| [1] Biswas A,Hutchins R.Embryonic stem cells.Stem Cells Dev.2007; 16(2):213-222.[2] Takahashi K,Tanabe K, Ohnuki M,et al.Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by definedfactors. Cell.2007;131(5):861-872. [3] Maherali N, Hochedlinger K.et al.Guidelines and Techniques for the Generation of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells.Cell Stem Cell.2008;3(6):595-605.[4] Tavernier G, Mlody B, Demeester J,et al. Current methods for inducing pluripotency in somatic cells. Adv Mater.2013;25(20): 2765-2771.[5] Balasubramanian S,Jasty S,Sitalakshmi G,et al.Influence of feeder layer on the expression of stem cell markers incultured limbal corneal epithelial cells.Indian J MedRes.2008;128(5): 616-622. [6] Page RL, Ambady S, Holmes WF,et al.Induction of stem cell gene expression in adult human fibroblasts withouttransgenes. Cloning Stem Cells.2009;11(3):417-426.[7] Camarasa M,Brison D,Kimber SJ,et al.Naturally immortalised mouse embryonic fibroblast lines support human embryonic stem cell growth. Cloning Stem Cells. 2009;11(3):453-462. [8] Xue F,Ma Y,Chen YE,et a1.Recombinant rabbit leukemia inhibitory factor and rabbit embryonic fibroblasts support the derivation and maintenance of rabbit embryonic stem cells. Cell Reprogram.2012;14(4):364-376.[9] Gepstein L.Derivation and potential applications of human embryonic stem cells.Circulation Res.2002;91 (10): 866-876.[10] Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS,et al.Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts.Science. 1998;282(5391):1145-1147.[11] Reubinoff BE,Pera MF,Fong CY,et al. Embryonic stem cell lines from human blastocysts:somatic differentiation invitro. Nat Biotechnol.2000;18(4):399-404.[12] Cowan CA, Klimanskaya I, McMahon J, et al. Derivation of embryonic stem-cell lines from human blastocysts. N Engl J Med.2004;350(13):353-356.[13] Chen H,Qian K,Hu J,et al.The derivation of two additional human embryonic stem cell lines from day 3 embryos with low morphological scores. Hum Reprod.2005;20(8)2201-2206.[14] Lin S,Talbot P.Methods for culturing mouse and human embryonic stem cells. Methods Mol Biol.2011;690:31-56.[15] 黄治军,吕中华,郑鹏,等.昆明小白鼠胚胎干细胞分离培养的影响因素[J].黑龙江畜牧兽医.2010;52(1):16-18.[16] 林真,沈晓丽,王孟丽,等.昆明小鼠胚胎成纤维细胞培养条件的研究[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2010,9(3):161-163.[17] Lim J W, Bodnar A.Proteome 1analysis of conditioned medium from mouse embryonic fibroblast feeder layers which support the growth of human embryonic stem cells. Proteomics. 2002;2(9):1187-203.[18] Li Z,Leung M,Hopper R,et al.Feeder-free self-renewal of human embryonic stem cells in 3D porous natural polymer scaffolds. Biomaterials.2010;31(3):404-412.[19] Awan A,Oliveri RS, Jensen PL,et al.Immunoflourescence and mRNA analysis of human embryonic stem cells(hESCs) grown under feeder-free conditions.Methods Mol Biol.2010; 584(4): 195-210.[20] Braam SR,Denning C,Mummery CL.Genetic manipulation of human embryonic stem cells in serum and feeder-free media.Methods Mol Biol.2010;584(42):413-423.[21] Hernandez D,Ruban L,Mason C.Feeder-free culture of human embryonic stem cells for scalable expansion in a reproducible manner.Stem Cells Dev.2011;20(6):1089-1098.[22] 方驰华,胡海北,郝建志,等.ICR小鼠胚胎成纤维细胞的分离培养及饲养层制备[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14 (23): 4299-4302.[23] 胡嘉波,麻全慧,胡三强,等.人胚胎干细胞饲养层的制备及生物学活性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(23): 4233-4236.[24] Zeng C, Pan F, Jones LA, et al. Evaluation of 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine staining as a sensitive and reliable method for studying cell proliferation in the adult nervous system. Brain Res. 2010;1319:21-32.[25] 韩建群,修瑞娟.两种细胞增殖分析方法的比较性研究[J].山东医药,2012,52(12):70-72. [26] [26]Buck SB,Bradford J,Gee KR,et al. Detection of S-phase cell cycle progression using 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine incorporation with click chemistry,an alternative to using 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine antibodies. Biotechniques.2008; 44(7):927-929.[27] ]Warren M,Puskarczyk K,Chapman SC. Chick embryo proliferation studies using EdU labeling. Dev Dyn. 2009;238 (4):944-949.[28] 刘雷,扬立业.EdU在检测细胞增殖中的应用[J].医学综述, 2010,16(19):2901-2904. [29] Khademhosseini A, Ferreira L, Blumling J 3rd, et al.Co-culture of human embryonic stem cells with murine embryonic fibroblasts on microwell-patterned substrates. Biomaterials.2006;27(36):5968-5977.[30] 腊晓琳,田海清,蔡霞.高效制备昆明鼠胚胎成纤维细胞饲养层[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(27):5002-5006.[31] 王志强,梁锐,陈明清,等.胰蛋白酶消化法和组织块法原代培养包皮成纤维细胞的比较[J].生命科学研究,2012,16(3):242-247.[32] 张万里,李伟,林学科,等.制作胚胎干细胞饲养层细胞条件的优化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(36):6768-6771. |
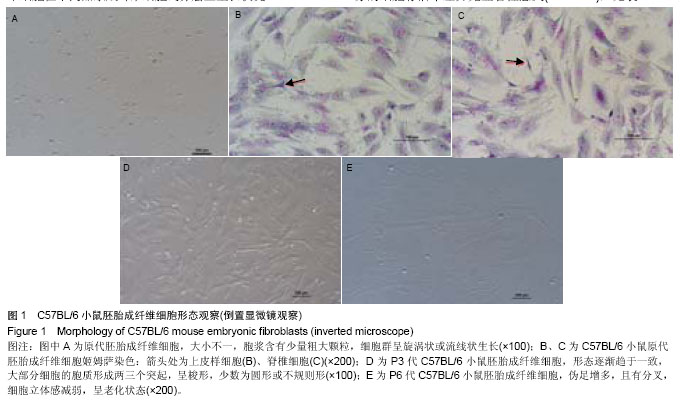
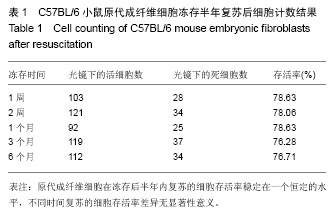
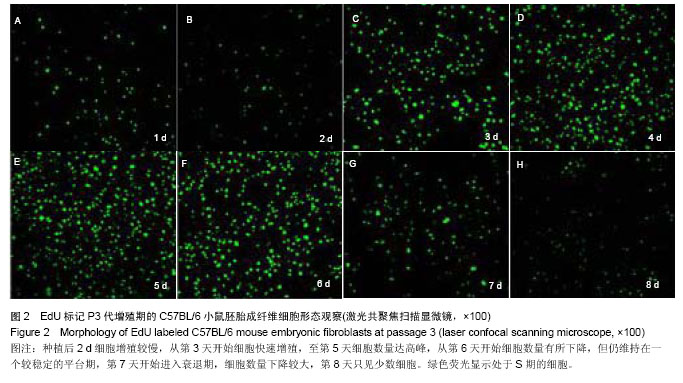
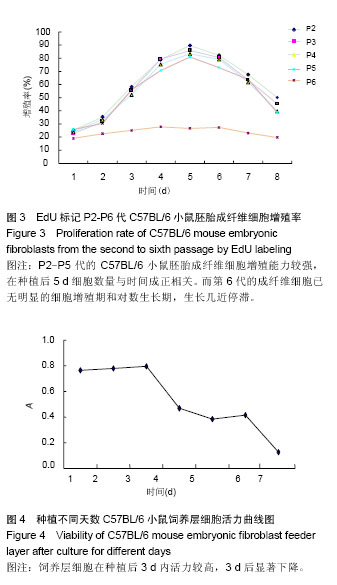
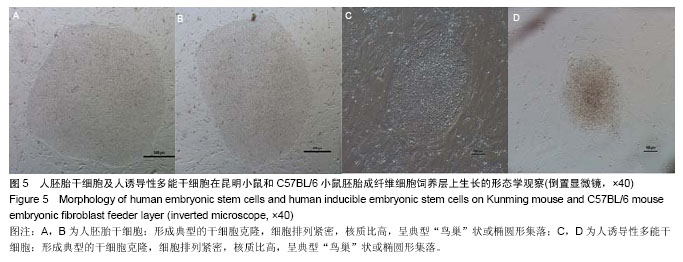
.jpg)