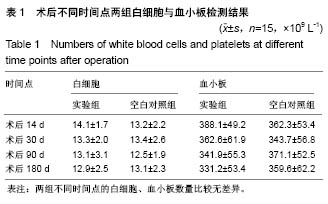
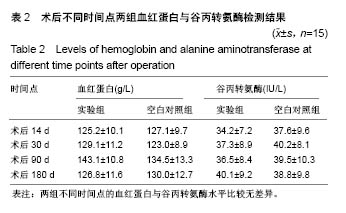
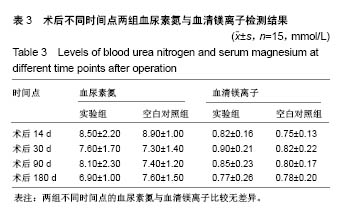
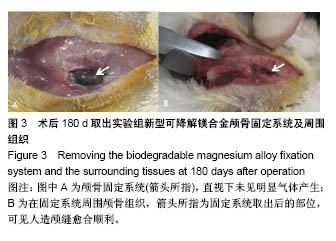
| [1] Peeters P,Bosiers M,Verbist J,et al.Preliminary results after application of absorbable metal stents in patients with critical limb ischemia.J Endovasc Ther.2005;12(1):1-5.[2] Bosiers M,Peeters P,D'Archambeau O,et al.AMS INSIGHT-Absorbable Metal Stent Implantation for Treatment of Below-the-Knee Critical Limb Ischemia:6-Month Analysis. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol.2009;32(3):424-435.[3] Erbel R,Di Mario C,Bartunek J,et al.Temporary scaff olding of coronary arteries with bioabsorbable magnesium stents: a prospective, non-randomised multicentre trial. Lancet. 2007; 369(9576):1869-1875.[4] Waksman R,Erbel R,Di MC,et al.Early-and long-term intravascular ultrasound and angiographic findings after bioabsorbable magnesium stent implantation in human coronary arteries.JACC Cardiovasc Interv.2009;2(4):312-320.[5] Windhagen H,Radtke K,Weizbauer A,et al.Biodegradable magnesium-based screw clinically equivalent to titanium screw in hallux valgus surgery: short term results of the first prospective, randomized, controlled clinical pilot study. Biomed Eng.2013;12(1):62-72.[6] 杨凯,朱悦琦,程英升.食管良性狭窄药物镁合金可降解支架研究现状及展望[J].介入放射学志,2015,24(5):452-456.[7] 郝杰,夏建民,王博,等.新型可降解镁合金胆道支架在胆总管探查术中预防狭窄的作用[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2017,38(5): 763-767.[8] Staiger MP,Pietak AM,Huadmai J,et al. Magnesium and its alloys as orthopedic biomaterials: a review. Biomaterials. 2006;27(9):1728-1734.[9] Znamenskii MS.Metallic osteosynthesis by means of an apparatus made of resorbing metal. Khirurgiia.1945;12:60-63.[10] 袁广银,张佳,丁文江.可降解医用镁基生物材料的研究进展[J].中国材料进展,2011,30(2):44-50.[11] 杨柯,杨化娟,张炳春.医用不锈钢的发展及展望[J].材料导报, 2005,19(6):56-59.[12] Wan Y,Xiong G,Luo H,et al.Preparation and characterization of a new biomedical magnesium-calcium alloy.Mater Design. 2008;29(10):2034-2037.[13] Troitskii VV,Tsitrin DN.The resorbing metallic alloy ‘Osteosinthezit’ as materia l for fastening broken bone. Khirurgiia.1944;8:41-44.[14] McBride ED.Absorbable metal in bone surgery.J Am Med Assoc.1938;111(27):2464-2467.