| [1] Hou J, Zhong T, Guo T, et al. Apelin promotes mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization under hypoxic-ischemic condition in vitro involving the upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor. Exp Mol Pathol. 2017;102(2):203-209.[2] Narita T, Suzuki K. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of heart failure. Heart Fail Rev. 2015;20(1):53-68.[3] Hou J, Wang L, Hou J, et al. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma Promotes Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Express Connexin43 via the Inhibition of TGF-β1/Smads Signaling in a Rat Model of Myocardial Infarction. Stem Cell Rev. 2015;11(6):885-899.[4] Karpov AA, Udalova DV, Pliss MG, et al. Can the outcomes of mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for myocardial infarction be improved? Providing weapons and armour to cells. Cell Prolif. 2017; 50(2). doi: 10.1111/cpr.12316. [5] Lu L, Wu D, Li L, et al. Apelin/APJ system: A bifunctional target for cardiac hypertrophy. Int J Cardiol. 2017;230:164-170.[6] Liang D, Han D, Fan W, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of apelin on transplanted mesenchymal stem cells in hindlimb ischemic mice via regulation of autophagy. Sci Rep. 2016;6:21914.[7] Zeng X, Yu SP, Taylor T, et al. Protective effect of apelin on cultured rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells against apoptosis. Stem Cell Res. 2012;8(3):357-367.[8] Park JS, Yang HN, Yi SW, et al. Neoangiogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells transfected with peptide-loaded and gene-coated PLGA nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2016;76:226-237.[9] 侯婧瑛,汪蕾,钟婷婷,等, apelin干预骨髓间充质干细胞在缺血缺氧条件下的生存和血管再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2017,21(1): 6-12.[10] Lv B, Hua T, Li F,et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 α protects mesenchymal stem cells against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced injury via autophagy induction and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(5):2492-2499.[11] Shi XF, Wang H, Xiao FJ, et al. MiRNA-486 regulates angiogenic activity and survival of mesenchymal stem cells under hypoxia through modulating Akt signal. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;470(3):670-677.[12] Zou Y, Wang B, Fu W, et al. Apelin-13 Protects PC12 Cells from Corticosterone-Induced Apoptosis Through PI3K and ERKs Activation. Neurochem Res. 2016;41(7):1635-1644.[13] Zhang J, Liu Q, Hu X, et al. Apelin/APJ signaling promotes hypoxia-induced proliferation of endothelial progenitor cells via phosphoinositide-3 kinase/Akt signaling. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(3): 3829-3834.[14] Dicarlo M, Bianchi N, Ferretti C, et al. Evidence Supporting a Paracrine Effect of IGF-1/VEGF on Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Commitment. Cells Tissues Organs. 2016;201(5):333-341.[15] Hou J, Long H, Zhou C, et al. Long noncoding RNA Braveheart promotes cardiogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):4.[16] 伍权华,侯婧瑛,郭天柱,等.吡格列酮联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗改善大鼠心肌梗死后的心功能[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(23):3698-3704.[17] 晏平,侯婧瑛,郑韶欣,等.过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ促进外源性骨髓间充质干细胞表达Cx43的作用及机制干细胞表达Cx43的作用及机制[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(23):3357-3365.[18] Ji ST, Kim H, Yun J, et al. Promising Therapeutic Strategies for Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Cardiovascular Regeneration: From Cell Priming to Tissue Engineering. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:3945403.