[1] BRUNO F, ARRIGONI F, PALUMBO P, et al. New advances in MRI diagnosis of degenerative osteoarthropathy of the peripheral joints.Radiol Med.2019;124(11):1121-1127.
[2] FAYAD LM, MUGERA C, SOLDATOS T, et al.T echnical innovation in dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of musculoskeletal tumors:an MR angiographic sequence using a sparse k-space sampling strategy.Skeletal Radiol.2013;42(7):993-1000.
[3] PRUESSMANN KP, WEIGER M, SCHEIDEGGER MB, et al. SENSE: sensitivity encoding for fast MRI.Magn Reson Med.1999;42(5):952-62.
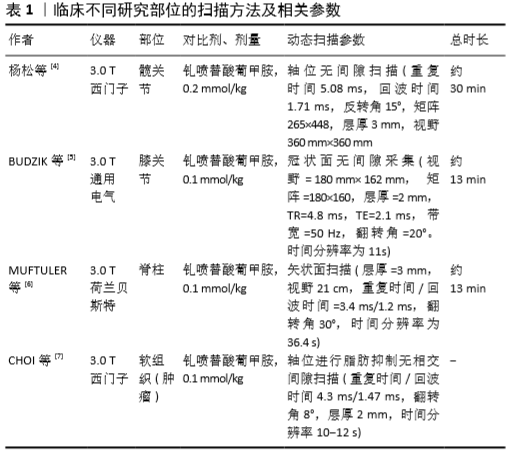
[4] 杨松,郭爽,马彦明,等.动态对比增强磁共振成像对正常成人股骨头不同区域的血供评价[J].实用放射学杂志,2019,35(11): 1805-1808,1816.
[5] Budzik JF, Ding J, Norberciak L, et al. Perfusion of subchondral bone marrow in knee osteoarthritis:A dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging preliminary study.Eur J Radiol.2017;88:129-134.
[6] MUFTULER LT, JARMAN JP, YU HJ, et al. Association between intervertebral disc degeneration and endplate perfusion studied by DCE-MRI.Eur Spine J.2015;24(4):679-685.
[7] CHOI YJ, LEE IS, SONG YS, et al. Diagnostic performance of diffusion-weighted (DWI) and dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) MRI for the differentiation of benign from malignant soft-tissue tumors.J Magn Reson Imaging.2019;50(3):798-809.
[8] HAFEZI-NEJAD N, DEMEHRI S, GUERMAZI A, et al. Osteoarthritis year in review 2017:updates on imaging advancements.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2018;26(3):341-349.
[9] GIGANTI F, MOORE CM. Magnetic resonance imaging in active surveillance-a modern approach.Transl Androl Urol.2018;7(1):116-131.
[10] KHALIFA F, SOLIMAN A, EL-BAZ A, et al. Models and methods for analyzing DCE-MRI:a review.Med Phys.2014;41(12):124301.
[11] HANSEN MIKKEL B, ANNA T, SØREN H, et al. Robust estimation of hemo-dynamic parameters in traditional DCE-MRI models.PLoS One. 2019;14(1):e0209891
[12] ZHANG Y, TAN Y, DONG C, et al. Chen H.Evaluating the scope of intramedullary invasion of malignant bone tumor by DCE-MRI quantitative parameters in an animal study.J Bone Oncol. 2019;19: 100269
[13] FUKUDA T, WENGLER K, DE CARVALHO R, et al. MRI biomarkers in osseous tumors.J Magn Reson Imaging.2019;50(3):702-718.
[14] NING L, SU M, XING X, et al. Morphological and dynamic contrast enhanced MR imaging features for the differentiation of chordoma and giant cell tumors in the Axial Skeleton.Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Jmri.2016;45(4):1068-1075.
[15] DE CONINCK T, JANS L, SYS G, et al. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging for differentiation between enchondroma and chondrosarcoma.Eur Radiol.2013;23(11):3140-3152.
[16] LEONARD L, MEYER HJ, SUROV A. Imaging characteristics of malignant and benign lesions of skeletal muscle.Radiologe. 2017;57(12): 1059-1070.
[17] THEODOROS S, SHIVANI A, ELIZABETH M, et al. Multiparametric Assessment of Treatment Response in High-Grade Soft-Tissue Sarcomas with Anatomic and Functional MR Imaging Sequences.Radiology.2016;278(3):831-840.
[18] Sujlana P, Skrok J, Fayad LM. Review of dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI:Technical aspects and applications in the musculoskeletal system.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018;47(4):875-890.
