内皮化速率。为了研究镍钛合金与成骨的关系,Lü等[21]首次通过信号通路聚合酶链反应(PCR)阵列研究裸镍钛合金和镀锡镍钛合金,提出镍钛合金会激活转化生长因子β和肌动蛋白细胞骨架两条通路,转化生长因子β信号通路促进细胞黏附;肌动蛋白骨架通路促进了细胞扩散和生长。尽管通过合金化或表面改性改善了传统材料的不足,但生物材料长期作为异物诱发排斥反应是不可避免的。有研究表明,与传统植入材料相比,可降解镁合金在CT和MRI下的伪影更少[22],为镁合金的临床应用进一步奠定了基础。
过去的骨缺损修复材料多重视骨诱导和骨传导能力,忽视材料在诱导血管方面的作用。LIU等[23]介绍了“H”型血管,认为成血管与成骨在修复过程中是协同的,通过研究小鼠胚胎前成骨细胞(MC3T3-E1)与人脐静脉内皮细胞初步猜测,5 mmol/L的镁离子会促进血小板衍生生长因子BB的表达来促进成骨成血管的耦联。有研究表明,血小板衍生生长因子BB通过Src/JAK2通路对MC3T3-E1产生积极影响[24]。缺镁会导致促炎因子的表达[25]。HU等[26]选用人骨髓间充质干细胞研究镁在促进软骨形成过程中的作用,发现镁对M1型巨噬细胞存在剂量依赖性抑制,镁离子通过拮抗钙离子内流来抑制巨噬细胞活化,下调相关促炎因子,为软骨形成创造有利条件。ZHANG等[27]进一步研究了镁离子的抗炎作用,实验中提出100 mg/L的镁离子可能通过抑制NF-kB通路诱导巨噬细胞M2表型,上调骨形态发生蛋白2和血管内皮生长因子协同成骨与成血管,并为成骨创造抗炎微环境,6,10 mmol/L镁离子可以影响PI3K/AKT通路提高成骨细胞活性和基质矿化水平[28]。李政垚等[29]实验首次提出镁离子浓度为4-6 mmol/L时人骨髓间充质干细胞增殖率显著提高,碱性磷酸酶达到高峰,但会严重阻碍胞外基质矿化。通过掺入Zn或Sr元素可以改善胞外基质矿化作用[30-31],提示镁材料与其他元素合金化是解决这一问题的有效手段。在口腔领域,胞外高镁环境会提高牙髓干细胞的活性[32],促进成牙本质细胞和成牙骨质细胞的分化,利于牙胚发育和矿化。有关镁合金在体液中的降解表达如下:
Mg → Mg2+ + 2e?
2H2O + 2e? → H2 + 2OH?
Mg2+ + 2OH? ? Mg(OH)2
Mg2+ + 2Cl? ? MgCl
2.3 镁合金材料的研究进展
2.3.1 纯Mg 纯镁降解快,与骨组织的再生速率不匹配。ZELLER-PLUMHOFF 等[33]首次提出镁的降解受有机成分调控,并存在相互连接的三维纳米多孔网络 ,其快速降解形成的高镁环境会增加碱性磷酸酶的表达,但抑制矿化[34]。BEHERA等[35]发现纯锌(Zn)和铈(Ce)可以改善纯镁的耐腐蚀性,并增加钙的沉积。表面改性可以提高抗腐蚀能力并有效减少合金化出现的细胞毒性。XU等[36]发现无论是蒸汽氧化还是微弧氧化,涂层只在早期改善耐腐蚀性,长期浸泡仍会出现高镁环境影响细胞活性,但体内环境中微弧氧化涂层表现更优,可能是由于缓冲系统使得高镁环境得到改善。MA等[37]通过微弧氧化制备的含硅涂层降低pH值可促进细胞的增殖,并提高了纯镁的生物相容性,其pH值的降低可能是由于低镁环境,因此在评价镁降解形成的微环境时pH值也可作为一个客观指标。LANG等[38]通过微弧氧化在纯镁中加入铜离子,Cu-0.5组细胞增殖黏附活性更高,成血管能力增强,血管内皮生长因子的表达也显著上调,表明Cu-0.5组更促进了血管内皮化。通过微弧氧化制备的植酸铜涂层提示了Cu的抗菌作用[39]。JIN等[40]先在实验中发现Mg-Zn-Zr-Nd的耐腐蚀性不如纯镁,后通过等离子体电解氧化在纯镁上制备氧化铜涂层, 发现氧化铜涂层的抗菌性能具有浓度依赖和时间依赖性,但长期会抑制细胞的增殖,并且随着Cu含量的增多材料的耐腐蚀性下降[41],涂层中的Cu可产生优异的短期抗菌作用,但长期影响以及适宜含量还需进一步优化。
低氟含量有利于血管生成[42-43]。CHENG等 [44]的体外实验表明,氟化镁涂层的纯镁在促进骨和血管形成方面更有优势,但体内骨代谢会抑制F2+的释放,因此氟化镁涂层的体内结果并未像体外结果一样显著,由于体内环境的复杂性,体外实验的结果只能用来参考,具体体内的实际效果还需大量临床验证。
层状双氢氧化物可以有效提高抗腐能力,是具有前景的涂层材料。CHENG等[45]发现纯镁上的Mg-Al层状双氢氧化物涂层显著促进细胞增殖,同时上调相关成骨基因促进内皮化,Mg-Al层状双氢氧化物薄膜对纯镁有较好的保护作用,降解更缓和,更有利于血管重建和新骨形成。考虑到涂层中不同元素的影响,WEIZBAUER等[46]对比Mg-Fe层状双氢氧化物和Mg-Al层状双氢氧化物薄膜,Mg-Al层状双氢氧化物材料能产生适当的宿主反应,Mg-Fe层状双氢氧化物降解导致局部Fe3+浓度升高,不利于组织重建,体内实验中Mg-Fe层状双氢氧化物几乎没有直接的骨-种植体接触,提示Mg-Al层状双氢氧化物是具有潜力的涂层候选材料。除了层状双氢氧化物涂层,RAHMAN等[47]在纯镁上制备仿生丝涂层,与裸纯镁和无涂层的阳极氧化纯镁相比,仿生涂层提高了纯镁的生物相容性和抗腐蚀能力,促进了血管内皮化,有望成为生物材料防腐涂层的一种有效方法。
PARK等 [48]使用掺锶磷酸钙包被纯镁,显著促进了内皮细胞增殖,加速成骨,随着锶(Sr)含量的增加,纯镁表面出现致密涂层,耐腐蚀性增强;体外实验显示掺锶磷酸钙涂层包被的纯镁提高了生物活性,并产生了抗炎作用,实验提出1Sr组在生物相容性和耐腐蚀性方面表现最优。为了进一步研究含锶涂层,MAKKAR等[49]在镁合金表面制备Ca-Sr-P涂层,涂层降低了溶血率,促进细胞的黏附、增殖和成骨标志物的表达;在兔模型中涂层同样促进骨形成和骨整合,进一步证明了掺锶磷酸钙涂层的应用前景,为改善降解提供新的选择,一定程度上促进了镁合金的研究。
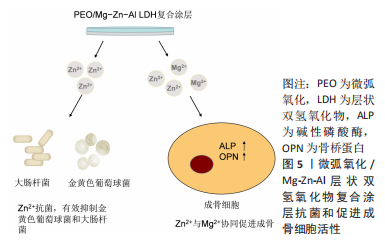
2.3.2 Mg-Al系合金 与纯镁相比,镁铝体系中的氢含量较低[50],其降解产生气体较纯镁少,在一定程度上减缓了皮下气肿的产生,同时铝元素可以提高镁合金材料的可铸性[51]。YANG等[52]认为可以通过阳离子表面活性剂提高层状双氢氧化物膜的性能,首次使用十四烷基三甲基溴化铵制备Mg-Al层状双氢氧化物薄膜,结果显示AZ31合金的耐腐蚀性随十四烷基三甲基溴化铵浓度增加而增加,阳离子表面活性剂提高了层状双氢氧化物的性能,间接提高了镁铝合金的抗腐蚀能力。有学者优化了层状双氢氧化物膜的制备过程,通过高温低pH值环境平衡了微弧氧化涂层的溶解速率和层状双氢氧化物涂层的生长速率,促进了内皮细胞的迁移黏附[53]。PENG等[54]采用Mg-Al层状双氢氧化物封闭微弧氧化孔隙,有效改善细胞黏附增殖,并提高了合金抗腐蚀能力。由于Zn2+可以抑制骨吸收[55],与Mg2+协同还能改善骨诱导作用[56-57],之后PENG等[58]在Mg-Al层状双氢氧化物中添加Zn元素填充微弧氧化孔隙,证明了含锌复合涂层有效抗菌,但降解产生的高锌环境会抑制细胞增殖,当Zn含量为1.17%时显著增强细胞黏附和相容性,同时锌离子与镁离子的协同表达出更高的碱性磷酸酶和骨桥蛋白(图5),促进新骨的形成。无论是提高涂层性能还是优化制作工艺,层状双氢氧化物膜均表现出良好的生物相容性和改善作用,增添Zn元素后可以进一步优化涂层,证明了层状双氢氧化物涂层具有巨大开发潜力和应用前景,为镁合金涂层设计提供新的参考。除此之外,LI等[59]将聚多巴胺加入层状双氢氧化物复合涂层中,有效改善材料腐蚀速率并促进细胞黏附,加速内皮化进程,层状双氢氧化物复合涂层可以减少聚多巴胺快速降解诱发的异物反应,进一步提高了涂层的生物相容性,为内皮细胞的黏附和增殖创造有利条件。TAN等[60]发现含硅涂层的AZ31B植入螺钉具有更好的机械强度且与时间呈正比,在需要长期修复的术区可能是较好的选择,为内皮细胞的增殖和新血管及新骨的形成提供适宜空间。
RAZAVI等[61]在镁铝锌合金(AZ91)表面制备微弧氧化/电泳沉积复合涂层,降低腐蚀速率并提高了材料生物活性,植入动物体内后没有气泡产生,并且新骨形成量高,与未涂层的植入物相比,复合涂层植入物周围的组织降低了炎症反应,保护了内皮细胞。为了研究锶的影响,MANDAL等[62]在Mg-1Zn-1Mn中加入锶,结果显示Sr0.05组成骨活力和物相容性最高,而随着锶的析出沉淀细胞活力略有下降,影响细胞生长,在含Sr的镁铝合金支架中要考虑晚期细胞活性的影响,虽然短期材料性能有所提高,但长期带来的抑制作用也不可忽视。
WU等[63]在AZ31合金中加入钙制备镁铝锌钙锰合金提高强度,增强其抗腐蚀能力,实验选用人气管上皮细胞,该合金显示出良好细胞相容性,具备气管支架的潜力。尽管上述通过复合涂层或其他元素合金化提高了镁铝合金的材料性能,但由于降解后Al3+所存在的潜在神经毒性,镁铝合金的研发应用仍存在阻碍。有研究表明,镁铝丝植入后诱发动脉粥样硬化和血压升高[64],因此对于镁铝合金的改善及应用还需要大量实验。
2.3.3 Mg-Zn系合金 锌(Zn)被称为“生命之花”,与生长发育、免疫及疾病的发生有密切的关系。锌元素可以提高镁合金的强度和生物活性,促进成骨细胞的分化[65-66]。应用壳聚糖表面改性涂层有效改善镁锌合金的耐腐蚀性和生物相容性,促进内皮细胞迁移和新骨形成[67],随着锌含量的增加,合金的耐腐蚀性能提高。有研究提出Mg-20%Zn综合性能最好[68]。MAHATO等[69]制备的羟基磷灰石和生物活性玻璃复合涂层同样提高了镁锌合金的耐腐蚀性能,在体外实验中促进血管生成、诱导成骨,体内实验则验证了其良好生物相容性,作为临床应用的生物合金材料,镁锌合金具备巨大潜力。
目前临床最常用的钛合金止血夹不能吸收,长期诱发超敏反应,通过合金化可以简单有效改善材料的性能[70]。DING等[71]制备了Mg-3Zn-0.2Ca合金止血夹结扎颈动脉,无渗血和炎症出现,实验中发现近心端止血夹降解速度较远心端止血夹快,可能与血流速度相关,在后续镁合金植入时可能应该考虑植入部位和材料的关系。聚多巴胺易于制备、生物相容性好,但血液相容性差,阿魏酸可以促进血管内皮化,改善膜的血液相容性[72]。
