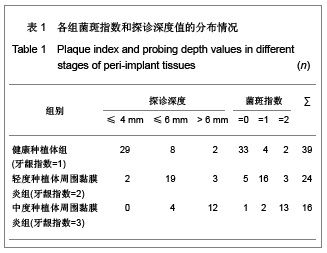
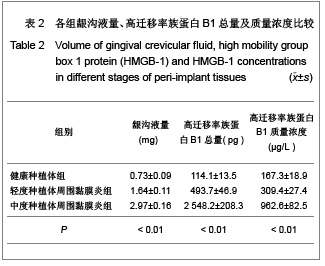
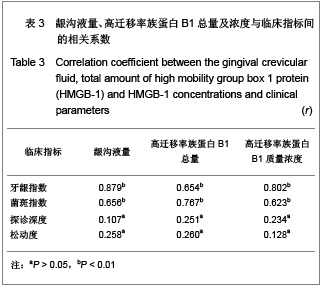
| [1] Wang H,Bloom O,Zhang M,et al. HMG-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice. Science.1999;285(5425):248-251.[2] Buhimschi CS,Baumbusch MA,Dulay AT,et al. Characterization of RAGE, HMGB-1, and S100beta in inflammation-induced preterm birth and fetal tissue injury. Am J pathol.2009;175(3):958-975.[3] Lamkanfi M,Sarkar A,Vande Walle L,et al. Inflammasome-dependent release of the alarmin HMGB1 in endotoxemia. J Immunol.2010;185(7):4385-4392.[4] Sundberg E,Fasth AE,Palmblad K,et al.High mobility group box chromosomal protein 1 acts as a proliferation signal for activated T lymphocytes. Immunobiology.2009;214(4): 303-309.[5] Muñoz-Planillo R,Franchi L,Miller LS,et al.A critical role for hemolysins and bacterial lipoproteins in Staphylococcus aureus-induced activation of the Nlrp3 inflammasome.J Immunol. 2009;183(6):3942-3948.[6] Willingham SB,Allen IC,Bergstralh DT,et al.NLRP3 (NALP3, Cryopyrin) facilitates in vivo caspase-1 activation, necrosis, and HMGB1 release via inflammasome-dependent and independent pathways. J Immunol.2009;183(3):2008-2015.[7] Lamkanfi M,Dixit VM.Manipulation of host cell death pathways during microbial infections.Cell Host Microbe.2010; 8(1):44-54.[8] Kang R,Tang D,Schapiro NE,et al.The receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) sustains autophagy and limits apoptosis, promoting pancreatic tumor cell survival. Cell Death Differ.2010;17(4):666-676.[9] Goldstein RS,Gallowitsch-Puerta M,Yang L,et al. Elevated high-mobility group box 1 level in patients with cerebral and myocardial ischemia. Shock.2010;25(6):571-574.[10] Abdulahad DA,Westra J,Bijzet J,et al.High mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) and anti-HMGB1 antibodies and their relation to disease characteristics in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(3): 71-79.[11] Henes FO,Chen Y,Bley TA,et al. Correlation of serum level of high mobility group box 1 with the burden of granulomatous inflammation in granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener's). Ann Rheum Dis.2009;70(11):1926-1929.[12] Evasic R,Block C.Fixture modification and osseous regeneration of the “ailing/failing” implant. J Oral Impant.1999; 25(2):135-137.[13] Fonseca RJ. Reconstructive preprosthetic oral and maxillofacial surgery. 2nd ed, Philadelphia: WB Saunders Company, 1997:192-199.[14] Yucekal-Tuncer B,Uygur C,Firatli E. Gingival crevicular fluid levels of aspartate amino transferase, sulfide ions and N-benzoyl-DL-arginine-2-naphthylamide in diabetic patients with chronic periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol.2003;30(12): 1053-1060.[15] Ebadian B,Razavi M,Soleimanpour S,et al. Evaluation of tissue reaction to some denture-base materials: An animal study. J Contemp Dent Pract.2008; 9(4):67-74. [16] Anderson U,Wang H,Palmblad K, et al. High mobility group 1 protein (HMG-1) stimulates proinflammatory cytokine synthesis in human monocytes. J Exp Med.2000;192(4): 565-570.[17] DeMarco RA,Fink MP,Lotze MT.Monocytes promote natural killer cell interferon gamma production in response to the endogenous danger signal HMGB1. Mol Immunol. 2005;42(4): 433-444.[18] Beijnum JR,Petersen K,Grifficen AW.Tumor endothelium is characterized by a matrix remodeling signature. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2009;1:216-225.[19] Luttedoh EC,Opsl SM,Pittman DD,et al. Inhibition of the RAGE products increases survival in experimental models of severe sepsis and systemic infection. Crit Care.2007;11(6): 122-126.[20] Park JS,Svetkauskaite D,He Q,et al. Involvement of Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in cellular activation by high mobility group box 1 protein. J Bid Chem.2004;279(9):7370-7377. [21] Palumbo R,Sampeolesi M,Marehis DF,et al. Extracellular HMGB-1 a signal of tissue damage, induces mesoangioblast migration and proliferation. J Cell Biol. 2004;164(3):441-449.[22] Morimoto Y,Kawahara KI,Tancharoen S,et al.Tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulates gingival epithelial cells to release high mobility-group box 1. J Periodontal Res.2008;43:76-83. [23] Luo L,Xie P, Gong P, et al.Expression of HMGB1 and HMGN2 in gingival tissues, GCF and PICF of periodontitis patients and peri-implantitis.Arch Oral Biol.2011;56(10):1106-1111. |