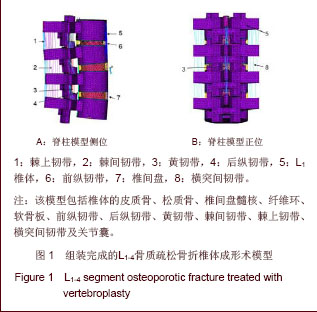
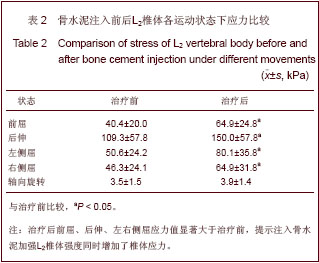
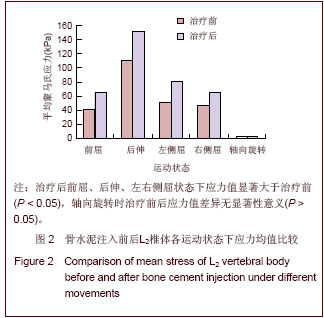
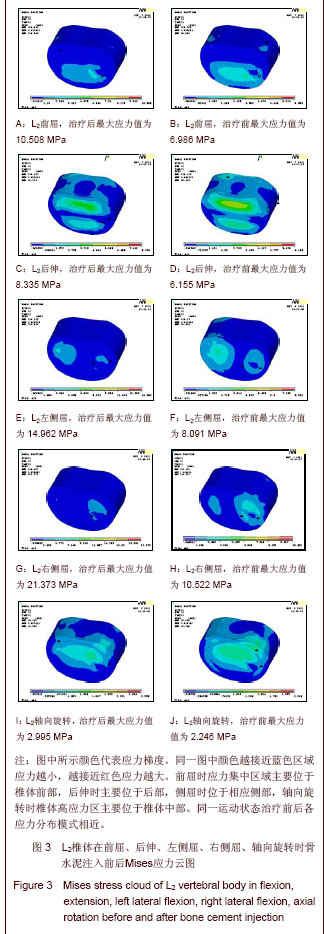
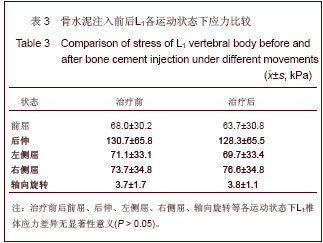
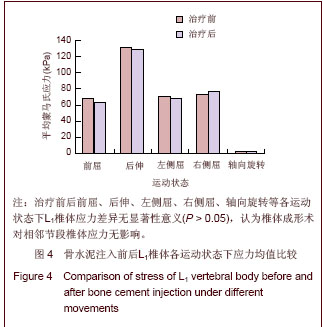
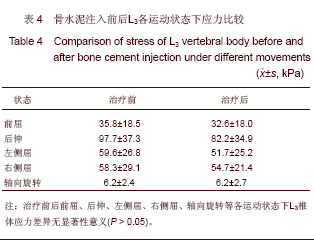
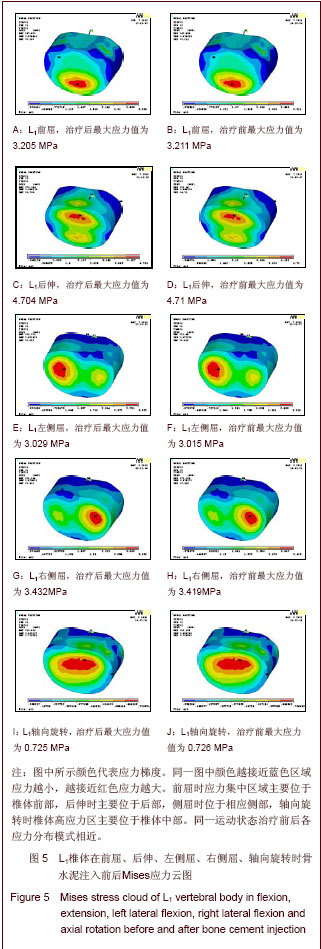
| [1] Tseng YY, Su CH, Lui TN, et al. Prospective comparison of the therapeutic effect of teriparatide with that of combined vertebroplasty with antiresorptive agents for the treatment of new-onset adjacent vertebral compression fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty. Osteoporos Int. 2012;23(5): 1613-1622.[2] Mazzantini M, Carpeggiani P, d'Ascanio A, Bombardieri S, Di Munno O: Long-term prospective study of osteoporotic patients treated with percutaneous vertebroplasty after fragility fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2011;22(5):1599-1607.[3] Hirakawa M, Kobayashi N, Ishiyama M, et al. Radiological findings as favorable predictors of pain relief in patients with osteoporotic compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty: a retrospective study of 156 cases. Jpn J Radiol. 2012;30(5):407-414.[4] Nagad P, Rawall S, Kundnani V, et al. Postvertebroplasty instability. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;16(4):387-393.[5] Trout AT, Kallmes DF. Does vertebroplasty cause incident vertebral fractures? A review of available data. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006;27(7):1397-1403.[6] Bliemel C, Oberkircher L, Buecking B, et al. Higher incidence of new vertebral fractures following percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty--fact or fiction? Acta Orthopaedica Belgica. 2012;78(2):220-229.[7] Movrin I. Adjacent level fracture after osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a nonrandomized prospective study comparing balloon kyphoplasty with conservative therapy. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2012;124(9-10):304-311.[8] Rho YJ, Choe WJ, Chun YI. Risk factors predicting the new symptomatic vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(5):905-911.[9] Li YA, Lin CL, Chang MC, et al. Subsequent vertebral fracture after vertebroplasty: incidence and analysis of risk factors. Spine. 2012;37(3):179-183.[10] Lee KA, Hong SJ, Lee S, et al. Analysis of adjacent fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty: does intradiscal cement leakage really increase the risk of adjacent vertebral fracture? Skeletal radiolo. 2011;40(12):1537-1542.