[1] JOHNELL O, KANIS JA. An estimate of the worldwide prevalence and disability associated with osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2006; 17(12): 1726-1733.
[2] JOHNELL O, KANIS JA. An estimate of the worldwide prevalence, mortality and disability associated with hip fracture. Osteoporos Int. 2004;15(11):897-902.
[3] GULLBERG B, JOHNELL O, KANIS JA. World-wide projections for hip fracture. Osteoporos Int. 1997;7(5):407-413.
[4] ABRAHAMSEN B, VAN STAA T, ARIELY R, et al. Excess mortality following hip fracture: a systematic epidemiological review. Osteoporos Int. 2009; 20(10):1633-1650.
[5] MUNDI S, PINDIPROLU B, SIMUNOVIC N, et al. Similar mortality rates in hip fracture patients over the past 31 years. Acta Orthop. 2014; 85(1):54-59.
[6] KLOP C, WELSING PM, COOPER C, et al. Mortality in British hip fracture patients, 2000-2010: a population-based retrospective cohort study. Bone. 2014;66:171-177.
[7] ROCHE JJ, WENN RT, SAHOTA O, et al. Effect of comorbidities and postoperative complications on mortality after hip fracture in elderly people: prospective observational cohort study. BMJ. 2005;331(7529): 1374.
[8] BHANDARI M, DEVEREAUX PJ, SWIONTKOWSKI MF, et al. Internal fixation compared with arthroplasty for displaced fractures of the femoral neck. A meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85(9):1673-1681.
[9] STOEN RO, NORDSLETTEN L, MEYER HE, et al. Hip fracture incidence is decreasing in the high incidence area of Oslo, Norway. Osteoporos Int. 2012;23(10):2527-2534.
[10] WANG SH, YANG JJ, SHEN HC, et al. Using a modified Pauwels method to predict the outcome of femoral neck fracture in relatively young patients. Injury. 2015;46(10):1969-1974.
[11] BARTONICEK J. Pauwels’ classification of femoral neck fractures: correct interpretation of the original. J Orthop Trauma. 2001;15(5):358-360.
[12] LIPORACE F, GAINES R, COLLINGE C, et al. Results of internal fixation of Pauwels type-3 vertical femoral neck fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(8):1654-1659.
[13] MARSH JL, SLONGO TF, AGEL J, et al. Fracture and dislocation classification compendium - 2007: Orthopaedic Trauma Association classification, database and outcomes committee. J Orthop Trauma. 2007;21(10 Suppl):S1-133.
[14] KUNAPULI SC, SCHRAMSKI MJ, LEE AS, et al. Biomechanical analysis of augmented plate fixation for the treatment of vertical shear femoral neck fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(3):144-150.
[15] YANG JJ, LIN LC, CHAO KH, et al. Risk factors for nonunion in patients with intracapsular femoral neck fractures treated with three cannulated screws placed in either a triangle or an inverted triangle configuration. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(1):61-69.
[16] HUANG HK, SU YP, CHEN CM, et al. Displaced femoral neck fractures in young adults treated with closed reduction and internal fixation. Orthopedics. 2010;33(12):873.
[17] HAIDUKEWYCH GJ, ROTHWELL WS, JACOFSKY DJ, et al. Operative treatment of femoral neck fractures in patients between the ages of fifteen and fifty years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86(8):1711-1716.
[18] Asnis SE, Wanek-Sgaglione L. Intracapsular fractures of the femoral neck. Results of cannulated screw fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994;76(12):1793-1803.
[19] WANG Z, YIN Y, LI Q, et al. Comparison of early complications between the use of a cannulated screw locking plate and multiple cancellous screws in the treatment of displaced intracapsular hip fractures in young adults: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):201.
[20] JOHNSON JP, BORENSTEIN TR, WARYASZ GR, et al. Vertically Oriented Femoral Neck Fractures: A Biomechanical Comparison of 3 Fixation Constructs. J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31(7):363-368.
[21] PARKER MJ. Results of internal fixation of Pauwels type-3 vertical femoral neck fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(2):490-491.
[22] Fixation using Alternative Implants for the Treatment of Hip fractures (FAITH) Investigators. Fracture fixation in the operative management of hip fractures (FAITH): an international, multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2017;389(10078):1519-1527.
[23] GOFFIN JM, PANKAJ P, SIMPSON AH. The importance of lag screw position for the stabilization of trochanteric fractures with a sliding hip screw: a subject-specific finite element study. J Orthop Res. 2013; 31(4):596-600.
[24] ZHOU L, LIN J, HUANG A, et al. Modified cannulated screw fixation in the treatment of Pauwels type III femoral neck fractures: A biomechanical study. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2020;74:103-110.
[25] LI J, YIN P, ZHANG L, et al. Medial anatomical buttress plate in treating displaced femoral neck fracture a finite element analysis. Injury. 2019; 50(11):1895-1900.
[26] SENSOZ E, OZKAL FM, ACAR V, et al. Finite element analysis of the impact of screw insertion distal to the trochanter minor on the risk of iatrogenic subtrochanteric fracture. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2018; 232(8):807-818.
[27] ALOLABI B, BAJAMMAL S, SHIRALI J, et al. Treatment of displaced femoral neck fractures in the elderly: a cost-benefit analysis. J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(6):442-446.
[28] DUCKWORTH AD, BENNET SJ, ADERINTO J, et al . Fixation of intracapsular fractures of the femoral neck in young patients: risk factors for failure. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(6):811-816.
[29] SLOBOGEAN GP, SPRAGUE SA, SCOTT T, et al. Complications following young femoral neck fractures. Injury. 2015;46(3):484-491.
[30] SAMSAMI S, SABERI S, SADIGHI S, et al. Comparison of Three Fixation Methods for Femoral Neck Fracture in Young Adults: Experimental and Numerical Investigations. J Med Biol Eng. 2015;35(5):566-579.
[31] LI J, ZHAO Z, YIN P, et al. Comparison of three different internal fixation implants in treatment of femoral neck fracture-a finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):76.
[32] ENOCSON A, LAPIDUS LJ. The vertical hip fracture - a treatment challenge. A cohort study with an up to 9 year follow-up of 137 consecutive hips treated with sliding hip screw and antirotation screw. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012;13:171.
[33] KEMKER B, MAGONE K, OWEN J, et al. A sliding hip screw augmented with 2 screws is biomechanically similar to an inverted triad of cannulated screws in repair of a Pauwels type-III fracture. Injury. 2017; 48(8):1743-1748.
[34] LI J, WANG M, ZHOU J, et al. Optimum Configuration of Cannulated Compression Screws for the Fixation of Unstable Femoral Neck Fractures: Finite Element Analysis Evaluation. Biomed Res Int. 2018; 2018:1271762.
[35] LI J, WANG M, LI L, et al . Finite element analysis of different configurations of fully threaded cannulated screw in the treatment of unstable femoral neck fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):272.
[36] AMINIAN A, GAO F, FEDORIW WW, et al. Vertically oriented femoral neck fractures: mechanical analysis of four fixation techniques. J Orthop Trauma. 2007;21(8):544-548.
[37] BASSO T, KLAKSVIK J, FOSS OA. Locking plates and their effects on healing conditions and stress distribution: A femoral neck fracture study in cadavers. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2014;29(5):595-598.
[38] TIANYE L, PENG Y, JINGLI X, et al. Finite element analysis of different internal fixation methods for the treatment of Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;112:108658.
[39] YE Y, CHEN K, TIAN K, et al. Medial buttress plate augmentation of cannulated screw fixation in vertically unstable femoral neck fractures: Surgical technique and preliminary results. Injury. 2017;48(10): 2189-2193.
[40] WANG G, TANG Y, WU X, et al. Finite element analysis of a new plate for Pauwels type III femoral neck fractures. J Int Med Res. 2020;48(2): 300060520903669.
[41] LUTTRELL K, BELTRAN M, COLLINGE CA. Preoperative decision making in the treatment of high-angle “vertical” femoral neck fractures in young adult patients. An expert opinion survey of the Orthopaedic Trauma Association’s (OTA) membership. J Orthop Trauma. 2014;28(9): e221-225.
[42] COLLINGE CA, MIR H, REDDIX R. Fracture morphology of high shear angle “vertical” femoral neck fractures in young adult patients. J Orthop Trauma. 2014;28(5):270-275.
[43] LI J, WANG M, ZHOU J, et al. Finite element analysis of different screw constructs in the treatment of unstable femoral neck fractures. Injury. 2020;51(4):995-1003.
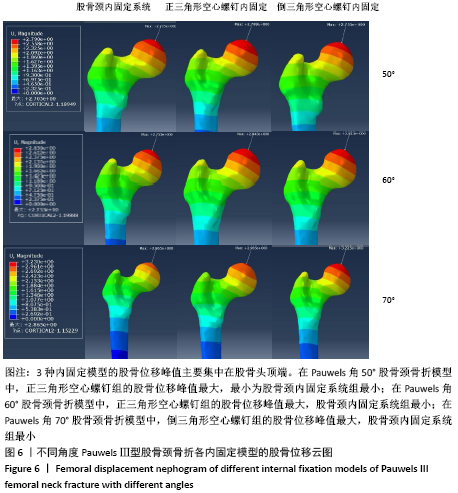
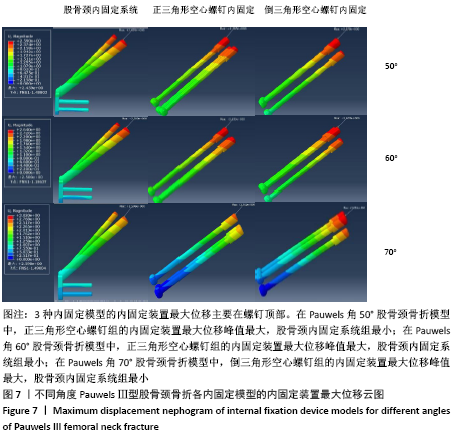
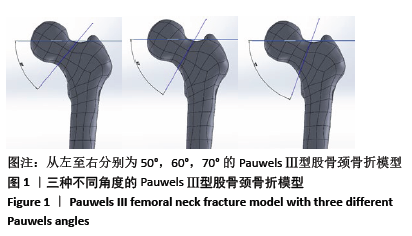
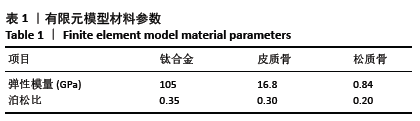
|