中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (28): 4450-4454.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.28.004
• 骨髓干细胞 bone marrow stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
原代骨髓基质细胞共培养对K562细胞伊马替尼敏感性及细胞周期的影响
王吉刚,周 凡,刘彦琴,白 颖,刘景华,吴丹彤
- 解放军沈阳军区总医院血液科,辽宁省沈阳市 110016
Influences of co-culture with primary bone marrow stromal cells on imatinib sensitivity and cell cycles of K562 cells
Wang Ji-gang, Zhou Fan, Liu Yan-qin, Bai Ying, Liu Jing-hua, Wu Dan-tong
- Department of Hematology, General Hospital of Shenyang Military Area Command of Chinese PLA, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China
摘要:
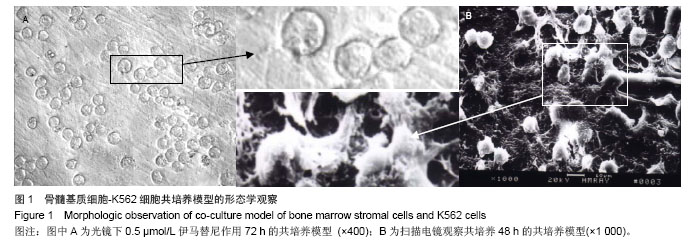
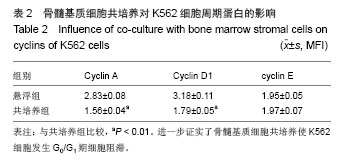
背景:与骨髓基质细胞黏附可介导白血病细胞耐药,而对于黏附功能缺陷的慢性髓细胞白血病而言,骨髓基质细胞在伊马替尼耐药形成中的作用及其机制尚不清楚。 目的:构建慢性髓细胞白血病骨髓基质细胞-K562细胞共培养模型,探讨慢性髓细胞白血病骨髓基质细胞共培养对K562细胞伊马替尼敏感性及细胞周期的影响。 方法:自慢性髓细胞白血病患者骨髓分离、培养骨髓基质细胞,与K562细胞共培养构建骨髓基质细胞-K562细胞共培养模型。MTT法检测伊马替尼IC50,Annexin V-FITC/PI标记暴露于0.5 μmol/L伊马替尼72 h的K562细胞,流式细胞仪检测K562细胞凋亡率。收集与骨髓基质细胞共培养72 h的K562细胞,流式细胞仪检测细胞周期及细胞周期蛋白(Cyclin A、Cyclin D1及cyclin E)的表达。 结果与结论:基质细胞共培养组及悬浮培养组K562细胞伊马替尼IC50分别为(0.52±0.02) μmol/L和(1.27± 0.05) μmol/L,两者比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01)。0.5 μmol/L伊马替尼处理72 h,共培养组及悬浮培养组凋亡率分别为(15.48±4.17)%和(32.01±6.83)%,两者比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01)。与骨髓基质细胞共培养72 h的K562细胞G0-G1期细胞的比例为(48.81±8.27)%,明显高于悬浮培养组(25.78±3.26)%(P < 0.01)。慢性髓细胞白血病骨髓基质细胞共培养能介导K562细胞对伊马替尼耐药,其机制可能与基质细胞共培养使K562细胞发生G0/G1细胞周期阻滞有关。
中图分类号:

.jpg)