[19] Li L, Li L, Zhang Z, et al. Hypoxia promotes bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell proliferation through apelin/APJ/autophagy pathway. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2015;47(5):362-367.[20] Li L, Zeng H, Chen JX. Apelin-13 increases myocardial progenitor cells and improves repair postmyocardial infarction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012;303(5):H605-618.[21] Tempel D, de Boer M, van Deel ED, et al. Apelin enhances cardiac neovascularization after myocardial infarction by recruiting aplnr+ circulating cells. Circ Res. 2012;111(5):585-598.[22] Kuchroo P, Dave V, Vijayan A, et al. Paracrine factors secreted by umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells induce angiogenesis in vitro by a VEGF-independent pathway. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(4): 437-450.[23] Rud'ko AS, Efendieva MK, Budzinskaya MV, et al. Influence of vascular endothelial growth factor on angiogenesis and neurogenesis. Vestn Oftalmol. 2017;133(3):75-81.[24] Crafts TD, Jensen AR, Blocher-Smith EC, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor: therapeutic possibilities and challenges for the treatment of ischemia. Cytokine. 2015;71(2):385-393.[25] Pedersen TO, Blois AL, Xue Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells induce endothelial cell quiescence and promote capillary formation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(1):23.[26] Mykhaylichenko VY, Kubyshkin AV, Samarin SA, et al. Experimental induction of reparative morphogenesis and adaptive reserves in the ischemic myocardium using multipotent mesenchymal bone marrow-derived stem cells. Pathophysiology. 2016;23(2):95-104.[27] Tang Y, Gan X, Cheheltani R, et al. Targeted delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor improves stem cell therapy in a rat myocardial infarction model. Nanomedicine. 2014;10(8):1711-1718.[28] Liu G, Li L, Huo D, et al. A VEGF delivery system targeting MI improves angiogenesis and cardiac function based on the tropism of MSCs and layer-by-layer self-assembly. Biomaterials. 2017;127:117-131. [29] Ikhapoh IA, Pelham CJ, Agrawal DK. Atherogenic Cytokines Regulate VEGF-A-Induced Differentiation of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Endothelial Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2015;2015:498328.[30] Xing Y, Hou J, Guo T, et al. microRNA-378 promotes mesenchymal stem cell survival and vascularization under hypoxic-ischemic conditions in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(6):130.[31] Yu JS, Cui W. Proliferation, survival and metabolism: the role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling in pluripotency and cell fate determination. Development. 2016;143(17):3050-3060.[32] Bader AM, Klose K, Bieback K, et al. Hypoxic Preconditioning Increases Survival and Pro-Angiogenic Capacity of Human Cord Blood Mesenchymal Stromal Cells In Vitro. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0138477.[33] Ma J, Zhao Y, Sun L, et al. Exosomes Derived from Akt-Modified Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improve Cardiac Regeneration and Promote Angiogenesis via Activating Platelet-Derived Growth Factor D. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(1):51-59.[34] Jia X, Pan J, Li X, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate angiogenesis and renal damage via promoting PI3k-Akt signaling pathway activation in vivo. Cytotherapy. 2016;18(7):838-845.[35] Huang C, Dai C, Gong K, et al. Apelin-13 protects neurovascular unit against ischemic injuries through the effects of vascular endothelial growth factor. Neuropeptides. 2016;60:67-74. |
.jpg)
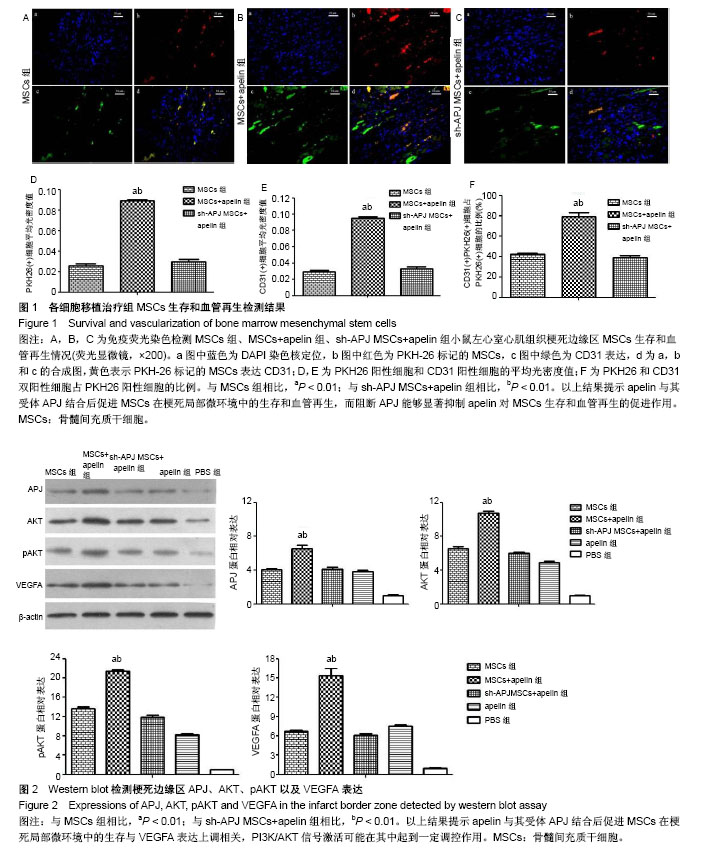
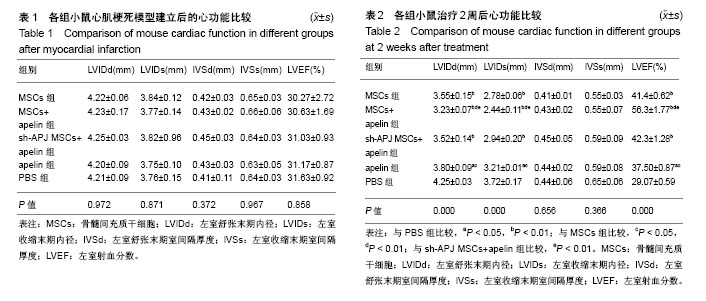
.jpg)