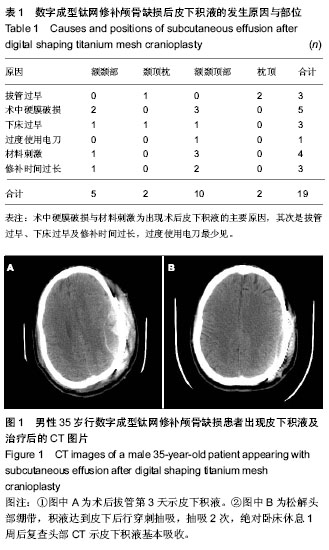
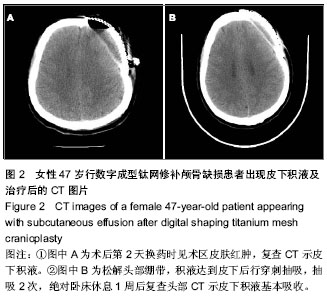
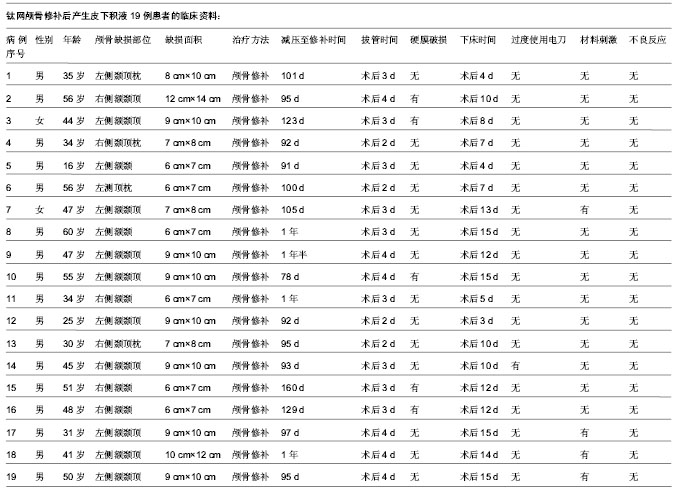
| [1] 喻敬国.162例钛网颅骨修补术后并发症临床分析[J].中国实用医药,2012,7(1):117-118.[2] Verret DJ,Ducic Y,Oxford L,et al.Hydroxyapatite cement in cranio-facial reconstruction.Ot olaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2005;133(6):897-899.[3] 齐欣,沈干,王增亮,等.三维钛网在颅骨缺损修复中的应用[J]. 组织工程与重建外科杂志,2010,6(4):218-219,224.[4] Iwawa T,Yamada J,Imai S,et al. The use of frozen autogenous bone flaps in delayed cranioplasty revisited. Neurosurgery. 2003;52(3):591-596.[5] 吴承远,刘玉光.临床神经外科学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2001: 217-218.[6] Jin GL, ZhangYL,Yu XB.Clinic application of the titanium alloy prostheses in defectof skull.Chin J Traumatol.1999;15: 472- 473.[7] 李进京,于龙,刘书深,等.颅脑损伤去大骨瓣减压术后早期颅骨修补28例临床体会[J].中国医学创新,2012,9(2):89-90.[8] Honeybul S. Complication of decompressive craniectomy for head injury. J Clin Neurosci. 2010;17:430-435.[9] 王璨,喻军华,黄锦峰,等.数字化塑形钛网颅骨修补术后并发症分析[J].中国临床神经外科杂志,2013,18(9):550.[10] 冯志刚,张小义,刘进,等.数字扫描成型钛网修补颅骨缺损的临床应用研究[J].实用医技杂志,2012,19(3):299-300.[11] 丁炳谦,李振江,刘志军.金属钛网颅骨修补术后感染的预防[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2011,21(12):2459-2460.[12] 别小华,史航宇,韩建林,等.颅骨修补术后修补材料与皮下积液的关系[J].齐齐哈尔医学院报,2007,28(19):2322-2324.[13] Martin MP, Olson S. Post-operative complications with titaniummesh.J Clin Neurosic. 2009;16(8):1080-1081.[14] 苏坐龙,宋丽娟.颅骨缺损修补术后并发症分析[J].实用医技杂志, 2010,17(8):758-759.[15] 程序曲,赵富文,褚荣涛.颅骨缺损修补术并发症88例临床分析[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2011,14(15):11-15.[16] 郝彩江,黄玉宝,柳兴军,等.颅骨修补术后并发症的预防进展[J].山东医药, 2012,52(26):93.[17] 张祖勇,李云漳.颅骨修补术后头皮下积液原因探讨[J].浙江医学, 1997,9(2):104.[18] 王玉峰,张鹏.自身颅骨、钛网和仿生颅骨的应用比较[J].中国临床康复,2003,7(19):2768-2769.[19] 尤渊明.颅骨修补术后并发症的预防及处理[J].中国现代医生, 2009,47(29):139-140.[20] 吴孟超,吴在德.黄家驷.外科学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2008: 7.[21] 胡家正,熊玉纯,徐义富.颅骨修补术后并发症预防和处理的几点体会[J].中华神经外科杂志,1991,8(2):142.[22] 仪立志,黄仕春,张浚.颅骨修补术后头皮下积液的防治[J].医学文选,2001,20(5):617.[23] 庄会林,柳宪华,施鹏.颅骨缺损的部位和大小与神经症状的关系[J].中国医师杂志,2002,4(11):1222-1223.[24] 刘明铎.实用颅脑损伤学[M].北京:人民军医出版社,1992.[25] 靳文义,张楠,刘智,等.外伤性颅骨缺损修补手术80例临床经验总结[J].中国综合临床,2006,20(5):439-440.[26] 王凤鹿,李莉,李文瑞,等.钛网颅骨修补术后并发症的防治[J].中国临床神经外科杂志,2013,18(4):255.[27] 王璨,喻军华,黄锦峰,等.数字化塑形钛网颅骨修补术后并发症分析[J].中国临床神经外科杂志,2013,18(9):550.[28] 张东强.钛网材料在颅骨损伤修补中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(25):4742.[29] 李祥.颅骨修补术常见并发症及预防[J].临床合理用药,2011, 4(12): 110.[30] 管国平,贾丛林,张斌.数字成型钛板颅骨修补术后并发症及其防治策略[J].现代实用医学,2012,4(10):1103-1105. |