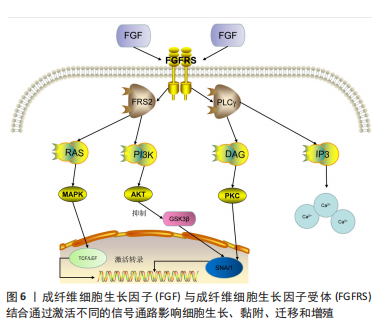
HAN等[73]在镁锌合金表面制备聚多巴胺/阿魏酸涂层表面改性来提高材料的生物相容性和抗降解能力,为医用镁合金提供了新的思路。内皮化不完全会延迟骨缺损愈合[74]。LI等[75]发现Mg-Zn-Mn提取物显著增加了细胞活力和成管能力(图6),成纤维细胞生长因子受体抑制剂降低,提示镁合金提取物通过影响成纤维细胞生长因子/成纤维细胞生长因子受体诱导人脐静脉内皮细胞形成,未来需要大量体内实验验证这一体外实验结果。虽然在纯镁和镁铝系合金中加入锶元素都有不同程度的性能优化,但SONG等[76]在Mg-2Zn-0.5Ca中加入Sr后发现其显著降低了材料的耐腐蚀性能,合金化元素选择与优化还需要进一步研究。
2.3.4 Mg-RE系合金 稀土元素(RE)已被广泛应用于电子、冶金、机械等多个领域,Mg-RE系合金的耐腐蚀能力和生物相容性更优 [77-78]。多孔结构的镁稀土合金体现出良好的抗菌特性,并在体外诱导成骨分化 [79-80],有开发应用前景。有报道提出新内膜的抑制可能与镁稀土合金有关[81],但有学者在实验中发现镁离子促进平滑肌细胞的增殖和迁移[82],结果的差异可能与镁离子浓度或稀土元素的加入有关。为了探究平滑肌细胞的行为,WU等[83]尽可能地模仿了体内环境将平滑肌细胞与材料浸提液共培养,结果显示镁离子诱导巨噬细胞由M1型逆转为M2型对抗炎症,并降低平滑肌细胞增殖迁移的相关基因,通过调节巨噬细胞改变平滑肌细胞表型影响新内膜的形成,证明降解产生的镁在一定浓度下可以有效减少或避免后期的再狭窄,但稀土元素抑制平滑肌细胞的机制还需要更多实验讨论。
为了改善传统药物洗脱支架的不足,上海交通大学研发了一种降解率更低的Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr合金 ,聚合物涂层包被雷帕霉素洗脱的Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr合金在6个月时仍具备足够机械强度,并通过控制雷帕霉素的释放来抑制平滑肌细胞增殖 [84]。SHI等[85-86]
的实验也证实了雷帕霉素对平滑肌细胞的抑制作用,涂层 Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr合金螺钉治疗内踝骨折也取得了良好的骨复位和功能恢复,在涂层提高材料强度的基础上协同药物减少新内膜的形成,虽具备一定的应用前景,但长期使用产生的耐药性是不可忽视的一大问题。
为了进一步优化镁稀土合金,JI等[87]比对了不同稀土元素的二元合金,适量稀土元素均会提高镁的抗降解能力,轻稀土元素对材料的耐腐蚀性能优化更好,并且没有明显细胞毒性,含非稀土元素的多元合金可能更适合于临床,这对未来的镁稀土合金设计的参考意义重大,通过不同需求改变稀土元素的含量,并且与非稀土元素合金化也许是未来一大研究热点。
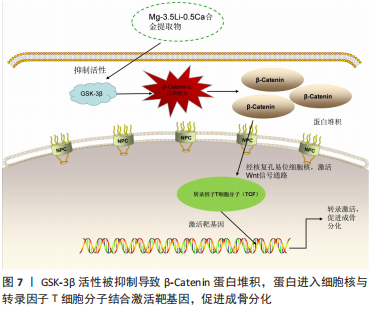
2.3.5 Mg-Li系合金 锂元素是人体内的常量元素,一定剂量可以治疗双向情感障碍[88-89],低浓度稳定内皮细胞,利于血管扩张[90]。锂元素可以提高材料的延展性但会降低机械强度。BIAN等[91]初步证明了Mg-8.5Li作为心血管支架的潜力,该支架在1个月实现内皮覆盖并且无血栓形成,具备良好的生物相容性。CUI等[92]在镁锂合金中加入钙元素以提高材料强度和生物相容性,实验发现材料的耐腐蚀性随锂增加而下降,并且只有
Mg-1Li-1Ca无细胞毒性。XIA等[93]制备了不同锂含量的镁锂合金,进一步提高了耐腐蚀性,材料降解的锂可能激活Wnt通路影响成骨分化(图7)。锂元素提高材料的延展性,钙元素增强机械强度和生物相容性,为未来的镁合金结构提供新思路。含锂合金LZ61、LZ91的延展性均被改善,并在体内外表现出一致的降解速率,且没有明显的细胞毒性,同时降解产生的锂元素可以抑制平滑肌细胞的增殖。LZ61合金在力学性能、耐腐蚀性和生物相容性方面表现出更好的平衡性[94],作为心血管支架LZ61具有巨大潜力。LI等[95]实验中的Mg-6Li-1Zn 合金具有更好的力学性能和生物降解性,并且锌的含量可以影响材料表面镁和锂的浓度,Mg-3.5Li-2Zn和Mg-3.5Li-4Zn的表面镁离子增多,而Mg-3.5Li-0.5Zn的表面锂离子较多,随着锌的增加,材料的降解行为也发生改变。LIU等[96]认为Mg-3.5Li-2Zn合金更适合作为心血管支架的植入材料,随培养时间延长,人脐静脉内皮细胞的NO释放增加,人主动脉血管平滑肌细胞的活性降低,有可能应用于支架晚期再狭窄的问题,更进一步证明了镁锂锌合金作为新型镁合金植入物的潜力,有关锂抑制平滑肌增殖的机制尚不明确,有待继续研究。
2.3.6 其他 镁钙合金在骨科领域非常有前途,为了改善快速腐蚀的问题,XIA等[97]构建了一种自修复涂层,组织学分析证明含涂层的Mg-1Ca合金具有更好的骨整合作用,并增强了内皮细胞活力和成骨分化能力。在SUN等[98]对比了微弧氧化涂层的 Mg-Sr 和 Mg-Ca 合金支架在治疗骨缺损方面的整合效果,结果显示 Mg-Sr 支架更耐腐蚀,而Mg-Ca 支架整体修复效果更显著,Sr与Ca对镁合金的改善侧重不同,猜测多元合金可能更符合临床需求。LI等[99]通过高压扭转工艺进一步提高了Mg-Sr与Mg-Ca合金的抗降解能力和生物相容性。Mg-Sr合金与Mg-Ca合金都具有修复骨缺损的骨替代物潜力[100-101]。 有研究表明,仅0.5%的Mn 就足以提高镁钙合金的化学稳定性和细胞相容性 [102]。
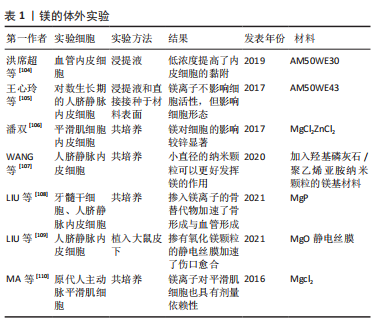
HU等[103]制备医用Mg-1.5Mn-2Zn合金评估了锰的影响,合金的显微硬度随着锰的增加而增加,并且Mg-1Mn-2Zn合金综合性能最好,无论是Ca、Sr还是Mn元素,生命元素的合金化已成为目前改善材料问题的常见办法,不同元素的改善靶向不同,如何尽可能的提高镁合金的全面适用性并且避免元素反应产生的细胞毒性是未来需要进一步研究的话题。有关镁的体外实验见表1。
| [1] 陈克难,郭传瑸.可降解医用镁基金属生物材料的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2021,48(3):322-328. [2] 王照华,杨越,徐景超,等.家兔股骨植入可降解型镁合金加压螺钉的生物效应与抗菌性能研究[J].医学信息,2021,34(19):88-91. [3] DISTHABANCHONG S, SRISUWARN P. Mechanisms of Vascular Calcification in Kidney Disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2019;26(6): 417-426. [4] ZHUANG Y, ZHANG C, CHENG M, et al. Challenges and strategies for in situ endothelialization and long-term lumen patency of vascular grafts. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(6):19. [5] ZHENG B, YIN WN, SUZUKI T, et al. Exosome-Mediated miR-155 Transfer from Smooth Muscle Cells to Endothelial Cells Induces Endothelial Injury and Promotes Atherosclerosis. Mol Ther. 2017;25(6):1279-1294. [6] KRüGER-GENGE A, BLOCKI A, FRANKE RP, et al. Vascular Endothelial Cell Biology: An Update. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(18):4411. [7] STURTZEL C. Endothelial Cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1003:71-91. [8] TANG H, LEE M, KIM EH, et al. siRNA-knockdown of ADAMTS-13 modulates endothelial cell angiogenesis. Microvasc Res. 2017;113:65. [9] KIRIAKIDIS S, HENZE AT, KRUSZYNSKA-ZIAJA I, et al. Factor-inhibiting HIF-1 (FIH-1) is required for human vascular endothelial cell survival. FASEB J. 2015;29(7):2814-2827. [10] KAKO F, GABUNIA K, RAY M, et al. Interleukin-19 induces angiogenesis in the absence of hypoxia by direct and indirect immune mechanisms. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016;310(11):C931. [11] HAACK T, ABDELILAH-SEYFRIED S. The force within: endocardial development, mechanotransduction and signaling during cardiac morphogenesis. Development. 