| [1] Hu HW. Nanjing:Southeast University Press, 2009.胡捍卫.组织胚胎学[M].2版.东南大学出版社,2009.http://www.seupress.com/book.details.php?id=2603[2] Aberdam D. Epidermal stem cell fate: what can we learn from embryonic stem cells. Cell Tissue Res. 2008;331(1):103-107.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Epidermal%20stem%20cell%20fate%3A%20what%20can%20we%20learn%20from%20embryonic%20stem%20cells[3] Li HH,Fu XB,Zhou G,et al. Zhonghua Yixue Zazhi. 2005;85(27):1885-1889.李海红,付小兵,周岗,等. 人骨髓间充质干细胞与汗腺细胞共同培养诱导细胞表型转化的初步研究[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2005,85(27):1885-1889.http://so.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/ViewHTML/PeriodicalPaper_zhyx200527006.aspx[4] Xu LQ,Sui J,Ding Y,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2007;11(7):1243-1246.徐龙强, 隋静,丁钰, 等. 大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞体外培养转化为神经细胞的实验[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007,11(7):1243-1246.http://so.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/ViewHTML/PeriodicalPaper_xdkf200707011.aspx[5] Li HH, Zhou G, Fu XB,et al. Antigen expression of human eccrine sweat glands. J Cutan Pathol. 2009;36(3):318-324. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19032382[6] Zeng B, Chen H, Zhu C, et al. Effects of combined mesenchymal stem cells and heme oxygenase-1 therapy on cardiac performance. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2008;34(4):850-856. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Effects%20of%20combined%20mesenchymal%20stem%20cells%20and%20heme%20oxygenase-1therapy%20on%20cardiac%20performance[7]Zhou G,Fu XB. Chuangshang Waike Zazhi. 2005;7(5):394-396.周岗,付小兵.汗腺中EGF、EGFR、IL和CKs等基因的表达特征及意义[J].创伤外科杂志, 2005,7(5):394-396. http://so.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/ViewHTML/PeriodicalPaper_cswkzz200505033.aspx[8] Zhuang Y, Chen X, Xu M, et al. Chemokine stromal cell-derived factor 1/CXCL12 increases homing of mesenchymal stem cells to injured myocardium and neovascularization following myocardial infarction.Chin Med J (Engl). 2009;122(2):183-187.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Chemo%20kine%20stromal%20cell-derived%20factor1%2FCXCL12increases%20homing%20of%20mesenchymal%20stem%20cells%20to%20injured%20myocardium%20and%20neovascularization%20following%20myocardial%20infarction[9] Sheng Z, Fu X, Cai S,et al. Regeneration of functional sweat gland-like structures by transplanted differentiated bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.Wound Repair Regen. 2009;17(3):427-435.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Regeneration%20of%20functional%20sweat%20gland-like%20structures%20by%20transplanted%20differentiated%20bone%20marrow%20mesenchymal%20stem%20cells[10] Zou Z, Zhang Y, Hao L,et al. More insight into mesenchymal stem cells and their effects inside the body. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2010;10(2):215-230.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=More%20insight%20into%20mesenchymal%20stem%20cells%20and%20their%20effects%20inside%20the%20body[11] Chen C,Li B,Guo JW. Jiefangjun Yixue Zazhi. 2010;35(8):946-949.陈朝,黎奔,郭建文.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的分离培养及CM-Dil标记的脑内示踪[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2010,35(8):946-949.http://so.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/ViewHTML/PeriodicalPaper_jfjyxzz201008012.aspx[12] Xu HF,He HY,Tang XX. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012;16(6):958-962.许慧芬,何惠宇,唐小雪. 物理联合化学或化学方法处理去抗原异种松质骨支架与骨髓间充质干细胞的细胞相容性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(6):958-962.http://so.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/ViewHTML/PeriodicalPaper_xdkf201206002.aspx[13] Wang SY,Wu D,Zhang L,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012;16(3):443-448.