中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (23): 3623-3629.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1305
• 肌肉肌腱韧带组织构建 tissue construction of the muscle, tendon and ligament • 上一篇 下一篇
类风湿关节炎滑膜组织中脯氨酸羟化酶及希佩尔林道肿瘤抑制蛋白的表达及意义
宋小莉1,苏 娟2,刘重阳1,张广源3,张 鑫4
- (1重庆医科大学附属第三医院风湿免疫科,重庆市 401120;青海大学附属医院,2风湿免疫科,3关节外科,4病理科,青海省西宁市 810001)
Expression and significance of prolyl hydroxylase and von-Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein in the synovial tissues of rheumatoid arthritis
Song Xiaoli1, Su Juan2, Liu Chongyang1, Zhang Guangyuan3, Zhang Xin4
- (1Department of Rheumatology, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 401120, China; 2Department of Rheumatology, 3Department of Joint Surgery, 4Department of Pathology, Affiliated Hospital of Qinghai University, Xining 810001, Qinghai Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
希佩尔林道肿瘤抑制蛋白:希佩尔林道病肿瘤抑制基因(Von Hippel-lindau,VHL)是位于3p25-26号染色体的抑癌基因。VHL蛋白开放阅读框架编码213个氨基酸,相对分子质量为24-30 ku,一个含有大量的酪氨酸激酶Ⅱ磷酸化位点,导致细胞内的磷酸化。另一个亚型主要位于54位密码子框内甲硫氨酸内部起始翻译产物,编码160个氨基酸,相对分子质量为18-20 ku,两者统称为希佩尔林道病肿瘤抑制蛋白(protein Von Hippellindau,pVHL)。
异源二聚体:二聚体是蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用的一种形式,它可以定义为2个有关的亚单元组成一个蛋白质-蛋白质复合物。如果组成二聚体的两个有关的亚单元是相同的则为同源二聚体,反之为异源二聚体。二聚作用是调节信号转导的一种常见形式,发生二聚作用的蛋白质彼此接近,使得它们可以相互作用。二聚作用可将相互作用的分子拉近,还能使底物与酶的活性位点以更适合催化作用的方位相互楔合,增加反应速度。
文题释义:
希佩尔林道肿瘤抑制蛋白:希佩尔林道病肿瘤抑制基因(Von Hippel-lindau,VHL)是位于3p25-26号染色体的抑癌基因。VHL蛋白开放阅读框架编码213个氨基酸,相对分子质量为24-30 ku,一个含有大量的酪氨酸激酶Ⅱ磷酸化位点,导致细胞内的磷酸化。另一个亚型主要位于54位密码子框内甲硫氨酸内部起始翻译产物,编码160个氨基酸,相对分子质量为18-20 ku,两者统称为希佩尔林道病肿瘤抑制蛋白(protein Von Hippellindau,pVHL)。
异源二聚体:二聚体是蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用的一种形式,它可以定义为2个有关的亚单元组成一个蛋白质-蛋白质复合物。如果组成二聚体的两个有关的亚单元是相同的则为同源二聚体,反之为异源二聚体。二聚作用是调节信号转导的一种常见形式,发生二聚作用的蛋白质彼此接近,使得它们可以相互作用。二聚作用可将相互作用的分子拉近,还能使底物与酶的活性位点以更适合催化作用的方位相互楔合,增加反应速度。
.jpg) 文题释义:
希佩尔林道肿瘤抑制蛋白:希佩尔林道病肿瘤抑制基因(Von Hippel-lindau,VHL)是位于3p25-26号染色体的抑癌基因。VHL蛋白开放阅读框架编码213个氨基酸,相对分子质量为24-30 ku,一个含有大量的酪氨酸激酶Ⅱ磷酸化位点,导致细胞内的磷酸化。另一个亚型主要位于54位密码子框内甲硫氨酸内部起始翻译产物,编码160个氨基酸,相对分子质量为18-20 ku,两者统称为希佩尔林道病肿瘤抑制蛋白(protein Von Hippellindau,pVHL)。
异源二聚体:二聚体是蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用的一种形式,它可以定义为2个有关的亚单元组成一个蛋白质-蛋白质复合物。如果组成二聚体的两个有关的亚单元是相同的则为同源二聚体,反之为异源二聚体。二聚作用是调节信号转导的一种常见形式,发生二聚作用的蛋白质彼此接近,使得它们可以相互作用。二聚作用可将相互作用的分子拉近,还能使底物与酶的活性位点以更适合催化作用的方位相互楔合,增加反应速度。
文题释义:
希佩尔林道肿瘤抑制蛋白:希佩尔林道病肿瘤抑制基因(Von Hippel-lindau,VHL)是位于3p25-26号染色体的抑癌基因。VHL蛋白开放阅读框架编码213个氨基酸,相对分子质量为24-30 ku,一个含有大量的酪氨酸激酶Ⅱ磷酸化位点,导致细胞内的磷酸化。另一个亚型主要位于54位密码子框内甲硫氨酸内部起始翻译产物,编码160个氨基酸,相对分子质量为18-20 ku,两者统称为希佩尔林道病肿瘤抑制蛋白(protein Von Hippellindau,pVHL)。
异源二聚体:二聚体是蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用的一种形式,它可以定义为2个有关的亚单元组成一个蛋白质-蛋白质复合物。如果组成二聚体的两个有关的亚单元是相同的则为同源二聚体,反之为异源二聚体。二聚作用是调节信号转导的一种常见形式,发生二聚作用的蛋白质彼此接近,使得它们可以相互作用。二聚作用可将相互作用的分子拉近,还能使底物与酶的活性位点以更适合催化作用的方位相互楔合,增加反应速度。摘要
背景:缺氧诱导因子在类风湿关节炎中的作用已经得到广泛证实,而作为缺氧诱导因子重要的调节因子脯氨酸羟化酶及希佩尔林道肿瘤抑制蛋白(von-Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein,pVHL)是否在类风湿关节炎中作用国内外尚无明确报道。
目的:分析类风湿关节炎和骨关节炎滑膜组织中脯氨酸羟化酶和pVHL的表达及其相互关系,探讨低氧信号蛋白在类风湿关节炎中的影响机制。
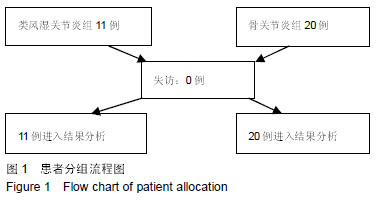
方法:取行膝关节置换的类风湿关节炎患者滑膜组织11例,并取行膝关节置换的骨关节炎患者滑膜组织20例做对照。研究的实施符合青海大学附属医院医院对研究的相关伦理要求,患者对治疗过程及试验过程完全知情同意。采用免疫组织化学Envision二步法,检测2组滑膜组织中脯氨酸羟化酶1,2,3及pVHL的表达。
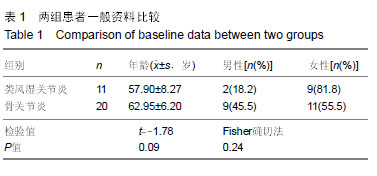
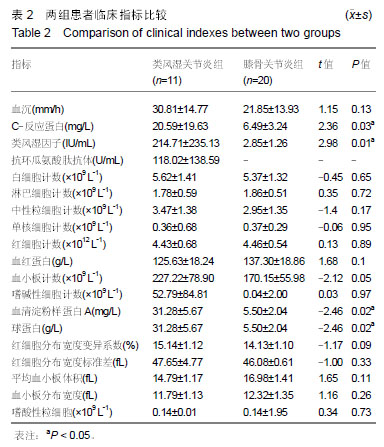
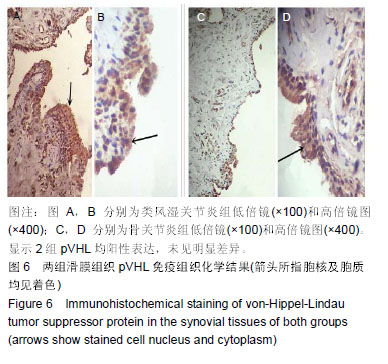
结果与结论:①免疫组织化学结果显示,脯氨酸羟化酶1,2,3及pVHL在类风湿关节炎和骨关节炎滑膜组织中均有表达;脯氨酸羟化酶1在类风湿关节炎滑膜组织中的表达显著低于骨关节炎组(P < 0.01),脯氨酸羟化酶2在类风湿关节炎滑膜组织中的表达显著高于骨关节炎组(P < 0.05);脯氨酸羟化酶3、pVHL的表达2组差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);②相关分析显示,类风湿关节炎组脯氨酸羟化酶2与脯氨酸羟化酶3(rs=-0.875,P < 0.01),脯氨酸羟化酶1与红细胞分布宽度标准差(rs=-0.374,P < 0.03),脯氨酸羟化酶2与血红蛋白(rs=-0.457,P < 0.01),脯氨酸羟化酶3与红细胞分布宽度标准差(rs=-0.363,P < 0.04)均呈负相关;脯氨酸羟化酶2与嗜酸性粒细胞(rs=0.363,P < 0.04),脯氨酸羟化酶2与球蛋白(rs=0.405,P < 0.02),均呈正相关;③类风湿关节炎组类风湿因子、C-反应蛋白、血清淀粉样蛋白A、球蛋白检测值均显著高于骨关节炎组(P < 0.05);④结果说明,脯氨酸羟化酶1和脯氨酸羟化酶2与类风湿关节炎的发生、发展密切相关,抑制脯氨酸羟化酶2的表达及激活脯氨酸羟化酶1的表达可能在类风湿关节炎滑膜组织的病理改变中起到重要保护作用,或可为类风湿关节炎发生的分子生物学途径及临床之中提供有针对性的治疗措施。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程 ORCID: 0000-0001-8422-3209(宋小莉)
中图分类号:

.jpg) 文题释义:
希佩尔林道肿瘤抑制蛋白:希佩尔林道病肿瘤抑制基因(Von Hippel-lindau,VHL)是位于3p25-26号染色体的抑癌基因。VHL蛋白开放阅读框架编码213个氨基酸,相对分子质量为24-30 ku,一个含有大量的酪氨酸激酶Ⅱ磷酸化位点,导致细胞内的磷酸化。另一个亚型主要位于54位密码子框内甲硫氨酸内部起始翻译产物,编码160个氨基酸,相对分子质量为18-20 ku,两者统称为希佩尔林道病肿瘤抑制蛋白(protein Von Hippellindau,pVHL)。
异源二聚体:二聚体是蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用的一种形式,它可以定义为2个有关的亚单元组成一个蛋白质-蛋白质复合物。如果组成二聚体的两个有关的亚单元是相同的则为同源二聚体,反之为异源二聚体。二聚作用是调节信号转导的一种常见形式,发生二聚作用的蛋白质彼此接近,使得它们可以相互作用。二聚作用可将相互作用的分子拉近,还能使底物与酶的活性位点以更适合催化作用的方位相互楔合,增加反应速度。
文题释义:
希佩尔林道肿瘤抑制蛋白:希佩尔林道病肿瘤抑制基因(Von Hippel-lindau,VHL)是位于3p25-26号染色体的抑癌基因。VHL蛋白开放阅读框架编码213个氨基酸,相对分子质量为24-30 ku,一个含有大量的酪氨酸激酶Ⅱ磷酸化位点,导致细胞内的磷酸化。另一个亚型主要位于54位密码子框内甲硫氨酸内部起始翻译产物,编码160个氨基酸,相对分子质量为18-20 ku,两者统称为希佩尔林道病肿瘤抑制蛋白(protein Von Hippellindau,pVHL)。
异源二聚体:二聚体是蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用的一种形式,它可以定义为2个有关的亚单元组成一个蛋白质-蛋白质复合物。如果组成二聚体的两个有关的亚单元是相同的则为同源二聚体,反之为异源二聚体。二聚作用是调节信号转导的一种常见形式,发生二聚作用的蛋白质彼此接近,使得它们可以相互作用。二聚作用可将相互作用的分子拉近,还能使底物与酶的活性位点以更适合催化作用的方位相互楔合,增加反应速度。