2016;143(3):373-386. [12] KAZMI R, BOYCE S, LWALEED B. Homeostasis of Hemostasis: The Role of Endothelium. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2015;41(6): 549-555. [13] NAUTA TD, MARLOES VDB, GIBBS S, et al. Identification of HIF-2α-regulated genes that play a role in human microvascular endothelial sprouting during prolonged hypoxia in vitro. Angiogenesis. 2017;20(1): 39-54. [14] SIRAGUSA M, FLEMING I. The eNOS signalosome and its link to endothelial dysfunction. Pflugers Archiv. 2016;468(7):1125-1137. [15] GORI T. Endothelial Function: A Short Guide for the Interventional Cardiologist. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(12):3838. [16] REN L, WONG HM, YAN CH, et al. Osteogenic ability of Cu-bearing stainless steel. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2015;103(7): 1433-1444. [17] YUAN Y, JIN S, QI X, et al. Osteogenesis stimulation by copper-containing 316L stainless steel via activation of akt cell signaling pathway and Runx2 upregulation. J Mater Sci Technol. 2019;35(11):2727-2733. [18] ZHANG L, DUAN Y, GAO Z, et al. Graphene enhanced anti-corrosion and biocompatibility of NiTi alloy. NanoImpact. 2017;7:7-14. [19] GUO Y, XU Z, WANG Q, et al. Corrosion resistance and biocompatibility of graphene oxide coating on the surface of the additively manufactured NiTi alloy. Prog Org Coat. 2022;164:106722. [20] ION R, LUCULESCU C, CIMPEAN A, et al. Nitride coating enhances endothelialization on biomedical NiTi shape memory alloy. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater. 2016;62:686-691. [21] LÜ X, QU Y, HONG Y, et al. A high-throughput study on endothelial cell adhesion and growth mediated by adsorbed serum protein via signaling pathway PCR array. Regen Biomater. 2018;5(1):25-34. [22] FILLI L, LUECHINGER R, FRAUENFELDER T, et al. Metal-induced artifacts in computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging: comparison of a biodegradable magnesium alloy versus titanium and stainless steel controls. Skeletal Radiol. 2015;44(6):849-856. [23] LIU W, GUO S, TANG Z, et al. Magnesium promotes bone formation and angiogenesis by enhancing MC3T3-E1 secretion of PDGF-BB. Biochem Bioph Res Co. 2020;528(4):664-670. [24] LIU Q, ZHOU Y, LI Z. PDGF-BB promotes the differentiation and pro-liferation of MC3T3-E1 cells through the Src/JAK2 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(4):3719-3726. [25] TURNER DL, FORD WR, KIDD EJ, et al. Effects of nebulised magnesium sulphate on inflammation and function of the guinea-pig airway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017;801:79-85. [26] HU T, XU H, WANG C, et al. Magnesium enhances the chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by inhibiting activated macrophage-induced inflammation. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):3406. [27] ZHANG X, CHEN Q, MAO X. Magnesium Enhances Osteogenesis of BMSCs by Tuning Osteoimmunomodulation. Biomed Res Int. 2019; 2019:7908205. [28] 王健,马翔宇,冯亚非,等.镁离子对成骨细胞活力和分化的促进作用及其机制研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2015,15(15):2836-2839. [29] 李政垚,刘洁颖,吴狄,等.高镁离子浓度对人骨髓间充质干细胞增殖与成骨分化的影响[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2020,13(5): 419-426. [30] ZHU D, SU Y, YOUNG ML, et al. Biological responses and mechanisms of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to Zn and Mg biomaterials. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2017;9(33):27453-27461. [31] CIPRIANO AF, LIN J, LIN A, et al. Degradation of bioresorbable Mg- 4Zn- 1Sr intramedullary pins and associated biological responses in vitro and in vivo. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2017;9(51):44332-44355. [32] KONG Y, HU X, ZHONG Y, et al. Magnesium-enriched microenvironment promotes odontogenic differentiation in human dental pulp stem cells by activating ERK/BMP2/Smads signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019; 10(1):378. [33] ZELLER-PLUMHOFF B, LAIPPLE D, SLOMINSKA H, et al. Evaluating the morphology of the degradation layer of pure magnesium via 3D imaging at resolutions below 40 nm. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(12): 4368-4376. [34] CHU W, LI T, JIA G, et al. Exposure to high levels of magnesium disrupts bone mineralization in vitro and in vivo. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(21): 1419. [35] BEHERA M, RAJPUT M, ACHARYA S, et al. Zinc and cerium synergistically enhance the mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and osteogenic activity of magnesium as resorbable biomaterials. Bioact Mater. 2021;16(4):044109. [36] XU A, TU HB, MW C, et al. Degradability and biocompatibility of magnesium-MAO: The consistency and contradiction between in-vitro and in-vivo outcomes - ScienceDirect. Arab J Chem. 2020;13(1): 2795-2805. [37] MA L, NIU J. Facile fabrication of silicon coating for improving biodegradation and cytocompatibility of pure magnesium by hydrothermal method. Metal Res Technol. 2019;116(4):416. [38] LIANG DY, LIANG PC, YI QQ, et al. Copper coating formed by micro-arc oxidation on pure Mg improved antibacterial activity, osteogenesis, and angiogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Biomed Microdevices. 2021;23(3):39. [39] SONG J, JIN P, LI M, et al. Antibacterial properties and biocompatibility in vivo and vitro of composite coating of pure magnesium ultrasonic micro-arc oxidation phytic acid copper loaded. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019;30(5):49. [40] JIN S, ZHANG D, LU X, et al. Mechanical properties, biodegradability and cytocompatibility of biodegradable Mg-Zn-Zr-Nd/Y alloys. J Mater Sci Technol. 2020;(12):190-201. [41] DAN ZA, QI HC, KY D, et al. Antibacterial activities against Porphyromonas gingivalis and biological characteristics of copper-bearing PEO coatings on magnesium. J Mater Sci Technol. 2021;61: 33-45. [42] LEI Z, LI F, CHEN X, et al. The in Vitro Osteogenic and Angiogenic Effects of Sodium-free Fluoride-containing Bioactive Glasses. Mater Lett. 2019;248:138-142. [43] LIU J, RAWLINSON SCF, HILL RG, et al. Fluoride incorporation in high phosphate containing bioactive glasses and in vitro osteogenic, angiogenic and antibacterial effects. Dent Mater. 2016;32(10): e221-e237. [44] CHENG S, WANG W, WANG D, et al. An in vitro and in vivo comparison of Mg(OH)(2)-, MgF(2)- and HA-coated Mg in degradation and osteointegration. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(12):3320-3333. [45] CHENG S, ZHANG D, LI M, et al. Osteogenesis, angiogenesis and immune response of Mg-Al layered double hydroxide coating on pure Mg. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(1):91-105. [46] WEIZBAUER A, KIEKE M, RAHIM MI, et al. Magnesium-containing layered double hydroxides as orthopaedic implant coating materials-An in vitro and in vivo study. J Biomed Mater Res B. 2016;104(3):525-531. [47] RAHMAN M, DUTTA NK, CHOUDHURY NR. Microroughness induced biomimetic coating for biodegradation control of magnesium. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;121:111811. [48] PARK JE, JANG YS, CHOI JB, et al. Evaluation of Corrosion Behavior and In Vitro of Strontium-Doped Calcium Phosphate Coating on Magnesium. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(21):6625. [49] MAKKAR P, KANG HJ, PADALHIN AR, et al. In-vitro and in-vivo evaluation of strontium doped calcium phosphate coatings on biodegradable magnesium alloy for bone applications. Appl Surf Sci. 2020;510:145333. [50] LYU J, ELMAN RR, SVYATKIN LA, et al. Theoretical and Experimental Research of Hydrogen Solid Solution in Mg and Mg-Al System. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(5):1667. [51] 李玉国.骨科可降解镁合金生物材料的研究进展[J].合成材料老化与应用,2021,50(6):155-158. [52] YANG Q, TABISH M, WANG J, et al. Enhanced Corrosion Resistance of Layered Double Hydroxide Films on Mg Alloy: The Key Role of Cationic Surfactant. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(6):2028. [53] LI CY, GAO L, FAN XL, et al. In vitro degradation and cytocompatibility of a low temperature in-situ grown self-healing Mg-Al LDH coating on MAO-coated magnesium alloy AZ31. Bioact Mater. 2020;5(2):364-376. [54] PENG F, WANG D, TIAN Y, et al. Sealing the Pores of PEO Coating with Mg-Al Layered Double Hydroxide: Enhanced Corrosion Resistance, Cytocompatibility and Drug Delivery Ability. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):8167. [55] CHENG H, MAO L, XU X, et al. The bifunctional regulation of interconnected Zn-incorporated ZrO2 nanoarrays in antibiosis and osteogenesis. Biomater Sci. 2015;3(4):665-680. [56] WANG X, LIU S, LI M, et al. The synergistic antibacterial activity and mechanism of multicomponent metal ions-containing aqueous solutions against Staphylococcus aureus. J Inorg Biochem. 2016;163:214-220. [57] POOLE K. At the Nexus of Antibiotics and Metals: The Impact of Cu and Zn on Antibiotic Activity and Resistance. Trends Microbiol. 2017; 25(10):820-832. [58] PENG F, WANG D, ZHANG D, et al. PEO/Mg-Zn-Al LDH Composite Coating on Mg Alloy as a Zn/Mg Ion-Release Platform with Multifunctions: Enhanced Corrosion Resistance, Osteogenic, and Antibacterial Activities. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018;4(12):4112-4121. [59] LI H, PENG F, WANG D, et al. Layered double hydroxide/poly-dopamine composite coating with surface heparinization on Mg alloys: improved anticorrosion, endothelialization and hemocompatibility. Biomater Sci. 2018;6(7):1846-1858. [60] TAN L, WANG Q, LIN X, et al. Loss of mechanical properties in vivo and bone-implant interface strength of AZ31B magnesium alloy screws with Si-containing coating. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(5):2333-2340. [61] RAZAVI M, FATHI M, SAVABI O, et al. Biodegradable Magnesium Bone Implants Coated with a Novel Bioceramic Nanocomposite. Materials (Basel). 2020;13(6):1315. [62] MANDAL T, DASGUPTA S, BARUI A, et al. Effect of strontium on microstructure, mechanical, and biological responses of Mg–Al–Zn–Sr alloys. Mater Sci Tech-Lond. 2022:1-17. [63] WU J, LEE B, SAHA P, et al. A feasibility study of biodegradable magnesium-aluminum-zinc-calcium-manganese (AZXM) alloys for tracheal stent application. Biomater Appl. 2019;33(8):1080-1093. [64] WEXLER BC. Pathophysiologic responses of spontaneously hypertensive rats to arterial magnesium--aluminum wire implants. Atherosclerosis. 1980;36(4):575-587. [65] 周盟,黄艺聪,康斌.骨科可降解镁合金生物材料的研究进展[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2020,13(5):433-440. [66] SARIAN MN, IQBAL N, SOTOUDEHBAGHA P, et al. Potential bioactive coating system for high-performance absorbable magnesium bone implants. Bioact Mater. 2022;12:42-63. [67] ZHENG Q, WANG Z, SUN Z, et al. In vivo and in vitro performances of chitosan-coated Mg-Zn-Zr-Gd-Ca alloys as bone biodegradable materials in rat models. J Biomater Appl. 2022;36(10):1786-1799. [68] HU Y, GUO X, QIAO Y, et al. Preparation of medical Mg-Zn alloys and the effect of different zinc contents on the alloy. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2022;33(1):9. [69] MAHATO A, DE M, BHATTACHARJEE P, et al. Role of calcium phosphate and bioactive glass coating on in vivo bone healing of new Mg-Zn-Ca implant. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2021;32(5): 55. [70] LI P, CHRISTINE S, ERNST S, et al. Mechanical Characteristics, In Vitro Degradation, Cytotoxicity, and Antibacterial Evaluation of Zn-4.0Ag Alloy as a Biodegradable Material. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(3):755. [71] DING P, LIU Y, HE X, et al. In vitro and in vivo biocompatibility of Mg-Zn-Ca alloy operative clip. Bioact Mater. 2019;4(1):236-244. [72] ZHANG E, FENG S. Blood compatibility of a ferulic acid (FA)-eluting PHBHHx system for biodegradable magnesium stent application. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015;52:37-45. [73] HAN Z, GUO H, ZHOU Y, et al. Composite Coating Prepared with Ferulic Acid to Improve the Corrosion Resistance and Blood Compatibility of Magnesium Alloy. Metals. 2022;12(4):545. [74] LIU C, CASTILLO AB. Targeting osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling for bone repair. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2018;26(7):e153-e155. [75] LI D, YUAN Q, YU K, et al. Mg–Zn–Mn alloy extract induces the angiogenesis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells via FGF/FGFR signaling pathway. Biochem Bioph Res Co. 2019;514(3):618-624. [76] SONG J, GAO Y, LIU C, et al. The effect of Sr addition on the microstructure and corrosion behaviour of a Mg-Zn-Ca alloy. Surf Coat Tech. 2022;437:128328. [77] PREDKO P, RAJNOVIC D, GRILLI ML, et al. Promising Methods for Corrosion Protection of Magnesium Alloys in the Case of Mg-Al, Mg-Mn-Ce and Mg-Zn-Zr: A Recent Progress Review. Metals. 2021;11(7):1133. [78] WANG HW. Preparation and Characterization of Mg-RE Alloy Sheets and Formation of Amorphous/Crystalline Composites by Twin Roll Casting for Biomedical Implant Application. Metals. 