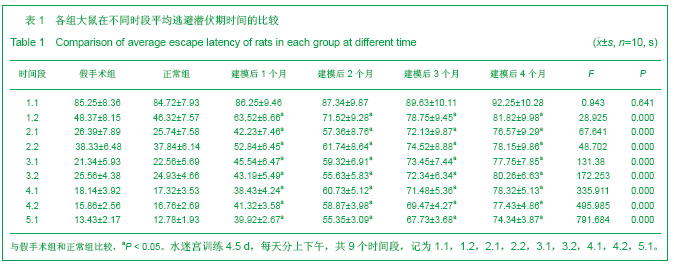
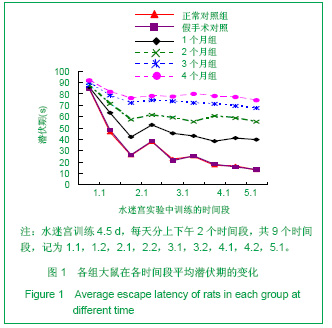
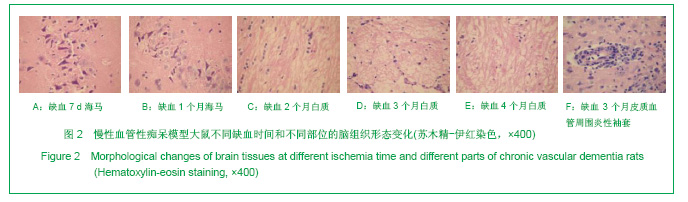
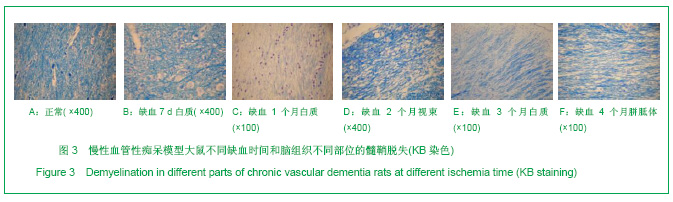
| [1] Xie HG, Cheng LQ, Wang LN, et al.Xiandai Kangfu. 2001; 5(1):58-60. 解恒革,程流泉,王鲁宁,等.Alzheimer病和血管性痴呆患者海马杏仁核体积的MRI对照研究[J].现代康复,2001,5(1):58-60.[2] 阿部晋卫,羽生春夫,新井久之,ほか.老年期痴呆の脑循环动态に关する研究[J].日本医学会志,1996,95:103 -111. [3] Otori T, Katsumata T,Muramatsu H,Long-term measurement of cerebral blood flow and metabolism in a rat chronic hypoperfusion model.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.2003;30(4):266-272.[4] Wakita H,Tomimoto H,Akiguchi I,Axonal damage and demyelination in the white matter after chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in the rat.Brain Res..2002;924(1):63-70.[5] Ransohoff RM,Perry VH.Microglial physiology:unique stimuli,specialized responses.Annu Rev Immunol.2009;27:1l19-145.[6] Barker A J,Ullian E M.Astrocytes and synaptic plasticity. Neuroscientist.2010;16(1):40-50.[7] Halassa MM,Haydon PG.Integrated brain circuits:astrocytic networks neuronal activity and behavior.Annu Rev Physiol. 2010;172:335-355. [8] Kerever A,Schnack J,Vellinga D,et al.Novel Extracellular Matrix Structures in the Neural Stem Cell Niche Capture the Neurogenic Factor Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 from the Extracellular Milieu.Stem Cells.2007;25(9):2146-2157. [9] Muhammad S, Barakat W,Stoyanov S,et al.The HMGB1 receptor RAGE mediates ischemic brain damage.J Neurosci. 2008;28:12023-12031.[10] Qiu J,Nishimura M,Wang Y,et al.Early release of HMGB-1 from neurons after the onset of brain ischemia.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.2008;28:927-938.[11] Wieraszkoa R,Ahmeda Z.Axonal release of glutamate analog,d-2,3-3H-Aspartic acid and l-14C-proline from segments of sciatic nerve following electrical and magnetie stimulation. Neurescience Letters.2009;458:19-22. [12] Wu C Y,Kaur C,Sivakumar V,et a1.Kv1.1 expression in microglia regulates production and release of proinflammatory cytokines,endothelins and nitric oxide. Neuroscience.2009;158(4):1500-1508.[13] Skaper SD.The brain as a target for inflammatory processes and neuroprotective strategies.Ann N Y Acad Sci.2007; 112(2): 23-34. [14] Kim EJ,Kown KJ,Park JY,et al.Effects of peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor agonists on LPS-induced neuronal death in mixed cortical neurons:associated with iNOS and COX-2.Brain Res.2002;941(1-2):1-10.[15] Liu K,Mori S,Takahashi HK,et al. Anti-high mobility group box 1 monoclonal antibody ameliorate brain infarction induced by transient ischemia in rats.FASEB J.2007;21:3904-3916. [16] Nicholas RS,Wing MG.Compston A. Nonactivated microglia promote oligodendrocyte precursor survival and maturation through the transcription factor NF-κB.Eur J Netrosci.2001; 13:959-967. [17] Elisabetta P,Barbara M.Microglia and neuroprotection:From in vitro studies to therapeutic applications.Progress in Neurobiology. 2010;92(3):293-315. [18] Ma L,Jia J,Chen SY,et al.Zhonghua Shenjing Yixue Zazhi. 2010:4(9):325-29. 马磊,贾济,陈绍洋,等.大麻素CB2受体参与电针预处理诱导的延迟相脑保护作用[J].中华神经医学杂志,2010:4(9):325-29. [19] Asya R,Ravid S,Michal S.The bright side of the glial scar in CNS repair.Nature Review Neuroscience.2009;10:235-241.[20] Ito U,Nagasao J,Kawakami E.Fate of disseminated dead neurons in the cortical ischemic penumbra:ultrastructure indicating a novel scavenger mechanism of microglia and astrocytes.Stroke.2007;38:2577-2583.[21] Eulenburg V,Gomeza J. Neurotransmitter transporters expressed in glial ce11s as regulators of synapse function. Brain Res Rev.2010;63(1-2):103-1012.[22] Yoshikawa T,Akiyoshi Y,Susumu T,et al.Ginsenoside Rbl Reduces Neurodegeneration in the Peri-infarct Area of a Thromboembolic Stroke Model in Non-human Primates.J Pharmacol Sci.2008;107(1):32-40. [23] Li J J,Wu L H,Cao Q,et al.Endothelins-1/3 and endothelin-A/B receptors expressing glial cells with special reference to activated microglia in experimentally induced cerebral ischemia in the adult rats.Neuroscience. 2010;167(3): 665-677.[24] Gasche Y,Soccal PM ,Kanemitsu M ,et al.M atrix metalloproteinases and diseases of the central nervous system with a special emphasis on ischemic brain.Front Biosci.2006;11:1289.[25] Ramos-Fernandez M,Bellolio MF, Stead LG,et al.Matrix metalloproteinase-9 as a marker for acute ischemic stroke:a systematic review.J Stroke Cerebrovaso Dis.2011;20(1): 47-54.[26] Gidday JM,Gasche YG,Copin JC,et al.Leukocyte-derived matrix metal1oproteinase-9 mediates blood-brain barrier breakdown and is proinflammatory after transient focal cerebral ischemia.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.2005;289: H558-H568.[27] Gu Z,Cui J,Brown S,et al.A highly specific inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-9 rescues laminin from proteolysis and neurons from apoptosis in transient focal cerebral ischemia.J Neurosci.2005;25 (27):6401-6408.[28] Rosell A, Alvarez-sabin J,Arenillas JF,et al.Matrix metalloproteinase protein array reveals a strong relation between MMP-9 and MMP-13 with diffusion-weighted in age lesion increase in human stroke.Stroke.2005;36:1415-1420.[29] Eldrup N, Gronholdt ML, Sillesen H,et al. Elevated matrix metalloproteinase-9 associated with stroke or cardiovascular death in patients with carotid stenosis.Circulation.2006;114: 1847-1854.[30] Rosell A,Cuadrado E,Ortega-Aznar A,et al MMP-9- positive neutrophil infiltration is associated to blood-brain barrier breakdown and basal lamina type IV collagen degradation during hemorrhagic transformation after human ischemic stroke. Stroke.2008;39(4):1121-1126.[31] Cuadrado E,Ortega L, Hernandez-Guillamon M,et al.Tissue plasminogen activator(t-PA)promotes neutrophil degranulation and MMP-9 release.J Leukoc Biol.2008;84(1): 207-214.[32] Kong XM,Yan HM,Wang YL,et al.Zhongguo Xueye Liubianxue Zazhi. 2010;20(2):209-211. 孔小明,阎红梅,王玉林,等.急性脑出血患者中基质金属蛋白酶-9的临床意义[J].中国血液流变学杂志,2010,20(2):209-211. [33] Lucivero V,Prontera DM,Mezzapesa M,et a1.Different roles of matrix metalloproteinases-2 and-9 after human iscbaemic stroke.Neurol Sci.2007;28(4):165-170.[34] Lee JK, Kwak HJ, Piao MS,et al.Quercetin reduces the elevated matrix metalloproteinases-9 level and improves functional outcome after cerebral focal ischemia in rats. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2011;153(6):1321-1329. |
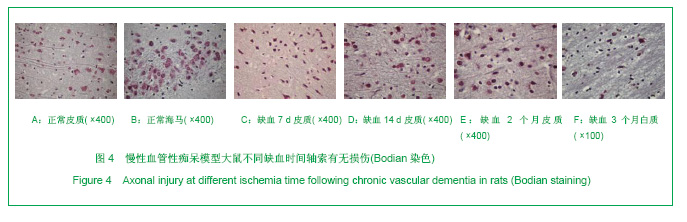
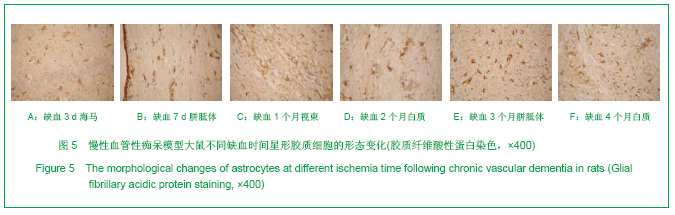
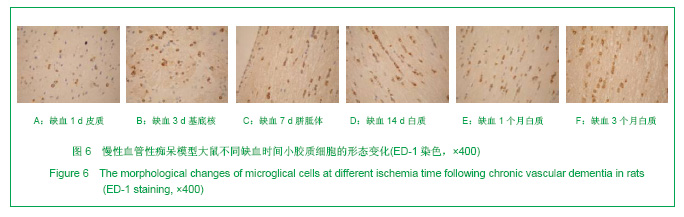
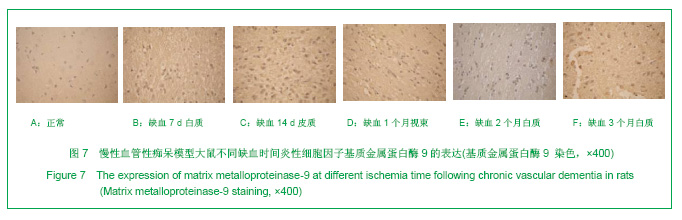
.jpg)