| [1]Russell KA, Chow NH, Dukoff D, et al. Characterization and Immunomodulatory Effects of Canine Adipose Tissue- and Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. PLoS One. 2016;11(12):e0167442.[2]Gnecchi M, Zhang Z, Ni A, et al. Paracrine mechanisms in adult stem cell signaling and therapy. Circ Res. 2008;103(11): 1204-1219.[3]Huang S, Wu Y, Gao D, et al. Paracrine action of mesenchymal stromal cells delivered by microspheres contributes to cutaneous wound healing and prevents scar formation in mice. Cytotherapy. 2015;17(7):922-931.[4]Zhang S, Chu WC, Lai RC, et al. Exosomes derived from human embryonic mesenchymal stem cells promote osteochondral regeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(12):2135-2140.[5]Lai RC, Arslan F, Lee MM, et al. Exosome secreted by MSC reduces myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 2010;4(3):214-222.[6]Nagaishi K, Mizue Y, Chikenji T, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy ameliorates diabetic nephropathy via the paracrine effect of renal trophic factors including exosomes. Sci Rep. 2016;6: 34842.[7]Shabbir A, Cox A, Rodriguez-Menocal L, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosomes Induce Proliferation and Migration of Normal and Chronic Wound Fibroblasts, and Enhance Angiogenesis In Vitro. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(14):1635-1647.[8]Li T, Yan Y, Wang B, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate liver fibrosis. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(6):845-854.[9]Wang QQ, Jing XM, Bi YZ, et al. Human Umbilical Cord Wharton's Jelly Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells May Attenuate Sarcopenia in Aged Mice Induced by Hindlimb Suspension. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:9272-9281.[10]Merryweather-Clarke AT, Cook D, Lara BJ, et al. Does osteogenic potential of clonal human bone marrow mesenchymal stem/stromal cells correlate with their vascular supportive ability. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):351.[11]Ogando CR, Barabino GA, Yang YK. Adipogenic and Osteogenic Differentiation of In Vitro Aged Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2018 Nov 28. doi: 10.1007/7651_2018_197. [Epub ahead of print][12]张贝莹,罗冬章,麦海涛,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植修复皮肤创伤[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(29): 4611-4616.[13]Zhang B, Wang M, Gong A, et al. HucMSC-Exosome Mediated-Wnt4 Signaling Is Required for Cutaneous Wound Healing. Stem Cells. 2015;33(7):2158-2168.[14]Baum CL, Arpey CJ. Normal cutaneous wound healing: clinical correlation with cellular and molecular events. Dermatol Surg. 2005;31(6):674-686[15]詹小舒,罗冬章,王丙云,等. 犬脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体修复皮肤创伤[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(25): 4021-4027.[16]Chen TS, Arslan F, Yin Y, et al. Enabling a robust scalable manufacturing process for therapeutic exosomes through oncogenic immortalization of human ESC-derived MSCs. J Transl Med. 2011;9:47.[17]Patel DB, Gray KM, Santharam Y, et al. Impact of cell culture parameters on production and vascularization bioactivity of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Bioeng Transl Med. 2017;2(2):170-179.[18]Cai ZY, Xiao M, Quazi SH, et al.Exosomes: a novel therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease?Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(5): 930-935.[19]Vrijsen KR, Maring JA, Chamuleau SA, et al. Exosomes from Cardiomyocyte Progenitor Cells and Mesenchymal Stem Cells Stimulate Angiogenesis Via EMMPRIN. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(19):2555-2565.[20]柳鑫,肖燕,江川,等.牙髓干细胞来源外泌体诱导内皮细胞血管生成能力的研究[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志, 2018,28(4): 187-196.[21]郑爱甜,吴标良.自噬与血管再生关系的研究进展[J].右江医学, 2017, 45(3):361-364.[22]Timmers L, Lim SK, Arslan F, et al. Reduction of myocardial infarct size by human mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium. Stem Cell Res. 2007;1(2):129-137.[23]Martinez MC, Andriantsitohaina R. Microparticles in angiogenesis: therapeutic potential. Circ Res. 2011;109(1):110-119.[24]Phinney DG, Pittenger MF. Concise Review: MSC-Derived Exosomes for Cell-Free Therapy. Stem Cells. 2017;35(4): 851-858.