2019;9(10):1075. [79] WANG Y, HUANG H, JIA G, et al. Fatigue and dynamic biodegradation behavior of additively manufactured Mg scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2021;135:705-722. [80] XIE K, WANG N, GUO Y, et al. Additively manufactured biodegradable porous magnesium implants for elimination of implant-related infections: An in vitro and in vivo study. Bioact Mater. 2022;8:140-152. [81] LI Y, WANG L, CHEN S, et al. Biodegradable Magnesium Alloy Stents as a Treatment for Vein Graft Restenosis. Yonsei Med. 2019;60(5):429-439. [82] ZHOU Y, LIU X, HUANG N, et al. Magnesium ion leachables induce a conversion of contractile vascular smooth muscle cells to an inflammatory phenotype. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2019; 107(4):988-1001. [83] WU J, JIN L, TAN JY, et al. The effects of a biodegradable Mg-based alloy on the function of VSMCs via immunoregulation of macrophages through Mg-induced responses. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(16):1292. [84] ZHU J, ZHANG X, NIU J, et al. Biosafety and efficacy evaluation of a biodegradable magnesium-based drug-eluting stent in porcine coronary artery. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):7330. [85] SHI Y, ZHANG L, CHEN J, et al. In vitro and in vivo degradation of rapamycin-eluting Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloy stents in porcine coronary arteries. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;80:1-6. [86] XIE K, WANG L, GUO Y, et al. Effectiveness and safety of biodegradable Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloy screws for the treatment of medial malleolar fractures. J Orthop Translat. 2021;27:96-100. [87] Jl A, Dong B, Yza B, et al. Comparative in vitro study on binary Mg-RE (Sc, Y, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb and Lu) alloy systems. Acta Biomater. 2020;102:508-528. [88] SZKLARSKA D, RZYMSKI P. Is Lithium a Micronutrient? From Biological Activity and Epidemiological Observation to Food Fortification. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2019;189(1):18-27. [89] QASSEM M, CONSTANTINOU L, TRIANTIS IF, et al. A Method for Rapid, Reliable, and Low-Volume Measurement of Lithium in Blood for Use in Bipolar Disorder Treatment Management. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2019;66(1):130-137. [90] BOSCHE B, MOLCANYI M, REJ S, et al. Low-Dose Lithium Stabilizes Human Endothelial Barrier by Decreasing MLC Phosphorylation and Universally Augments Cholinergic Vasorelaxation Capacity in a Direct Manner. Front Physiol. 2016;7:593. [91] BIAN D, ZHOU X, LIU J, et al. Degradation behaviors and in-vivo biocompatibility of a rare earth- and aluminum-free magnesium-based stent. Acta Biomater. 2021;124:382-397. [92] CUI L, SUN L, ZENG R, et al. In vitro degradation and biocompatibility of Mg-Li-Ca alloys—the influence of Li content. Sci China Mater. 2018; 61(4):607-618. [93] XIA D, LIU Y, WANG S, et al. In vitro and in vivo investigation on biodegradable Mg-Li-Ca alloys for bone implant application. Sci China Mater. 2019;62:256-272. [94] WU J, ZHAO D, OHODNICKI JM, et al. In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation of Multiphase Ultrahigh Ductility Mg-Li-Zn Alloys for Cardiovascular Stent Application. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018;4(3):919-932. [95] LI J, ZHOU P, WANG L, et al. Investigation of Mg-xLi-Zn alloys for potential application of biodegradable bone implant materials. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2021;32(4):43. [96] LIU Y, WU Y, BIAN D, et al. Study on the Mg-Li-Zn ternary alloy system with improved mechanical properties, good degradation performance and different responses to cells. Acta Biomater. 2017;62:418-433. [97] XIA D, JIA Z, SHEN Y, et al. pH Stimuli-Responsive, Rapidly Self-healable Coatings Enhanced the Corrosion Resistance and Osteogenic Differentiation of Mg-1Ca Osteoimplant. Small. 