中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (34): 5442-5446.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1406
• 组织工程口腔材料 tissue-engineered oral materials • 上一篇 下一篇
3D打印技术在颧骨颧弓骨折复位钛板固定中的应用
欧邦宾,李迎霞,刘庭庭
- 兴义市人民医院颌面外科,贵州省兴义市 562400
Application of 3D printing technology in reduction and fixation of zygomatic arch fracture
Ou Bangbin, Li Yingxia, Liu Tingting
- Department of Maxillofacial Surgery, Xingyi People's Hospital, Xingyi 562400, Guizhou Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
颧骨颧弓骨折复位:颧骨颧弓骨折易引起患者颌面形态破坏和咀嚼功能障碍,骨折复位固定已成为理想治疗方法,但因颧骨颧弓特殊的解剖结构及严格的颌面形态恢复要求,术者需准确定位骨折部位、移位程度及骨折线走行,方能实施精准复位,获得理想的手术效果。
3D打印术:作为计算机技术、三维重建影像学技术、虚拟模拟技术等核心技术相融合的产物,在骨折术中,其主要应用价值在于将虚拟的手术设计方案转化为现实手术的实施过程,为手术效果的提高提供一种由虚拟转化为现实的有效途径。
背景:在治疗颧骨颧弓骨折的过程中,因颧骨颧弓特殊的解剖结构及严格的颌面形态恢复要求,术者需准确定位骨折部位、移位程度及骨折线走行方能实施精准复位,获得理想的手术效果。
目的:研究3D打印技术在颧骨颧弓骨折复位固定中的应用价值。
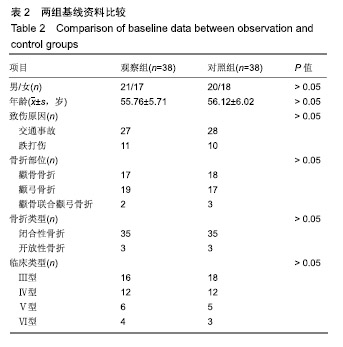
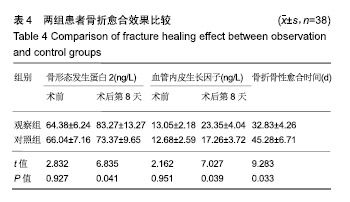
方法:纳入兴义市人民医院2017年1月至2018年6月收治的76例颧骨颧弓骨折患者,采用随机数字表法分为2组:对照组(n=38)行传统的切开复位钛板内固定治疗;观察组(n=38)术前制作3D骨折模型,在模型的基础上设计、实施切开复位钛板内固定治疗。评价2组骨折复位效果;记录并发症发生情况;术前及术后第8天采集空腹静脉血,检测血清骨形态发生蛋白2和血管内皮生长因子质量浓度;影像学判断骨性愈合时间。试验已获得兴义市人民医院伦理委员会批准。
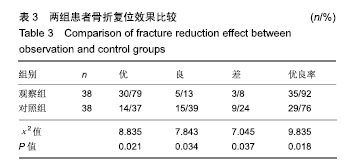
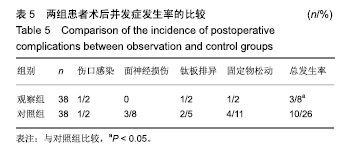
结果与结论:①观察组骨折复位优良率高于对照组(92%,76%,P < 0.05);②观察组骨性愈合时间短于对照组[(32.83±4.26),(45.28±6.71) d,P < 0.05];③术后第8天,两组骨形态发生蛋白2和血管内皮生长因子质量浓度均高于治疗前(P < 0.05),观察组骨形态发生蛋白2和血管内皮生长因子质量浓度高于对照组(P < 0.05);④观察组并发症发生率低于对照组(8%,26%,P < 0.05);⑤结果表明在颧骨颧弓骨折复位固定治疗中,应用3D打印技术能有效提高骨折复位效果与骨折愈合效果,降低手术相关并发症的发生率。
中图分类号:
R459.9

.jpg)
.jpg)