[25]Fang S, Xu C, Zhang Y, et al. Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal MicroRNAs Suppress Myofibroblast Differentiation by Inhibiting the Transforming Growth Factor-β/SMAD2 Pathway During Wound Healing. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(10):1425-1439.[26]Wang W, Guo Z, Yang S, et al. Upregulation of miR-199 attenuates TNF-α-induced Human nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis by downregulating MAP3K5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;505(3):917-924.[27]Dai BH, Geng L, Wang Y, et al. microRNA-199a-5p protects hepatocytes from bile acid-induced sustained endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e604.[28]Shatseva T, Lee DY, Deng Z, et al. MicroRNA miR-199a-3p regulates cell proliferation and survival by targeting caveolin-2. J Cell Sci. 2011;124(Pt 16):2826-2836.[29]EL Andaloussi S, Mäger I, Breakefield XO, et al. Extracellular vesicles: biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013;12(5):347-357.[30]McNeill B, Ostojic A, Rayner KJ, et al. Collagen biomaterial stimulates the production of extracellular vesicles containing microRNA-21 and enhances the proangiogenic function of CD34+ cells. FASEB J. 2019;33(3):4166-4177.[31]Zhou Y, Zhu Y, Zhang L, et al. Human Stem Cells Overexpressing miR-21 Promote Angiogenesis in Critical Limb Ischemia by Targeting CHIP to Enhance HIF-1α Activity. Stem Cells. 2016; 34(4):924-934.[32]王婷婷,王桂香,张俊绘,等. miRNA let-7对疾病调控机制的研究进展[J].中国医药导报,2018,15(34): 53-56.[33]杜越,吕延杰. MicroRNA Let-7家族与心血管疾病的关系及其应用前景[J]. 药学进展,2017,41(7):504-508.[34]Aguirre A, Montserrat N, Zacchigna S, et al. In vivo activation of a conserved microRNA program induces mammalian heart regeneration. Cell Stem Cell. 2014;15(5):589-604.[35]Lin ST, Huang Y, Zhang L, et al. MicroRNA-23a promotes myelination in the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(43):17468-17473.[36]郑永法.放疗通过miR-23a/PTEN通路促进HUVEC增殖及迁移的机制研究[D].武汉:武汉大学, 2016. |
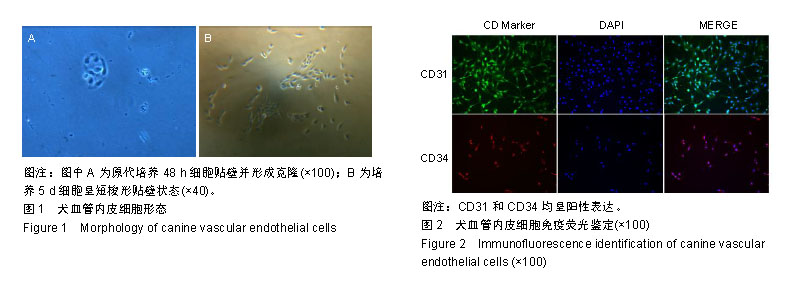
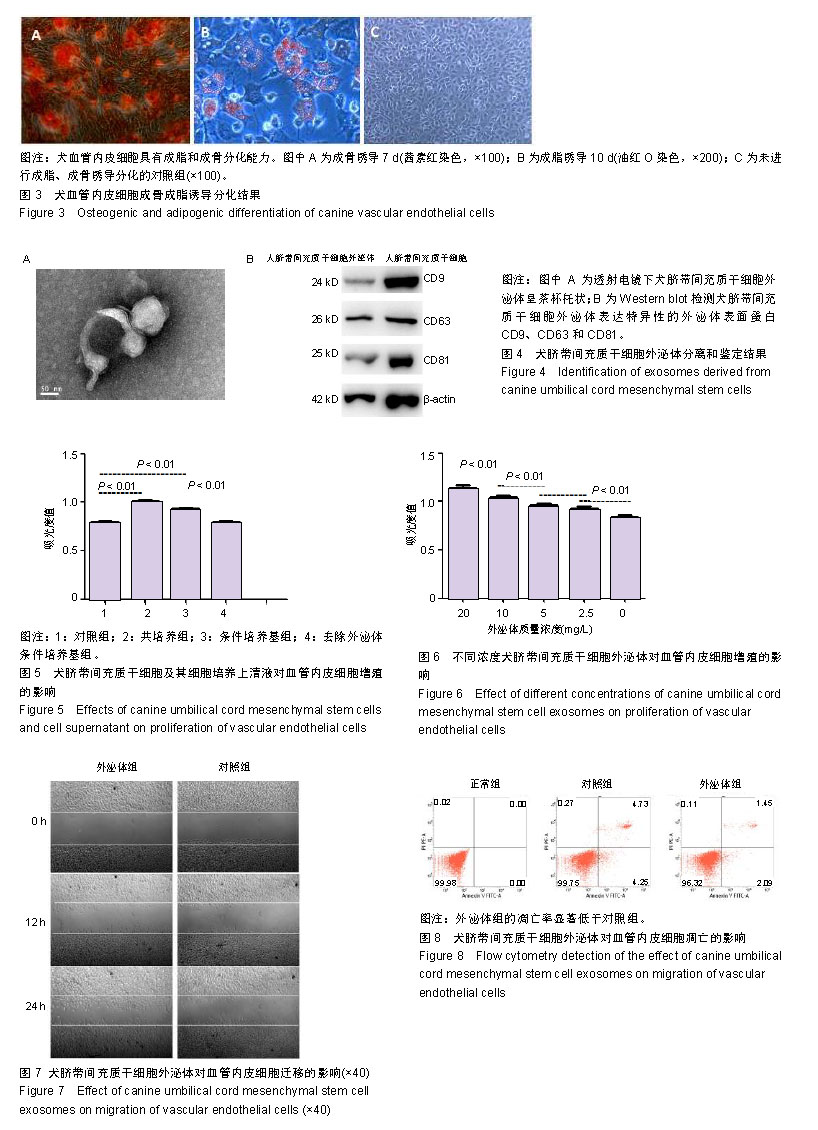
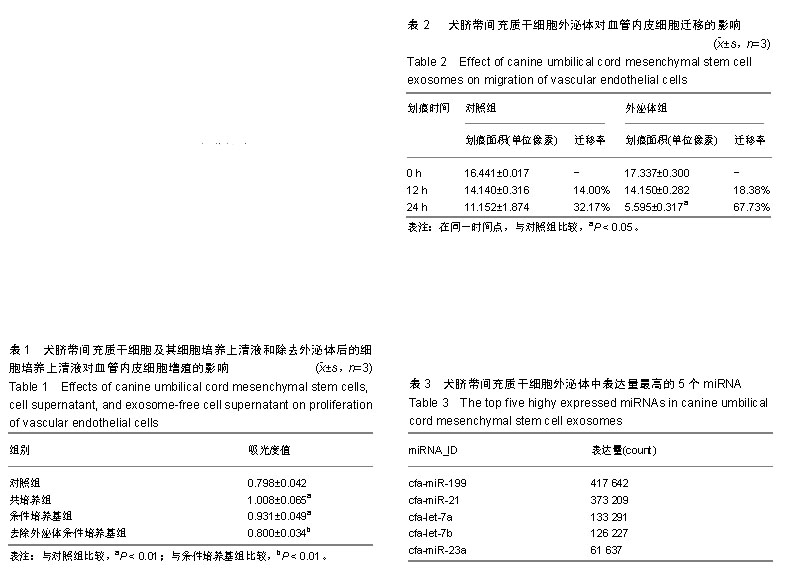
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)