[19] GRANDE FD, SUBHAWONG T, WEBER K, et al. Detection of Soft-Tissue Sarcoma Recurrence: Added Value of Functional MR Imaging Techniques at 3.0 T.Radiology.2014;271(2):130844.
[20] AMIT P, PATRO DK, BASU D, et al. Role of dynamic MRI and clinical assessment in predicting histologic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in bone sarcomas.Am J Clin Oncol. 2014;37(4): 384-390.
[21] POTTECHER P, SIBILEAU E, AHO S, et al. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging in osteoid osteoma:relationships with clinical and CT characteristics.Skeletal Radiol. 2017;46(7):935-948.
[22] LEPLAT C, HOSSU G, CHEN B, et al. Contrast-Enhanced 3-T Perfusion MRI With Quantitative Analysis for the Characterization of Musculoskeletal Tumors:Is It Worth the Trouble.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2018;211(5):1092-1098.
[23] DYKE JONATHAN P, LAZARO LIONEL E, HETTRICH CAROLYN M, et al. Regional analysis of femoral head perfusion following displaced fractures of the femoral neck.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015;41(2): 550-554.
[24] JUNG-EUN C, JOON YW, IN-ONE K, et al. Effect of arterial deprivation on growing femoral epiphysis: quantitative magnetic resonance imaging using a piglet model.Korean J Radiol. 2015;16:617-625.
[25] KAMANO M, NARITA S, HONDA Y, et al. Contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for femoral neck fracture.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;(350):179-186.
[26] KONISHIIKE T. Acute fracture of the neck of the femur.An assessment of perfusion of the head by dynamic MRI.J Bone Joint Surg Br.1999; 81(4):596-599.
[27] LAMER S, DORGERET S, KHAIROUNI A, et al. Femoral head vascularisation in Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease:comparison of dynamic gadolinium-enhanced subtraction MRI with bone scintigraphy.Pediatr Radiol.2002;32(8):580-585
[28] 章猛奇.股骨颈骨折后股骨头血运检测方法的比较分析(附15例病例研究)[D].遵义:遵义医科大学, 2019.
[29] JOHNSON JOEY P, JUSTIN K, GOODMAN AVI D, et al. Treatment of femoral neck fractures in patients 45-64 years of age.Injury.2019; 50(3):708-712.
[30] LAZARO LE, DYKE JP, THACHER RR, et al. Focal osteonecrosis in the femoral head following stable anatomic fixation of displaced femoral neck fractures.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017;137(11):1529-1538.
[31] CANINTIKA AF, DILOGO IH. Teriparatide for treating delayed union and nonunion: A systematic review.J Clin Orthop Trauma.2020;11(Suppl 1): S107-S112.
[32] SCHOIERER O, BLOESS K, BENDER D, et al. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging can assess vascularity within fracture non-unions and predicts good outcome.Eur Radiol. 2014;24(2): 449-459.
[33] FISCHER C, NISSEN M, SCHMIDMAIER G, et al. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) for the prediction of non-union consolidation.Injury. 2017;48(2):357-363.
[34] WESTGEEST J, WEBER D, DULAI SK, et al. Factors Associated With Development of Nonunion or Delayed Healing After an Open Long Bone Fracture:A Prospective Cohort Study of 736 Subjects.J Orthop Trauma.2016;30(3):149-155.
[35] CHRISTIAN F, EVA-MARIA P, MICHAEL T, et al. Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Sonography and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Preoperative Diagnosis of Infected Nonunions.J Ultrasound Med.2016;35(5):933-942.
[36] NG AWH, GRIFFITH JF, TALJANOVIC MS, et al. Is dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI useful for assessing proximal fragment vascularity in scaphoid fracture delayed and non-union.Skeletal Radiol. 2013; 42(7):983-992.
[37] DONATI OF, ZANETTI M, NAGY L, et al. Is dynamic gadolinium enhancement needed in MR imaging for preoperative assessment of scaphoidal viability in patients with scaphoid nonunion.Radiology. 2011;260:808-816.
[38] LARRIBE M, GAY A, FREIRE V, et al. Usefullness of dynamic contrastenhanced MRI in evaluation of the viability of acute scaphoid fracture.Skeletal Radiol.2014;43:1697-1703.
[39] KORCHI AM, CENGARLE-SAMAK A, OKUNO Y, et al. Inflammation and Hypervascularization in a Large Animal Model of Knee Osteoarthritis:Imaging with Pathohistologic Correlation.J Vasc Interv Radiol.2019;30(7):1116-1127.
[40] LEE JH, DYKE JP, BALLON D, et al. Subchondral fluid dynamics in a model of osteoarthritis:use of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009;17(10):1350-1355.