[15] Revell PA,Damien E,Zhang XS,et al.The effect of mangesium ions on bone bonding to hydroxyapatite Coating on Titanium Alloy Implants.Key Eng Mater.2004;254-256:447-450.[16] Zreiqat H, Howlett CR, Zannettino A, et al. Mechanisms of magnesium-stimulated adhesion of osteoblastic cells to commonly used orthopaedic implants.J Biomed Mater. 2002; 62(2):175-184.[17] Yamasaki Y,Yoshida Y,Okazaki M,et al.Action of FG-MgCO3 Ap-collagen composite in promoting bone formation. Biomaterials.2003;24(27):4913-4920.[18] 李子剑,张克,娄思权,等.镁钙合金的细胞毒性研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2007,22(9):740-742.[19] Yamasaki Y,Yoshida Y,Okaz aki M,et al.Synthesis of functionally graded MgCO3 apatite accelerating osteoblast adhesion.J Biomed Mater Res.2002;62(1):99-105.[20] Janning C,Willbold E,Vogt C,et al.Magnesium hydroxide temporarily enhancing osteoblast activity and decreasing the osteoclast number in peri-implant bone remodelling. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(5):1861-1868.[21] Zreiqat H,Valenzuela SM,Nissan BB,et al.The effect of surface chemistry modification of titanium alloy on signalling pathways in human osteoblasts. Biomaterials. 2005;26(36): 7579-7586.[22] Sternberg K,Gratz M,Koeck K,et al.Magnesium used in bioabsorbable stents controls smooth muscle cell proliferation and stimulates endothelial cells invitro.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2012;100(1):41-50.[23] Castellani C,Lindtner RA,Hausbrandt P,et al.Bone-implant interface strength and osseointegration: Biodegradable magnesium alloy versus standard titanium control.Acta Biomater.2011;7(1):432-440.[24] Wang J,Tang J,Zhang P,et al.Surface modification of magnesium alloys developed for bioabsorbable orthopedic implants: a general review.J Biomed Mater Res. 2012;100B (6):1691-1701.[25] 孔祥东,郝永强,王磊,等.新型医用可降解镁合金(JDBM)螺钉的生物安全性研究[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志, 2015,11(3): 124-127.[26] Wang Y,Ouyang Y,Pang X,et al.Effects of degradable MG-ND-ZN-ZR alloy on osteoblastic cell function.Int J Imnmnopath Ph.2012;25(3):597-606. |
.jpg)
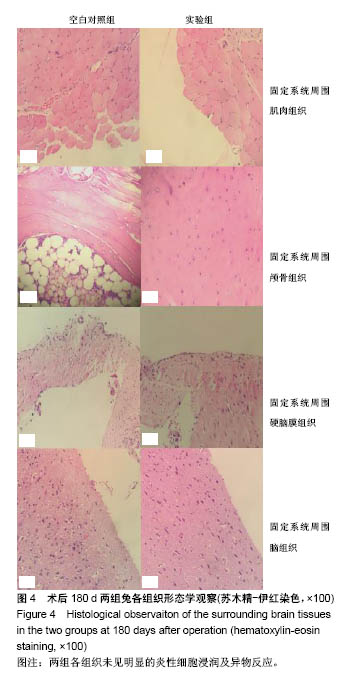
.jpg)
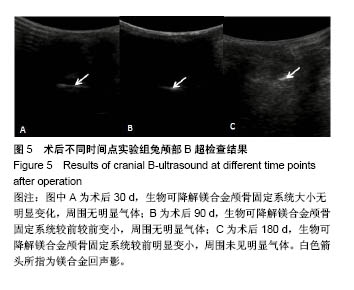
.jpg)
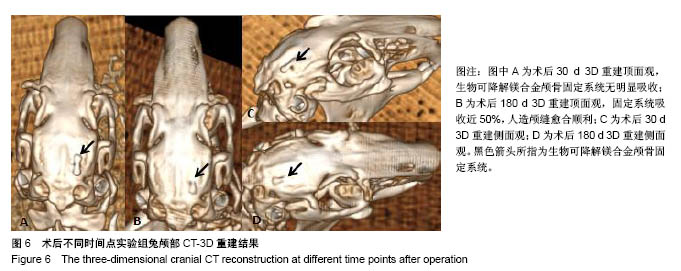
.jpg)