2022:e2106056. doi: 10.1002/smll.202106056. [98] SUN H, WANG Y, SUN C, et al. In vivo comparison of the degradation and osteointegration properties of micro-arc oxidation-coated Mg-Sr and Mg-Ca alloy scaffolds. Biomed Mater Eng. 2022;33(3):209-219. [99] LI W, LIU X, ZHENG Y, et al. In vitro and in vivo studies on ultrafine-grained biodegradable pure Mg, Mg-Ca alloy and Mg-Sr alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(18):5071-5087. [100] ZHANG S, SUN X, KANG C, et al. Study on repairing canine mandibular defect with porous Mg-Sr alloy combined with Mg-Sr alloy membrane. Regen Biomater. 2020;7(3):331-336. [101] ZHAO C, PAN F, ZHANG L, et al. Microstructure, mechanical properties, bio-corrosion properties and cytotoxicity of as-extruded Mg-Sr alloys. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;70(Pt 2):1081-1088. [102] MUNTEANU C, VLAD DM, SINDILAR EV, et al. Novel Mg-0.5Ca-xMn Biodegradable Alloys Intended for Orthopedic Application: An In Vitro and In Vivo Study. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(23):7262. [103] HU Y, DONG D, WANG X, et al. Synthesis and Properties of Mg-Mn-Zn Alloys for Medical Applications. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(8):1855. [104] 洪席超,文静,于世德,等.两种镁合金浸提液对血管内皮细胞粘附功能的影响[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2019,20(2):87-91. [105] 王心玲,胡桐楠,储冰峰.镁合金材料与人内皮细胞的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(18):2846-2851. [106] 潘双.镁离子与锌离子对人血管内皮细胞和平滑肌细胞迁移功能的影响[J].锦州医科大学学报,2017,38(2):10-12. [107] WANG Z, ZHU S, WANG L, et al. Preparing a novel magnesium-doped hyaluronan/polyethyleneimine nanoparticle to improve endothelial functionalisation. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2020;14(2):142-147. [108] LIU C, YANG G, ZHOU M, et al. Magnesium Ammonium Phosphate Composite Cell-Laden Hydrogel Promotes Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis In Vitro. ACS Omega. 2021;6(14):9449-9459. [109] LIU M, WANG X, LI H, et al. Magnesium oxide-incorporated electrospun membranes inhibit bacterial infections and promote the healing process of infected wounds. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(17):3727-3744. [110] MA J, ZHAO N, ZHU D. Biphasic responses of human vascular smooth muscle cells to magnesium ion. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(2): 347-356. [111] ZHAO N, ZHU D. Endothelial responses of magnesium and other alloying elements in magnesium-based stent materials. Metallomics. 2015;7(1):118-128. [112] GAI X, LIU C, WANG G, et al. A novel method for evaluating the dynamic biocompatibility of degradable biomaterials based on real-time cell analysis. Regen Biomater. 2020;7(3):321-329. [113] WANG JL, SONG MS, CONTRERAS KG, et al. In Vitro Biocompatibility of Surface Corrosion Films upon Magnesium. Corrosion. 2021;77(2):218-227. [114] AI C, LEE Y HD, TAN XH, et al. Osteochondral tissue engineering: Perspectives for clinical application and preclinical development. J Orthop Translat. 2021;30:93-102. [115] RAHIM MI, TAVARES A, EVERTZ F, et al. Phosphate conversion coating reduces the degradation rate and suppresses side effects of metallic magnesium implants in an animal model. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2017;105(6):1622-1635. [116] GAO J, SU Y, QIN YX. Calcium phosphate coatings enhance biocompatibility and degradation resistance of magnesium alloy: Correlating in vitro and in vivo studies. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(5):1223-1229. |
| [1] | 陈世崧, 刘晓红, 徐志云. 人工生物瓣膜的研究现状及展望[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1096-1102. |
| [2] | 史业弘, 王 成, 陈世玖. 小口径人工血管的早期血栓形成与预防[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1110-1116. |
| [3] | 刘 欢, 李 涵, 马云豪, 仲维剑, 马国武. 部分脱矿牙本质颗粒在上颌窦提升中的成骨性能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(3): 354-359. |
| [4] | 梁韩莹, 马云豪, 李 涵, 李东阳, 仲维剑, 马国武. 部分脱矿自体牙本质颗粒在种植位点保存术中的成骨效能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(16): 2488-2492. |
| [5] | 杨 峰, 赵 骞, 张世轩, 赵铁男, 冯 博. 雷帕霉素联合CD133抗体支架预防血管再狭窄的有效性和安全性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(4): 579-584. |
| [6] | 李传鸿, 俞 兴, 杨永栋, 杨凯坦, 赵 赫. 经寰枕后间隙蛛网膜下腔注射是脊髓损伤模型大鼠可供选择的给药方式[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(33): 5376-5383. |
| [7] | 郭洋妍, 喻正文, 张 剑. 镁合金生物材料动物体内实验的研究热点[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(22): 3556-3565. |
| [8] | 王书韵, 谢君辉, 余学锋. 间充质干细胞治疗糖尿病肾病的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(1): 148-152. |
| [9] | 张 超, 吕 欣. 髋臼骨折固定后的异位骨化:危险因素、预防及其治疗进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [10] | 李芳, 吴可通, 赵珺, 李刚. 血管支架及其在动脉瘤治疗中的发展趋势[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(34): 5561-5569. |