[41] NUSMAN CM, HEMKE R, LAVINI C, et al. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging can play a role in predicting flare in juvenile idiopathic arthritis.Eur J Radiol. 2017;88:77-81.
[42] MAGDALENA K, AGNIESZKA O, ZBIGNIEW Ż, et al. Role of Microparticles in the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Joint Diseases.Int J Mol Sci.2019;20(21):5453.
[43] RIIS RGC, GUDBERGSEN H, HENRIKSEN M, et al. Synovitis assessed on static and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and its association with pain in knee osteoarthritis:A cross-sectional study.Eur J Radiol.2016,85(6):1099-1108.
[44] RIIS RGC, GUDBERGSEN H, SIMONSEN O, et al. The association between histological,macroscopic and magnetic resonance imaging assessed synovitis in end-stage knee osteoarthritis:a cross-sectional study.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2017;25(2):272-280.
[45] VORDENBÄUMEN S, SCHLEICH C, LÖGTERS T, et al. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of metacarpophalangeal joints reflects histological signs of synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis. 2014;16(5):452.
[46] DE VRIES BA, VAN DER HEIJDEN RA, POOT DHJ, et al. Quantitative dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI blood perfusion in Hoffa’s fatpad signal abnormalities in patients with and without osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2020;28:S279.
[47] SAVVOPOULOU V, MARIS TG, VLAHOS L, et al. Differences in perfusion parameters between upper and lower lumbar vertebral segments with dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI (DCE MRI).Eur Radiol. 2008;18(9):1876-1883.
[48] MA HT, LV H, GRIFFITH JF, et al. Perfusion and bone mineral density as function of vertebral level at lumbar spine.Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc.2012;3488-3491.
[49] DOLAN P, LUO J, POLLINTINE P, et al. Intervertebral disc decompression following endplate damage:implications for disc degeneration depend on spinal level and age.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2013;38(17):1473-1481.
[50] CHAO ST, KOYFMAN SA, WOODY N, et al. Recursive partitioning analysis index is predictive for overall survival in patients undergoing spine stereotactic body radiation therapy for spinal metastases.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.2012;82(5):1738-1743.
[51] KUMAR KA, PECK KK, KARIMI S, et al. A Pilot Study Evaluating the Use of Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Perfusion MRI to Predict Local Recurrence After Radiosurgery on Spinal Metastases.Technol Cancer Res Treat.2017;16(6):857-865.
[52] FAYAD LM, JACOBS MA, WANG X, et al. Musculoskeletal tumors: how to use anatomic, functional, and metabolic MR techniques.Radiology.2012;265(2):340-356.
[53] STACY C, SASAN K, PECK KYUNG K, et al. Measurement of blood perfusion in spinal metastases with dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging:evaluation of tumor response to radiation therapy.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2013;38(22):E1418-1424.
[54] SPRATT DE, AREVALO-PEREZ J, LEEMAN JE, et al. Early magnetic resonance imaging biomarkers to predict local control after high dose stereotactic body radiotherapy for patients with sarcoma spine metastases.Spine J.2016;16(3):291-298.
[55] OHGIYA Y, HASHIMOTO T, GOKAN T, et al. Dynamic MRI for distinguishing high-flow from low-flow peripheral vascular malformations. AJR Am J Roentgenol.2005;185(5):1131-1137.
[56] OZKAN U, OĞUZKURT L, TERCAN F, et al. MRI and DSA findings in popliteal artery entrapment syndromeDiagn Interv Radiol. 2008; 14(2):106-110.
[57] MURAKAMI AM, CHANG A, FOO LF. Traumatic Lateral Plantar Artery Pseudoaneurysm and the Use of Time-Resolved MR Angiography.HSS J.2010;6(2):214-218.
[58] KOELEMAY MJ, LIJMER JG, STOKER J, et al. Magnetic resonance angiography for the evaluation of lower extremity arterial disease:a meta-analysis.JAMA.2001;285(10):1338-1345.
[59] LIAO GJ, HENZE BANCROFT LC, STRIGEL RM, et al. Background parenchymal enhancement on breast MRI:A comprehensive review.J Magn Reson Imaging.2020;51(1):43-61.
[60] SCHLEMMER HP. Multiparametric MRI of the prostate :Important radiological findings for urologists.Radiologe.2017;57(8):621-630.
[61] CORVINO A, SANDOMENICO F, SETOLA SV, et al. Morphological and dynamic evaluation of complex cystic focal liver lesions by contrast-enhanced ultrasound:current state of the art.J Ultrasound. 2019;22(3):251-259. |