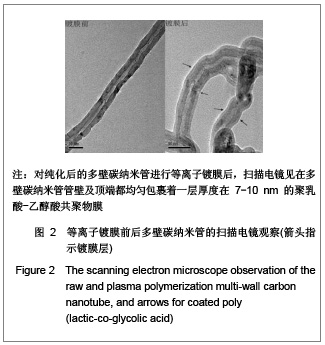
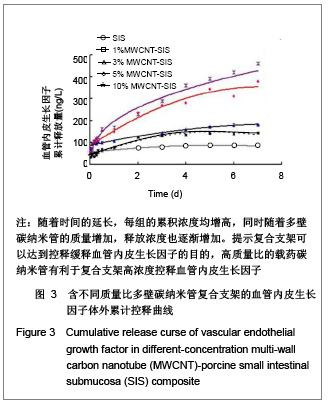
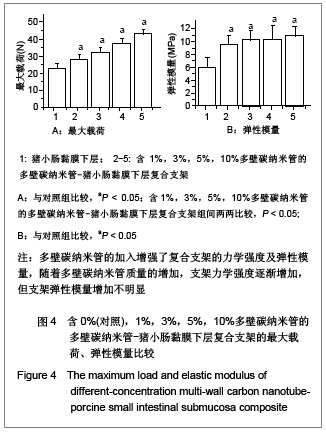
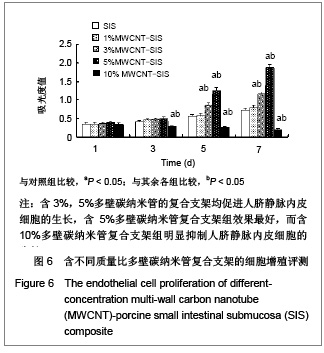
| [1] Böhm G,Steinau G,Krähling E,et al.Is biocompatibility affected by constant shear stress?--comparison of three commercially available meshes in a rabbit model.J Biomater Appl.2011; 25(7):721-741.[2] Liu Z,Tang R,Zhou Z,et al.Comparison of two porcine-derived materials for repairing abdominal wall defects in rats. PLoS One. 2011; 6(5): e20520.[3] Bellon JM,Rodriguez M,Garcia-Honduvilla N,et al.Comparing the behavior of different polypropylene meshes (heavy and lightweight) in an experimental model of ventral hernia repair.J Biomed Mater Res Part B Appl Biomater.2009; 89(2): 448-455.[4] Iannitti DA,Hope WW,Norton HJ,et al.Technique and outcomes of abdominal incisional hernia repair using a synthetic composite mesh: a report of 455 cases.J Am Coll Surg.2008;206(1):83-88.[5] Hashizume R,Fujimoto KL,Hong Y,et al.Morphological and mechanical characteristics of the reconstructed rat abdominal wall following use of a wet electrospun biodegradable polyurethane elastomer scaffold. Biomaterials.2010;31(12): 3253-3265.[6] Franklin ME Jr,Gonzalez JJ Jr,Michaelson RP,et al.Preliminary experience with new bioactive prosthetic material for repair of hernias in infected fields.Hernia.2002; 6(4):171-174.[7] Franklin ME Jr,Gonzalez JJ Jr,Glass JL.Use of porcine small intestinal submucosa as a prosthetic device for laparoscopic repair of hernias in contaminated ?elds:2-year follow-up. Hernia. 2004;8(3):186-189.[8] Lai JY,Chang PY,Lin JN.Body wall repair using small intestinal submucosa seeded with cells.J Pediatr Surg.2003;38(12): 1752-1755.[9] Junge K,Klinge U,Klosterhalfen B,et al. Influence of mesh materials on collagen deposition in a rat model. J Invest Surg. 2002;15(6):319-328.[10] Xu Y,Wang J,Hu JP,et al.Zhongguo Keji Lunwen Zaixian. 2010; 5(6):423-426. 许永,王静,胡金平,等. 多壁碳纳米管的纯化及表面修饰[J].中国科技论文在线,2010,5(6):423-426.[11] Penttinen R,Grönroos JM.Mesh repair of common abdominal hernias: a review on experimental and clinical studies. Hernia. 2008;12(4):337-344.[12] Dufrane D,Mourad M,van Steenberghe M,et al.Regeneration of abdominal wall musculofascial defects by a human acellular collagen matrix. Biomaterials.2008;29(14): 2237-2248.[13] Luo JC,Yang ZM.Zhongguo Xiufu Chongjian Waike Zazhi. 2003;17(5):425-428. 罗静聪,杨志明.小肠黏膜下层的制备及其特性的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2003,17(5):425-428.[14] Zhang D,Kandadai MA,Cech J,et al.Poly(L-lactide) (PLLA)/multiwalled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) composite: characterization and biocompatibility evaluation. Phys Chem. 2006;110(26):12910-12915.[15] Wang HL,Zhou XG,Yu HJ,et al.Cailiao Daobao. 2008;22(z1): 146-149. 王洪磊,周新贵,于海蛟,等. 碳纳米管增强复合材料的研究进展[J].材料导报,2008,22(z1):146-149.[16] Wang SF,Shen L,Zhang WD,et al. Preparation and mechanical properties of chitosan/carbon nanotubes composites.Biomacromolecules.2005; 6(6):3067-3072. |