王少云,吴迪,张丽,等. 骨髓间充质干细胞复合小肠黏膜下层构建组织工程皮肤修复糖尿病皮肤缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(3):443-448.http://so.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/ViewHTML/PeriodicalPaper_xdkf201203014.aspx[14] Liu TY,Xiong F,Lin J,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012;16(1):70-75.柳太云,熊符,林军,等. 人骨髓间充质干细胞移植促进脑梗死大鼠神经细胞再生和神经功能恢复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(1):70-75.http://so.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/ViewHTML/PeriodicalPaper_xdkf201201015.aspx[15] Zhou G,Fu XB,Chen W,et al. Chuangshang Waike Zazhi. 2006;8(1):65-68.周岗,付小兵,陈伟,等. 胎儿皮肤EGF、EGFR基因表达特征及与汗腺形成的关系研究[J]. 创伤外科杂志, 2006,8(1):65-68.http://so.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/ViewHTML/PeriodicalPaper_cswkzz200601023.aspx[16] Zhou G,Wen B,Fu XB. Ganran Yanzheng Xiufu. 2005;6(3):170-172.周岗,温博,付小兵. 汗腺发育及其调控研究进展[J]. 感染、炎症、修复,2005,6(3):170-172.http://so.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/ViewHTML/PeriodicalPaper_gryzxf200503012.aspx[17]Zong SK,Liang ZQ,Ou BJ. Zhongguo Xiufu Chongjian Waike Zazhi. 2010;24(2):150-155.宗守凯,梁自乾,欧邦军. 局部应用重组人EGF对糖尿病大鼠烫伤创面EGF受体及其mRNA表达的影响[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2010,24(2):150-155.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=1&CurRec=1&recid=&filename=ZXCW201002007&dbname=CJFD2010&dbcode=CJFQ&pr=&urlid=&yx=[18] Saga K. Structure and function of human sweat glands studied with histochemistry and cytochemistry. Prog Histochem Cytochem. 2002;37(4):323-386.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Porg%20Histoehem%20Cytoehem.2006%3B37(4)%3A323[19] Ahmed B, Yazdanie N. Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (HED). J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2006;16(1):61-63.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Ahmed%20B%2C%20Yazdanie%20N.%20Hypohidrotic%20ectodermal%20dysplasia%20(HED)[20] Wislet-Gendebien S, Hans G, Leprince P, et al. Plasticity of cultured mesenchymal stem cells: switch from nestin-positive to excitable neuron-like phenotype. Stem Cells. 2005;23(3):392-402.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Pye%20Stem%20Cells.2005%2C23(3)%3A392[21] Zhou LF,Wu JJ,Lei X,et al. Zhongguo Xiufu Chongjian Waike Zazhi. 2010;23(2): 891-895.周立奉,伍津津,雷霞,等. 三维培养汗腺腺上皮细胞形成汗腺样结构的初步研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2009,23(2):891-895.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=1&CurRec=1&recid=&filename=ZXCW200902009&dbname=CJFD2009&dbcode=CJFQ&pr=&urlid=&yx=[22] Sa YL,Hua YK,Gao JM,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012; 16(1):31-34.撒亚莲,华映坤,高建梅,等.人羊膜诱导人骨髓间充质干细胞向表皮样细胞的分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(1):31-34.http://so.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/ViewHTML/PeriodicalPaper_xdkf201201006.aspx[23] Ye XF,He YL,Wang XF,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(10) :1711-1714.叶小凤,何援利,王雪峰,等. 全骨髓法体外培养分离大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞及PKH26标记[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(10) :1711-1714.http://so.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/ViewHTML/PeriodicalPaper_xdkf201110001.aspx[24] De Francesco R, Migliaccio G. Challenges and successes in developing new therapies for hepatitis C. Nature. 2005;436(7053):953-960.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Challenges%20and%20successes%20in%20new%20developing%20therapies%20for%20hepatitis.[25] Deng CL,Yang SL,Zheng JH,et al. Zuzhi Gongcheng yu Chongjian Waike Zazhi. 2009;5(5):250-252.邓辰亮,杨松林,郑江红,等. 诱导表皮干细胞向汗腺上皮细胞分化的研究[J]. 组织工程与重建外科杂志, 2009,5(5):250-252.http://so.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/ViewHTML/PeriodicalPaper_zzgcycjwkzz200905003.aspx[26] Xu YA,Huang S,Fu XB,et al. Jiefangjun Yixue Zazhi. 2011;36(3):211-214.许永安,黄沙,付小兵,等. 特定微环境诱导人脐带沃顿胶间充质干细胞向汗腺样细胞分化的实验研究[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2011,36(3):211-214.http://so.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/ViewHTML/PeriodicalPaper_jfjyxzz201103003.aspx[27] Cai S,Fu XB,Lei YH,et al. Disan Junyi Daxue Xuebao. 2008;30(21) :1998-2002.蔡飒,付小兵,雷永红,等. 在体诱导表皮细胞去分化的初步实验研究[J]. 第三军医大学学报, 2008,30(21) :1998-2002.http://so.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/ViewHTML/PeriodicalPaper_dsjydxxb200821008.aspx[28] Bi WW,Guo W,Zhao CM,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2007;11(28):5519-5522.毕薇薇,郭巍,赵春明,等. 成人骨髓间充质干细胞的体外培养及生物学特性[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007,11(28):5519-5522.http://so.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/ViewHTML/PeriodicalPaper_xdkf200728018.aspx[29] Jin PH,Zhang RH. Zuzhi Gongcheng yu Chongjian Waike Zazhi. 2006;2(6):354-356.晋培红,张如鸿. 皮肤缺损创伤动物模型的制备[J]. 组织工程与重建外科杂志, 2006,2(6):354-356.http://so.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/ViewHTML/PeriodicalPaper_zzgcycjwkzz200606018.aspx[30] Qiu RS,Yang B. Zuzhi Gongcheng yu Chongjian Waike Zazhi. 2006;2(5): 294-296.丘日升,杨斌. 皮肤创伤修复中Wnt信号途径对皮肤干细胞增殖分化的调控机制[J]. 组织工程与重建外科杂志, 2006,2(5): 294-296.http://so.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/ViewHTML/PeriodicalPaper_zzgcycjwkzz200605019.aspx[31] Deng CL,Yang GH,Cao YL. Zuzhi Gongcheng yu Chongjian Waike Zazhi. 2006;2(3) :174-176.邓辰亮,杨光辉,曹谊林. 生长因子促皮肤创面愈合的研究进展[J]. 组织工程与重建外科杂志, 2006,2(3) :174-176.http://so.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/ViewHTML/PeriodicalPaper_zzgcycjwkzz200603017.aspx[32] Xu YA,Fu XB. Zhongguo Xiufu Chongjian Waike Zazhi. 2010;24(2):161-164.许永安,付小兵. 毛囊干细胞增殖与分化相关信号通路研究进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2010,24(2):161-164.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=4&CurRec=1&recid=&filename=ZXCW201002009&dbname=CJFD2010&dbcode=CJFQ&pr=&urlid=&yx=[33] Li HH,Fu XB,Ouyang YS,et al. Zhonghua Chuangshang Zazhi. 2006;22(2):81-86.李海红,付小兵,欧阳云淑,等. 人骨髓间充质干细胞表型转化为汗腺细胞的体外研究[J]. 中华创伤杂志, 2006,22(2):81-86.http://so.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/ViewHTML/PeriodicalPaper_zhcs200602001.aspx[34] Chen XY,He L,Liu L,et al. Zhongguo Pifu Xingbingxue Zazhi. 陈欣玥,何黎,刘玲,等. 毛囊混合细胞诱导毛囊重建的研究[J]. 中国皮肤性病学杂志, 2011,25(1):15-17.http://so.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/ViewHTML/PeriodicalPaper_zgpfxbxzz201101005.aspx[35] Nakai H, Fuess S, Storm TA,et al.Unrestricted hepatocyte transduction with adeno-associated virus serotype 8 vectors in mice. J Virol. 2005;79(1):214-224.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Unrestricted%20hepatocyte%20transduction%20with%20adeno-associated%20virus%20serotype%208%20vector%20in%20mice[36] Zhou G,Xie XH,Fu XB,et al. Zhonghua Shiyan Waike Zazhi. 2007;24(10):1186-1188.周岗,谢晓华,付小兵,等. 汗腺细胞与骨髓间充质干细胞共培养过程中基因表达变化及意义[J]. 中华实验外科杂志, 2007,24(10):1186-1188.http://so.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/ViewHTML/PeriodicalPaper_zhsywk200710011.aspx[37] Wang Z, Zhu T, Qiao C,et al. Adeno-associated virus serotype 8 efficiently delivers genes to muscle and heart. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23(3):321-328.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Adeno-associated%20virus%20serotype%208%20efficiently%20delivers%20genes%20to%20muscle%20and%20heart.[38] Li MR,Han WD,Fu XB. Yixue Yanjiu Zazhi. 2011;40(7):148-150.李美蓉,韩为东,付小兵. 获得组织再生需要细胞类型的多种途径[J]. 医学研究杂志, 2011,40(7):148-150. http://so.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/ViewHTML/PeriodicalPaper_yxyjtx201107045.aspx[39] Lungwitz U, Breunig M, Blunk T,et al. Polyethylenimine-based non-viral gene delivery systems. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2005;60(2):247-266.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15939236 |

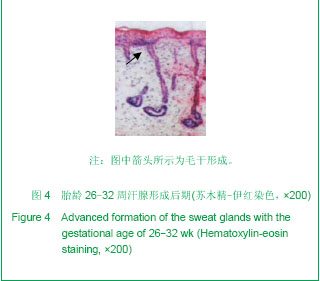

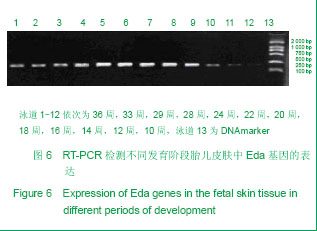
.jpg)