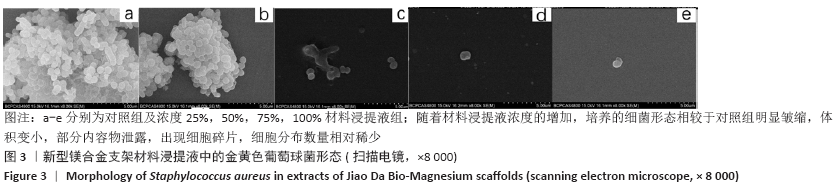
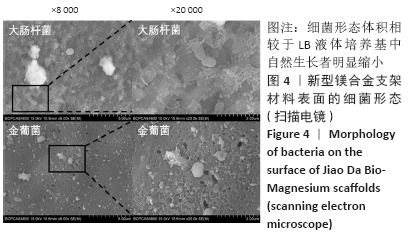
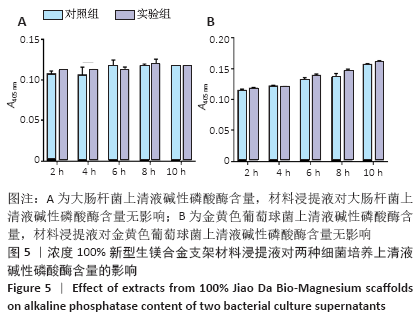
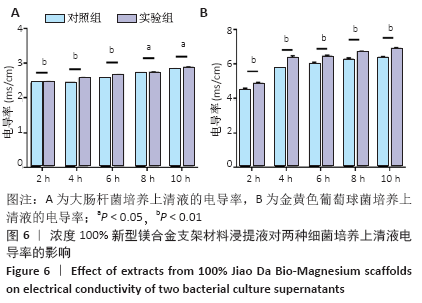
[1] 成翔宇,纪斌,庞金辉.骨折的生物学内固定及内固定材料性能分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(22):4121-4124.
[2] 杨柯,任玲,张余,等.新型抗菌功能医用金属研究[J].中国材料进展,2012,31(9):20-26.
[3] 曲立杰,李慕勤,刘苗,等.超声-微弧氧化医用镁合金体外降解性研究[J].稀有金属材料与工程,2014,43(S1):96-100.
[4] Niu J, Yuan G, Liao Y, et al. Enhanced biocorrosion resistance and biocompatibility of degradable Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloy by brushite coating.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013;33(8):4833-4841.
[5] 马剑雄,高峰,柏豪豪,等.可降解生物材料在骨科内固定中的研究及应用进展[J].生物医学工程与临床,2016,20(3):323-327.
[6] 孔祥东,郝永强,王磊,等.新型医用可降解镁合金(JDBM)螺钉的生物安全性研究[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2015,11(3):124-127.
[7] 袁广银,牛佳林.可降解医用镁合金在骨修复应用中的研究进展[J].金属学报,2017,53(10):1168-1180.
[8] 郭宇,娄译心,周延民,等.镁合金成骨作用及机制的研究进展[J].口腔医学研究,2016,32(5):541-544.
[9] YOSHIZAWA S, BROWN A, BARCHOWSKY A, et al. Role of magnesium ions on osteogenic response in bone marrow stromal cells.Connect Tissue Res. 2014;55 Suppl 1:155-159.
[10] 王湛,杨军,李建军.新型骨科植入物镁合金材料抗菌性能的体外实验研究[J].中国医科大学学报,2014,43(12):1142-1144.
[11] ZHAO C, HOU P, NI J, et al. Ag-Incorporated FHA Coating on Pure Mg: Degradation and in Vitro Antibacterial Properties.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(8):5093-5103.
[12] Jia G, Hou Y, Chen C, et al. Precise fabrication of open porous Mg scaffolds using NaCl templates: Relationship between space holder particles, pore characteristics and mechanical behavior. Mater Design. 2018;140:106-113.
[13] 奚廷斐.医疗器械生物学评价标准[M].北京:中国标准出版社, 2012.
[14] 张新虎,何静,沈慧敏.苍耳提取物对番茄灰霉病菌的抑制作用及抑菌机理初探[J].草业学报,2008(3):99-104.
[15] 云宝仪,周磊,谢鲲鹏,等.黄芩素抑菌活性及其机制的初步研究[J].药学学报,2012,47(12):1587-1592.
[16] 李昌勤,赵琳,薛志平,等.隐丹参酮抑菌作用机制研究[J].中国药学杂志,2012,47(21):1706-1710.
[17] 王倩,谢明杰.木犀草素对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌活性及其机制[J].微生物学报,2010,50(9):1180-1184.
[18] 王海涛,王倩,谢明杰.大豆异黄酮对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌机制研究[J].中国农业科学,2009,42(7):2586-2591.
[19] 马骏,李国庆,曹力.结核杆菌黏附不同人工关节假体材料的能力研究[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(47):8807-8812.
[20] ROBINSON DA, GRIFFITH RW, SHECHTMAN D, et al. In vitro antibacterial properties of magnesium metal against Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(5): 1869-1877.
[21] 蓝国波,张余.抗菌金属植入材料的研究进展[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2012,6(6):961-966.
[22] 杨小卫,李小康,郭征,等.骨科金属置入物并发感染的动物模型构建方法及效果评价[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(16): 1505-1509.
[23] Shirai T, Shimizu T, Ohtani K, et al. Antibacterial iodine-supported titanium implants. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(4):1928-1933.
[24] Donlan RM. Biofilms and device-associated infections. Emerg Infect Dis. 2001;7(2):277-281.
[25] 任玲,杨春光,杨柯.抗菌医用金属材料的研究与发展[J].中国医疗设备,2017,32(1):1-6.
[26] ARCIOLA CR, CAMPOCCIA D, GAMBERINI S, et al. Detection of slime production by means of an optimised Congo red agar plate test based on a colourimetric scale in Staphylococcus epidermidis clinical isolates genotyped for ica locus.Biomaterials.2002;23(PII S0142-9612 (02)00171-021):4233-4239.
[27] DAYAGHI E, BAKHSHESHI-RAD HR, HAMZAH E, et al. Magnesium-zinc scaffold loaded with tetracycline for tissue engineering application: In vitro cell biology and antibacterial activity assessment.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;102:53-65.
[28] JI XJ, GAO L, LIU JC, et al. Corrosion resistance and antibacterial properties of hydroxyapatite coating induced by gentamicin-loaded polymeric multilayers on magnesium alloys. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019;179:429-436.
[29] MAO L, SHEN L, CHEN J, et al. Enhanced bioactivity of Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloy achieved with nanoscale MgF2 surface for vascular stent application. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(9):5320-5330.
[30] SONG J, JIN P, LI M, et al. Antibacterial properties and biocompatibility in vivo and vitro of composite coating of pure magnesium ultrasonic micro-arc oxidation phytic acid copper loaded. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019;30(5):49.
[31] LIU C, FU X, PAN H, et al. Biodegradable Mg-Cu alloys with enhanced osteogenesis, angiogenesis, and long-lasting antibacterial effects. Sci Rep. 2016;6:27374.
[32] SIKDER P, BHADURI SB, ONG JL, et al. Silver (Ag) doped magnesium phosphate microplatelets as next-generation antibacterial orthopedic biomaterials. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020;108(3): 976-989.
[33] WINDHAGEN H, RADTKE K, WEIZBAUER A, et al. Biodegradable magnesium-based screw clinically equivalent to titanium screw in hallux valgus surgery: short term results of the first prospective, randomized, controlled clinical pilot study. Biomed Eng Online. 2013;12:62.
[34] LEE JW, HAN HS, HAN KJ, et al. Long-term clinical study and multiscale analysis of in vivo biodegradation mechanism of Mg alloy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(3):716-721.
[35] ZENG J, REN L, YUAN Y, et al. Short-term effect of magnesium implantation on the osteomyelitis modeled animals induced by Staphylococcus aureus. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2013;24(10): 2405-2416.
[36] LI Y, LIU G, ZHAI Z, et al. Antibacterial properties of magnesium in vitro and in an in vivo model of implant-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(12):7586-7591.
[37] Ren L, Lin X, Tan L, et al. Effect of surface coating on antibacterial behavior of magnesium based metals. Mater Lett. 2011;65(23-24): 3509-3511.
[38] WU H, WU G, WANG G, et al. Systematic Study of Inherent Antibacterial Properties of Magnesium-based Biomaterials. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(15):9662-9673.
[39] 袁广银,章晓波,牛佳林,等.新型可降解生物医用镁合金JDBM的研究进展[J].中国有色金属学报,2011,21(10):2476-2488.
[40] BJARNSHOLT T, KIRKETERP-MOLLER K, KRISTIANSEN S, et al. Silver against Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. APMIS. 2007;115(8): 921-928.
[41] MA R, WANG W, YANG P, et al. In vitro antibacterial activity and cytocompatibility of magnesium-incorporated poly(lactide-co-glycolic acid) scaffolds. Biomed Eng Online. 2020;19(1):12.
[42] YAMAMOTO A, HIROMOTO S. Effect of inorganic salts, amino acids and proteins on the degradation of pure magnesium in vitro. Mater Sci Eng C-Biomimetic Supramol Syst. 2009;29(5):1559-1568.
[43] 甄珍,奚廷斐,郑玉峰.生物可降解金属材料体外腐蚀测试体系综述(英文)[J]中国有色金属学报(英文版),2013,23(8):2283-2293.
[44] HIROMOTO S, YAMAMOTO A, MARUYAMA N, et al. Influence of pH and flow on the polarisation behaviour of pure magnesium in borate buffer solutions. Corros Sci. 2008;50(12):3561-3568.
[45] FENG H, WANG G, JIN W, et al. Systematic Study of Inherent Antibacterial Properties of Magnesium-based Biomaterials. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(15):9662-9673.
[46] He G, Wu Y, Zhang Y, et al. Addition of Zn to the ternary Mg-Ca-Sr alloys significantly improves their antibacterial properties. J Mater Chem B. 2015;3(32):6676-6689.
[47] ZOU YH, WANG J, CUI LY, et al. Corrosion resistance and antibacterial activity of zinc-loaded montmorillonite coatings on biodegradable magnesium alloy AZ31. Acta Biomater. 2019;98:196-214.
[48] 于潞,杨敏,李默,等.金黄色葡萄球菌与大肠埃希菌在不同环境下存活率的比较[J].中国病原生物学杂志,2016,11(2):110-115.
[49] 薛东芳,邹宗尧,陈彪,等.黄连总生物碱与小檗碱对嗜水气单胞菌细胞膜损伤机制的研究[J].中国中药杂志,2015,40(9):1787-1792.
|