| [1]Peng F, Du Q, Peng C, et al. A Review: The Pharmacology of Isoliquiritigenin. Phytother Res. 2015; 29(7): 969-977.[2]Chen G, Zhu L, Liu Y, et al. Isoliquiritigenin, a flavonoid from licorice, plays a dual role in regulating gastrointestinal motility in vitro and in vivo. Phytother Res. 2009; 23(4): 498-506.[3]Wu TY, Khor TO, Saw CL, et al. Anti-inflammatory/Anti-oxidative stress activities and differential regulation of Nrf2-mediated genes by non-polar fractions of tea Chrysanthemum zawadskii and licorice Glycyrrhiza uralensis.AAPS J. 2011;13(1):1-13.[4]Jin XY, Sohn DH, Lee SH. Isoliquiritigenin suppresses tumor necrosis factor-α-induced inflammation via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ in intestinal epithelial cells . Arch Pharm Res.2016;39(10):1465-1471.[5]Traboulsi H,Cloutier A,Boyapelly K,et al. he Flavonoid Isoliquiritigenin Reduces Lung Inflammation and Mouse Morbidity during Influenza Virus Infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015; 59(10): 6317-6327.[6]Cronin H,Draelos ZD.Top 10 botanical ingredients in 2010 anti-aging creams. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2010;9(3):218-225.[7]Yerra VG,Kalvala AK,Kumar A.Isoliquiritigenin reduces oxidative damage and alleviates mitochondrial impairment by SIRT1 activation in experimental diabetic neuropathy. J Nutr Biochem. 2017;47:41-52.[8]覃月穆,姜泽群,马艳霞,等.异甘草素对人肺癌细胞株H460增殖、凋亡及NF-κB信号通路的影响[J].天然产物研究与开发, 2018, 30(5):847-855.[9]邓云秋.异甘草素对人胶质瘤细胞系U251增殖、凋亡的影响及相关机制研究[J].医学理论与实践,2018,31(9):1260-1261,1270.[10]Wang JR,Luo YH,Piao XJ,et al.Mechanisms underlying isoliquiritigenin-induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest via ROS-mediated MAPK/STAT3/NF-κB pathways in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Drug Dev Res.2019.[Epub ahead of print][11]哈尼克孜•吐尔逊,古再丽努尔•麦麦提图尔荪,木合布力•阿布力孜,等. 异甘草素诱导人宫颈癌细胞增殖的影响及作用机制的研究[J].重庆医学,2017,46(24): 3324-3327,3331.[12]Zhang XR, Wang SY, Sun W, et al. Isoliquiritigenin inhibits proliferation and metastasis of MKN28 gastric cancer cells by suppressing the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2018. [Epub ahead of print][13]Li N,Yang L,Deng X,et al.Effects of isoliquiritigenin on ovarian cancer cells. Onco Targets Ther.2018;11:1633-1642.[14]Jin H,Seo GS,Lee SH.Isoliquiritigenin-mediated p62/SQSTM1 induction regulates apoptotic potential through attenuation of caspase-8 activation in colorectal cancer cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018;841:90-97.[15]Hu FW,Yu CC,Hsieh PL,et al.Targeting oral cancer stemness and chemoresistance by isoliquiritigenin-mediated GRP78 regulation.Oncotarget.2017;8(55):93912-93923.[16]Peng F, Tang H, Liu P, et al. Isoliquiritigenin modulates miR-374a/PTEN/Akt axis to suppress breast cancer tumorigenesis and metastasis.Sci Rep.2017;7(1):9022.[17]Si L,Yang X,Yan X,et al.Isoliquiritigenin induces apoptosis of human bladder cancer T24 cells via a cyclin-dependent kinase-independent mechanism.Oncol Lett.2017;14(1): 241-249.[18]周锦霞,伍林,王建国.异甘草素微胶囊的制备及释放性的研究[J].现代食品科技,2010,26(10): 1132-1135,1159.[19]龚又明,覃军,邓广海,等.异甘草素羟丙基-β-环糊精包合物的透皮吸收研究[J].食品与药品,2017,19(4): 291-294.[20]车小琼,孙庆申,赵凯.甲壳素和壳聚糖作为天然生物高分子材料的研究进展[J].高分子通报,2008,21(2):45-49.[21]马茜,范娟.壳聚糖纳米粒载体的应用研究进展[J].西北药学杂志, 2015,30(2): 213-215. [22]吴立明,习温瑜,管正红.壳聚糖纳米粒制备的研究进展[J].齐鲁药事,2008,27(11):682-685.[23]Fangueiro JF, Parra A, Silva AM, et al. Validation of a high performance liquid chromatography method for the stabilization of epigallocatechin gallate. Int J Pharm. 2014; 475(1/2): 181-190; [24]高奋,杨慧宇,边云飞,等.载血管紧张素转换酶短发卡RNA-聚乙二醇-壳聚糖纳米粒制备以及生物学特性[J].中国药物与临床, 2015, 15(1):29-33.[25]Ahmed A,Zhang C,Guo J,et al. Fabrication and characterization of Gd-DTPA-Loaded Chitosan-Poly (acrylic acid) nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging.Macromol Biosci.2015;15(8): 1105-1114. [26]何媛,张雅溶,李秋霞,等. 透明质酸修饰姜黄素壳聚糖纳米粒的制备及初步细胞毒性考察[J].中国医药工业杂志, 2015,46(2): 162-167.[27]Tian XX, Groves MJ.Formulation and biological activity of antineoplastic proteoglycans derived from Mycobacterium vaccaein chitosan nanoparticles. J Pharm Pharmacol.1999; 51(2):151-157.[28]Nagamoto T,Hattori Y,Takayama K,et al.Novel chitosan particles and chitosan-coated emulsion inducing immune response via intranasal vaccine delivery. Pharm Res.2004; 21(4): 671.[29]Bodmeier R,Chen H,Paeratakul O. A novel approach to the delivery of microparticles or nanoparticles. Pharm Res. 1989;6(5):413-417.[30]Calvo P,Remunan-Lopez C,Vila-Jato JL,et al.Novel hydrophilic chitosan/polyethylene oxide nanoparticles as proteins carriers.J Appl Polym Sci.1997; 63:125-132.[31]张亚会,李喜香,包强,等.甘草次酸-壳聚糖纳米粒的制备及其质量评价[J].中草药,2015,46(15):2232-2237.[32]欧歌,廖德华,张凯,等.采用离子交联法制备壳聚糖胰岛素纳米粒的研究进展[J].中南药学,2013,11(2):116-119,156.[33]奚宏伟,魏长征,王文斌,等.壳聚糖-三聚磷酸钠纳米粒对于肝组织严重出血模型的止血效果[J].现代生物医学进展, 2014, 14(15):2831-2834,2885.[34]刘占军,张卫国,于九皋,等.负载紫杉醇壳聚糖纳米粒的制备、表征与释药性能[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009,13(3): 493-495.[35]刘康,秦梦,杨婷婷,等.槲皮素/壳聚糖纳米粒的制备、表征及其体外抗氧化活性研究[J].中国生化药物杂志,2016,36(11):17-21.[36]任振堃,高闻,刘畅,等.载柚皮素壳聚糖纳米粒的制备及其体外细胞评价[J].中国医院药学杂志,2017,37(20):2056-2060.[37]吴振宇,陈钟,黄华,等.离子凝胶法制备壳聚糖纳米微粒[J].南通大学学报(医学版),2005,26(1):20-22.[38]陈瑞,赵群,邵江娟,等.雷公藤甲素壳聚糖纳米粒的制备与初步评价[J].辽宁中医杂志,2016,43(4):806-808,895.[39]彭琳,李利锋,韩刚,等.载姜黄素羧甲基壳聚糖纳米粒的制备和性能[J].中国医药工业杂志,2016,47(2): 178-182 |
.jpg)
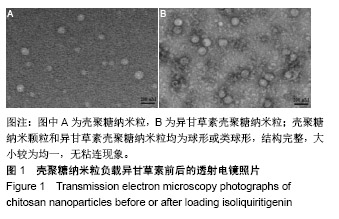
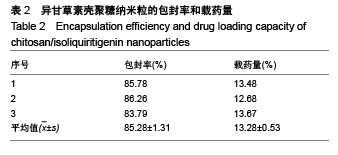
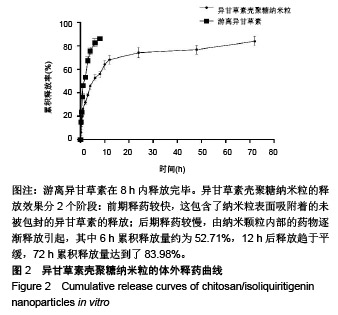
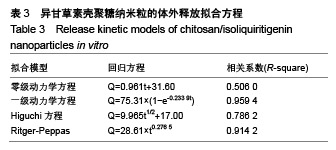

.jpg)