[11] Chen LH, Hsieh MK, Liao JC, et al. Repeated percutaneous vertebroplasty for refracture of cemented vertebrae. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(7):927-933.[12] Fei Q, Wang BQ, Yang Y, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(26):4757-4762.费琦,王炳强,杨雍,等.计算机模拟椎体成形对邻近节段力学影响的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(26):4757-4762.[13] Long QL, Mi SJ, Li HY. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(22):4277-4280.隆全利,宓士军,李海云.应用有限元分析单侧与双侧入路椎体成形后的生物力学变化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13(22):4277-4280.[14] Yoo CM, Park KB, Hwang SH, et al. The analysis of patterns and risk factors of newly developed vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2012; 52(4):339-345.[15] Fagan MJ, Julian S, Mohsen AM. Finite element analysis in spine research. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2002;216(5):281-298.[16] Boger A, Heini P, Windolf M, et al. Adjacent vertebral failure after vertebroplasty: a biomechanical study of low-modulus PMMA cement. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(12):2118-2125.[17] Hu Y, Xie H, Yang SH. Yiyong Shengwu Lixue. 2006;21(3): 246-250.胡勇,谢辉,杨述华.三维有限元分析在脊柱生物力学中应用研究[J].医用生物力学, 2006,21(3):246-250.[18] Han KS, Rohlmann A, Yang SJ, et al. Spinal muscles can create compressive follower loads in the lumbar spine in a neutral standing posture. Med Eng Phys. 2011;33(4):472-478.[19] Li ZY,Shen Y,Wang LF,et al. Zhongguo Jizhu Jisui Zazhi. 2009; 19(5):388-391.李志远,申勇,王林峰,等.椎体成形术治疗老年骨质疏松椎体压缩骨折对邻近节段生物力学的影响[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2009, 19(5):388-391.[20] Weisse B, Aiyangar AK, Affolter C, et al. Determination of the translational and rotational stiffnesses of an L4-L5 functional spinal unit using a specimen-specific finite element model. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2012;13:45-61.[21] Aquarius R, Homminga J, Verdonschot N, et al. The fracture risk of adjacent vertebrae is increased by the changed loading direction after a wedge fracture. Spine. 2011;36(6):E408-412.[22] Chiang CK, Wang YH, Yang CY, et al. Prophylactic vertebroplasty may reduce the risk of adjacent intact vertebra from fatigue injury: an ex vivo biomechanical study. Spine. 2009; 34(4):356-364.[23] Shi L, Lu S, Xu YQ. Xinan Junyi. 2007;9(4):9-10.石磊,陆声,徐永清.腰椎骨质疏松三维有限元模型的建立及应用[J].西南军医, 2007, 9(4):9-10.[24] Matsumoto T, Ohnishi I, Bessho M, et al. Prediction of vertebral strength under loading conditions occurring in activities of daily living using a computed tomography-based nonlinear finite element method. Spine. 2009;34(14): 1464-1469. |