| [11] | 申瑞秋, 刘志明, 宋俊祎, 胡碧茹. 具有一氧化氮释放功能的人工血管材料[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(28): 4531-4538. |
| [12] | 纪 琦, 喻正文, 张 剑. 3D打印金属基生物材料工艺和临床应用的问题与趋势[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(16): 2597-2604. |
| [13] | 赵彬彬, 仲维剑, 马国武, 李永奇, 王 宁. 三种不同骨移植材料成骨效果的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(10): 1507-1510. |
| [14] | 霍少川, 王海彬, 唐宏宇, 王粤淇, 陈群群, 冯梓誉, 李义凯. 补肾健脾活血中药干预膝骨关节炎模型大鼠软骨细胞IL-1β/ERRα/SOX9/Col2α1信号通路的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(35): 5577-5581. |
| [15] | 崔庆达, 王海革, 赵海军, 刘 伟, 毕郑钢. 跨骺钢板固定一定周期取出:继续观察一段时间后骺板的生长抑制情况[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(3): 372-377. |
27 GPa),可有效减少应力遮挡效应。除此之外,镁离子还是许多酶的关键辅助因子[3]。虽然镁合金在生物相容性方面具有优势,但其不可控的快速降解及产生的皮下气肿是该材料亟待解决的问题。传统材料虽不能自行降解,但其高耐腐蚀能力得以保证术区在愈合过程中为组织修复提供足够的空间,在受力区承受一定的质量,镁合金的快速降解可能导致其无法为最终新骨形成建立适宜的环境,因此,传统材料与镁合金均有各自的优劣。该文首先介绍了与血管化有关的内皮细胞,由于过去多注重于材料与骨形成之间的关系,忽略修复过程中血管的作用,导致体内植入材料不长久,后探讨部分传统材料目前的改善方法和结论以及镁合金降解后对周围组织的影响,最后重点综述了近年较热门的镁合金,通过改善镁合金存在的问题,探讨在组织愈合过程中不同元素的加入对细胞组织的影响,为后续镁合金结构优化和设计提供新的思路。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
1.1 资料来源
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在2022年3月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 检索时限为2015-2022年。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed、中国知网数据库、Web of Science和Elsevier等。
1.1.4 检索词 中文“主题”检索词为“金属生物材料,镁合金材料,血管支架,内皮化,动物实验,体外实验”,英文“Subject”检索词为“Metal biomaterials,Magnesium alloy materials,Vascular stent, Reendothelializations,Animal experiment,in vitro”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著和综述。
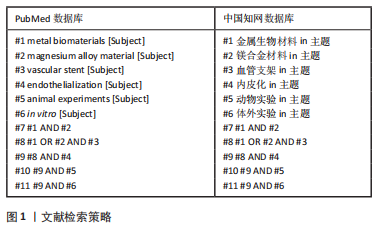
1.1.6 检索策略 中、英文文献检索策略,见图1。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①有关镁合金材料实验研究的文献;②有关内皮细胞培养研究的文献;③优先选择近5年发表的,同一领域主题中心相近、论据可靠的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①与研究目的无相关性的文章;②重复性研究文章;③论点论据不明确文章。
1.3 质量评估及数据提取 应用计算机检索,按照筛选标准,通过阅读文题、摘要进行初步筛选,排除与主题相关性差及重复陈旧的文献,最终纳入116篇文献,纳入的文献包括研究原著和综述。文献检索流程图,见图2。
等[110]与ZHAO等[111] 的研究都表明,镁离子对内皮细胞的影响是与其浓度有关的,在低浓度下对内皮细胞和平滑肌细胞均有促进作用,但浓度过高则出现毒性,抑制内皮细胞迁移并减弱细胞与基质的黏附。改善镁合金降解不仅可以为组织重建提供足够空间,还能创造促进细胞行为的微环境,材料植入后便处于体内的复杂环境,其动态降解过程调控细胞行为,而包括缓冲系统在内的复杂环境也进一步影响着材料。为了更好地验证镁合金对细胞是否具有毒性,有学者提出一种在细胞动态行为下检测材料对细胞影响的新方法并以MTT做对比[112],结果虽然均证明材料无毒性,但此种新方法的出现可能更好地说明细胞在周期内都无明显损害。除此之外,有学者认为目前的研究多注重于材料降解所形成的环境对细胞的影响[113],忽略材料本身降解出现的表面沉淀和形态改变,虽然细胞处于降解后的微环境,但材料表面形态对于细胞的活性和增殖是具有重大意义的。材料由于降解新形成的表面形态和结构是否可以对细胞进行进一步的调控,新形成的结构是否对细胞有毒性,材料植入后降解速率降低是否跟自身降解产生的沉淀有关等,因此,关于材料降解的动态行为下对细胞的调控是非常值得探索的。在镁合金中加入某些元素使其在体内环境中处于主动动态过程,在不同阶段调控术区细胞的行为也许在未来是一种可行的方法。由于体内环境的复杂性,体外实验的结果并不能完全等同于体内实验:首先,材料的浸提液并不能完全模拟材料对细胞的刺激,在考虑材料离子对细胞影响的情况下应尽量模拟植入的形态;其次,材料降解后形成的微环境中并不总是单一离子,而是复杂离子的综合,新形成的环境如何影响内皮细胞以及如何控制镁合金的降解使微环境最适宜的调控细胞行为是需要进一步研究的问题。目前常见的改善镁合金降解的方法有纯化、合金化、表面改性,无论是哪种方法,在实验文中均看到耐腐蚀性有不同程度的提高,并且不同元素的合金化对镁合金的改善是不同方面的,未来可能针对不同需求而选择不同合金化的镁合金以适应临床患者的情况。除引入其他元素外,改进镁合金的制作工艺来解决存在的降解问题也可能是一大值得尝试的方法,比如高压扭转工艺可以有效改善纯镁及镁合金的性能[99],有研究表明大于300 μm的材料孔径更适合血管和新骨的形成[114],并且降低腐蚀速率[115-116],因此无论是材料表面的粗糙程度还是内部结构,对细胞的黏附和迁移都具有重大影响,未来应进一步探究。该文对内皮化的相关机制和信号通路并未详细阐述,一些体外积极结果的实验还需大量体内实验验证。文章重点综述近年来较热门的镁合金材料,以期探讨其可能存在的降解机制和对细胞的影响,为未来优化镁合金材料提供参考。
3.2 该篇综述的特点 文章首先介绍了内皮化与内皮细胞,之后总结了近几年来对于镁合金材料的研究,综述了在改善镁合金材料问题上不同学者的方法,归纳总结镁合金材料动物实验和体外细胞培养中镁的作用,目前镁合金材料的研究多集中于改善降解提高生物相容性,该综述对比镁合金材料的体内外实验,探讨了对该材料未来研究的办法和观点。
3.3 该篇综述的局限 该综述只采纳了近几年的文献,对镁离子和内皮化的机制综述还不够深入,未来应扩大文献范围,进行更深一层的研究。
3.4 该篇综述的意义 通过归纳总结多篇近年来的文献,阐述镁合金材料的优良性能,不同元素合金化对镁合金材料的降解速率有明显改善。体外实验应更准确地模拟植入后的细胞生长环境,材料在体液中始终处于降解过程,在此过程中材料表面所发生的变化对内皮细胞迁移黏附的影响值得进一步研究。镁离子可以安全代谢,但降解后新产生的复杂环境是否对细胞有毒性尚不清楚,在未来的实验中是否需要考虑血液缓冲对内皮细胞迁移黏附和材料的降解问题,人体存在的血液缓冲系统是否影响镁离子和内皮细胞的关系还不明确。目前已知镁合金材料具有促成骨、促成血管和抑菌作用,对于植入后的即时反应、反冲效应和血管的负性重塑、管腔的面积丢失等问题,许多研究在实验中并未完全阐明,而且无论是动物体内实验还是体外实验其结果都具有局限性,未来还需要大量的学者投入研究,相信随着医学发展,镁合金材料的应用会更广泛,让医学更好地为人民服务。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
镁合金生物材料:在纯镁中加入Al、Zn、Ca、Mn、RE等无细胞毒性的合金元素可改善镁合金材料的力学性能、生物相容性、组织相容性,同时能在受植区为细胞黏附和骨的成长提供环境和支持。内皮化:血管受病理性或生理性刺激时内皮细胞被招募,迁移至受损区并增殖或内皮祖细胞通过归巢于内皮损伤部位,诱导血管生成,以修复损伤形成新血管。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
镁合金由于其优异的生物相容性和可降解能力成为21世纪备受青睐的新型生物组织工程材料。目前大量研究表明镁合金在植入体内后会促进新骨形成,影响术区炎症因子的表达,但其过快的降解速度和降解过程中出现的皮下气肿是目前存在的问题。通过研究成骨前期镁合金对新生血管的影响,更进一步了解镁合金植入后降解相关的影响因素。对比不同材料与镁合金对术区血管内皮化的差别,总结目前改善镁合金降解问题的不同方法,优化合金化过程中选用的合金元素和含量,在改善镁合金降解速率的基础上,避免细胞毒性,增强材料强度,为后续临床研究和应用提供参考。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||