中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (2): 275-279.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.02.016
• 皮肤粘膜组织构建 skin and mucosal tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
丹酚酸B对小鼠皮肤光老化的保护效应
周湘君1,叶才果2,杨广丽3,刘林生4
- 1广东医学院药理教研室,广东省东莞市 523808
2广东医学院肿瘤研究所,广东省东莞市 523808
3广东食品药品技术学院药物制剂技术系,广东省广州市 510000
4佛山市中医院药剂科,广东省佛山市 528000
Protective action of salvianolic acid B on skin photoaging in mice
Zhou Xiang-jun1, Ye Cai-guo2, Yang Guang-li3, Liu Lin-sheng4
- 1 Department of Pharmacology, Guangdong Medical University, Dongguan 523808, Guangdong Province, China
2 Institute of Tumor, Guangdong Medical University, Dongguan 523808, Guangdong Province, China
3 Department of Pharmaceutical Preparations, Guangdong Food and Drug Vocational College, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China
4 Department of Pharmacy, Foshan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Foshan 528000, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
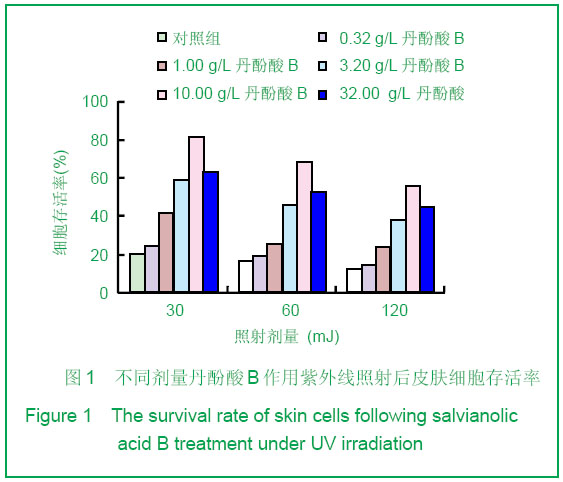
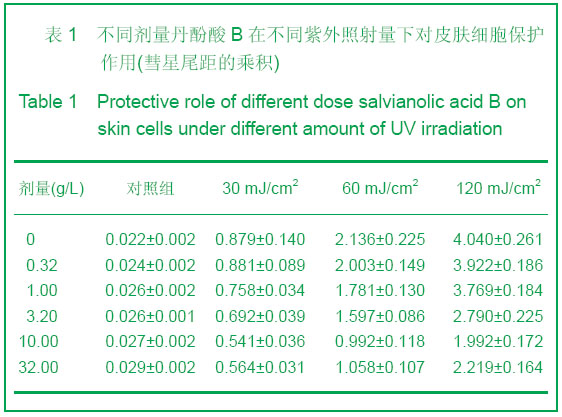
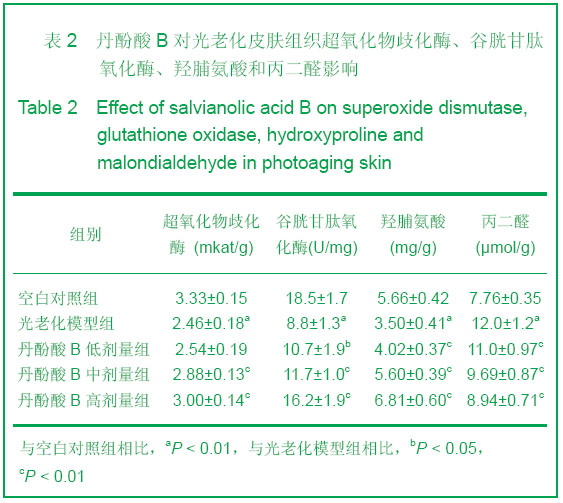
背景:中药及其提取物在改善皮肤组织结构、提高抗氧化酶活性、抑制基质金属蛋白酶高表达、增强皮肤免疫防御功能等多方面对皮肤光老化起着防治作用。 目的:验证丹酚酸B对皮肤光老化的保护作用。 方法:同时建立小鼠皮肤体外细胞培养紫外线损伤模型及小鼠紫外照射致皮肤衰老模型,给予不同剂量的丹酚酸B,通过MTT法, 单细胞凝胶电泳等观察各组皮肤细胞损伤程度以及丹酚酸B对细胞损伤的保护作用,小鼠灌胃口服不同剂量丹酚酸B,通过对皮肤组织羟脯氨酸、超氧化物歧化酶等含量的检测,评价丹酚酸B是否具有抑制皮肤光老化的作用。 结果与结论:紫外照射可使皮肤丙二醛含量明显上升,羟脯氨酸含量,超氧化物歧化酶和谷胱甘肽氧化酶活性下降。丹酚酸B能有效地对紫外线引起细胞致死性损伤起到保护作用,能显著降低皮肤组织丙二醛含量,提高羟脯氨酸含量,超氧化物歧化酶和谷胱甘肽氧化酶活性而起到抑制皮肤光老化作用。结果证实丹酚酸B具有保护皮肤光老化作用。
中图分类号: