| [1] Lin JD, Tan LA, Wei C, et al. The posterior superior iliac spine and sacral laminar slope: key anatomical landmarks for freehand S2-alar-iliac screw placement. J Neurosurg Spine. 2018;29(4): 429-434. [2] O’Brien JR, Yu W, Kaufman BE, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of S2 alar-iliac screws: effect of length and quad-cortical purchase as compared with iliac fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(20): E1250-1255. [3] Sutterlin CE 3rd, Field A, Ferrara LA, et al. Range of motion, sacral screw and rod strain in long posterior spinal constructs: a biomechanical comparison between S2 alar iliac screws with traditional fixation strategies. J Spine Surg. 2016;2(4):266-276. [4] Burns CB, Dua K, Trasolini NA, et al. Biomechanical Comparison of Spinopelvic Fixation Constructs: Iliac Screw Versus S2-Alar-Iliac Screw. Spine Deform. 2016;4(1):10-15. [5] Hoernschemeyer DG, Pashuck TD, Pfeiffer FM. Analysis of the s2 alar-iliac screw as compared with the traditional iliac screw: does it increase stability with sacroiliac fixation of the spine? Spine J. 2017; 17(6):875-879. [6] Jain A, Hassanzadeh H, Strike SA, et al. Pelvic Fixation in Adult and Pediatric Spine Surgery: Historical Perspective, Indications, and Techniques: AAOS Exhibit Selection. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015; 97(18):1521-1528. [7] 张楠威,于滨生.经S2骶髂螺钉技术在脊柱骨盆稳定性重建中应用的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2018,32(6):764-768.[8] Moshirfar A, Rand FF, Sponseller PD, et al. Pelvic fixation in spine surgery. Historical overview, indications, biomechanical relevance, and current techniques. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87 Suppl 2: 89-106. [9] Schwend RM, Sluyters R, Najdzionek J. The pylon concept of pelvic anchorage for spinal instrumentation in the human cadaver. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(6):542-547. [10] 项泱,谭军,任甜甜,等.髂骨螺钉置入技术研究进展[J].现代实用医学, 2016, 28(10):1261-1264.[11] Lombardi JM, Shillingford JN, Lenke LG, et al. Sacropelvic Fixation: When, Why, How? Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2018;29(3): 389-397. [12] 刘臻,李劼,赵志慧,等.重度神经肌源性脊柱侧凸伴骨盆倾斜三种内固定模式的比较研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(4):193-203.[13] Mazur MD, Ravindra VM, Dailey AT, et al. Rigid Posterior Lumbopelvic Fixation without Formal Debridement for Pyogenic Vertebral Diskitis and Osteomyelitis Involving the Lumbosacral Junction: Technical Report. Front Surg. 2015;2:47. [14] 王孝宾,王冰,李晶,等.经骶2髂骨螺钉内固定在腰骶段结核稳定性重建中的应用[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2017,27(5):392-398.[15] 谢雁春,项良碧,刘军,等.经皮骶2髂骨三皮质螺钉治疗老年无神经症状下腰椎椎间盘炎的近期疗效分析[J].介入放射学杂志,2018,27(1): 53-57.[16] Yamada K, Higashi T, Kaneko K, et al. Optimal trajectory and insertion accuracy of sacral alar iliac screws. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2017; 51(4):313-318. [17] Abdul-Jabbar A, Yilmaz E, Iwanaga J, et al. Neurovascular Relationships of S2AI Screw Placement: Anatomic Study. World Neurosurg. 2018;116:e108-e112. [18] Ray WZ, Ravindra VM, Schmidt MH, et al. Stereotactic navigation with the O-arm for placement of S-2 alar iliac screws in pelvic lumbar fixation. J Neurosurg Spine. 2013;18(5):490-495. [19] Martin CT, Witham TF, Kebaish KM. Sacropelvic fixation: two case reports of a new percutaneous technique. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(9):E618-621. [20] Funao H, Kebaish KM, Isogai N, et al. Utilization of a Technique of Percutaneous S2 Alar-Iliac Fixation in Immunocompromised Patients with Spondylodiscitis. World Neurosurg. 2017;97:757. e11-757. e18. [21] Hu X, Lieberman IH. Robotic-guided sacro-pelvic fixation using S2 alar-iliac screws: feasibility and accuracy. Eur Spine J. 2017; 26(3): 720-725. [22] Laratta JL, Shillingford JN, Lombardi JM, et al. Accuracy of S2 Alar-Iliac Screw Placement Under Robotic Guidance. Spine Deform. 2018;6(2):130-136. [23] 马宇龙,赵永辉,罗浩天,等.个体化导航模板辅助第2骶椎髂骨螺钉置钉的临床应用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2018,20(4):329-333.[24] Park YS, Hyun SJ, Park JH, et al. Radiographic and Clinical Results of Freehand S2 Alar-Iliac Screw Placement for Spinopelvic Fixation: An Analysis of 45 Consecutive Screws. Clin Spine Surg. 2017;30(7): E877-E882. [25] Fang T, Russo GS, Schroeder GD, et al. The Accurate Free-hand Placement of S2 Alar Iliac (S2AI) Screw. Clin Spine Surg. 2018 Mar 16. doi:10.1097/BSD. 0000000000000623. [Epub ahead of print][26] Shillingford JN, Laratta JL, Tan LA, et al. The Free-Hand Technique for S2-Alar-Iliac Screw Placement: A Safe and Effective Method for Sacropelvic Fixation in Adult Spinal Deformity. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100(4):334-342. [27] Ishida W, Elder BD, Holmes C, et al. S2-Alar-Iliac Screws are Associated with Lower Rate of Symptomatic Screw Prominence than Iliac Screws: Radiographic Analysis of Minimal Distance from Screw Head to Skin. World Neurosurg. 2016;93:253-260.[28] Ilyas H, Place H, Puryear A. A Comparison of Early Clinical and Radiographic Complications of Iliac Screw Fixation Versus S2 Alar Iliac (S2AI) Fixation in the Adult and Pediatric Populations. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2015;28(4):E199-205. [29] 谢雁春,王丹妮,吴骏,等.骶2髂骨三皮质螺钉和髂骨螺钉的临床并发症比较[J].局解手术学杂志,2017,26(6):415-418.[30] Smith EJ, Kyhos J, Dolitsky R, et al. S2 Alar Iliac Fixation in Long Segment Constructs, a Two- to Five-Year Follow-up. Spine Deform. 2018;6(1):72-78. [31] Kebaish KM. Sacropelvic fixation: techniques and complications. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(25):2245-2251. [32] Jain A, Kebaish KM, Sponseller PD. Sacral-Alar-Iliac Fixation in Pediatric Deformity: Radiographic Outcomes and Complications. Spine Deform. 2016;4(3):225-229. [33] Guler UO, Cetin E, Yaman O, et al. Sacropelvic fixation in adult spinal deformity (ASD); a very high rate of mechanical failure. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(5):1085-1091. [34] O'Brien JR, Yu WD, Bhatnagar R, et al. An anatomic study of the S2 iliac technique for lumbopelvic screw placement. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(12):E439-442. [35] Mazur MD, Mahan MA, Shah LM, et al. Fate of S2-Alar-Iliac Screws After 12-Month Minimum Radiographic Follow-up: Preliminary Results. Neurosurgery. 2017;80(1):67-72. [36] Elder BD, Ishida W, Lo SL, et al. Use of S2-Alar-iliac Screws Associated With Less Complications Than Iliac Screws in Adult Lumbosacropelvic Fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017;42(3): E142-E149. [37] 刘臻,曾昌淳,赵志慧,等.经第2骶椎骶髂螺钉与髂骨螺钉技术治疗成人退变性脊柱侧后凸的矫形疗效比较[J].中华外科杂志, 2018,56(2): 139-146.[38] Xu R, Ebraheim NA, Douglas K, et al. The projection of the lateral sacral mass on the outer table of the posterior ilium. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996;21(7):790-794; discussion 795. [39] Ishida W, Elder BD, Holmes C, et al. Comparison Between S2-Alar-Iliac Screw Fixation and Iliac Screw Fixation in Adult Deformity Surgery: Reoperation Rates and Spinopelvic Parameters. Global Spine J. 2017;7(7):672-680. [40] Montero CS, Meneses DA, Alvarado F, et al. Outcomes and complications of S2 alar iliac fixation technique in patients with neuromuscular scoliosis: experience in a third level pediatric hospital. J Spine Surg. 2017;3(4):519-524. [41] Tsuchiya K, Bridwell KH, Kuklo TR, et al. Minimum 5-year analysis of L5-S1 fusion using sacropelvic fixation (bilateral S1 and iliac screws) for spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(3):303-308. [42] O?Shaughnessy BA, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, et al. Should symptomatic iliac screws be electively removed in adult spinal deformity patients fused to the sacrum? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(13):1175-1181. [43] Chang TL, Sponseller PD, Kebaish KM, et al. Low profile pelvic fixation: anatomic parameters for sacral alar-iliac fixation versus traditional iliac fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34(5):436-440. [44] Yagi M, Akilah KB, Boachie-Adjei O. Incidence, risk factors and classification of proximal junctional kyphosis: surgical outcomes review of adult idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(1):E60-68. [45] Mummaneni PV, Park P, Fu KM, et al. Does Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Posterior Instrumentation Reduce Risk of Proximal Junctional Kyphosis in Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery? A Propensity-Matched Cohort Analysis. Neurosurgery. 2016; 78(1):101-108. [46] Mazur MD, Ravindra VM, Schmidt MH, et al. Unplanned reoperation after lumbopelvic fixation with S-2 alar-iliac screws or iliac bolts. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015;23(1):67-76. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
文题释义: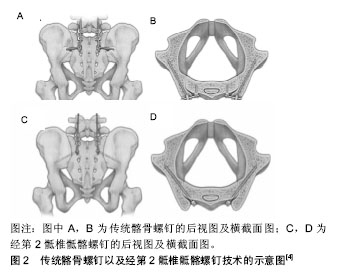
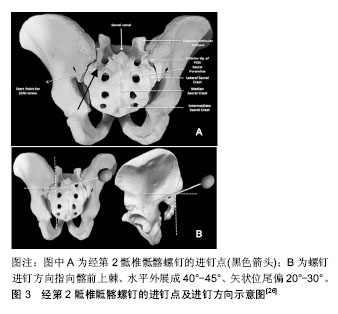

.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
文题释义: