| [1] Dorfman GS.Percutaneous inferior vena caval filters. Radiology.1990;174(2):987-992.[2] Kaufman JA, Kinney TB, Streiff MB,et al.Guidelines for the use of retrievable and convertible vena cava filters: report from the Society of Interventional Radiology multidisciplinary consensus conference.J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2006;17(3): 449-459.[3] Shah AH,Lichliter A,Cura M.Inferior vena cava filter removal after prolonged dwell time of 2310 days.Proc(Bayl Univ Med Cent).2016;29(3):292-294.[4] Reis SP,Kovoor J,Sutphin PD,et al.Safety and Effectiveness of the Denali Inferior Vena Cava Filter: Intermediate Follow-Up Results.Vasc Endovascular Surg.2016;50(6):.[5] Stavropoulos SW,Chen JX,Sing RF,et al.Analysis of the Final DENALI Trial Data: A Prospective, Multicenter Study of the Denali Inferior Vena Cava Filter.J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2016; 27(10):1531-1538.e1.[6] 高喜翔,张建,陈兵,等.ε-己内酯与L-丙交酯共聚物降解性能及其生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2010,14(47):8791-8794.[7] 高喜翔,张建,陈兵,等.超声波对高分子材料降解过程启动的控制[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(30):4868-4872.[8] Ferris EJ,McCowan TC,Carver DK,et al.Percutaneous inferior vena caval filters: follow-up of seven designs in 320 patients. Radiology.1993;188:851-856.[9] The PREPIC Study Group.Eight-Year Follow-Up of Patients With Permanent Vena Cava Filters in the Prevention of Pulmonary Embolism: The PREPIC (Prévention du Risque d’Embolie Pulmonaire par Interruption Cave) Randomized Study.Circulation.2005;112:416-422.[10] Jaff MR,Goldhaber SZ,Tapson VF.High utilization of vena cava filters in deep venous thrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 2005;93:1117-1119.[11] Passman MA.Complications of inferior vena cava filters.J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2017;5(1):7.[12] Byrne M,Mannis GN,Nair J,et al.Inferior vena cava filter thrombosis.Clin Case Rep.2016; 4(2):162-164.[13] Wang SL,Siddiqui A,Rosenthal E.Long-term complications of inferior vena cava filters.J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2017;5(1):33.[14] Sarosiek S,Rybin D,Weinberg J,et al.Association Between Inferior Vena Cava Filter Insertion in Trauma Patients and In-Hospital and Overall Mortality.Jama Surg.2016;152(1):75.[15] Mohan CR,Hoballah JJ,Sharp WJ,et al. Comparative efficacy and complications of vena caval filters. J Vasc Surg. 1995;21: 235-245.[16] Stein P,Kayali F,Olson R.Twenty-one-year trends in the use of inferior vena cava filters.Arch Intern Med. 2004;164: 1541-1545.[17] Athanasoulis C,Kaufman J,Halpern E,et al.Inferior vena caval filters: review of a 26-year single-center clinical experience. Radiology.2000;216:54-66.[18] Bovyn G,Ricco JB,Reynaud P,et al.Long-duration temporary vena cava filter: A prospective 104-case multicenter study.J Vasc Surg.2006;43:1222-1229.[19] Grassi CJ.Inferior vena caval filters: Analysis of five currently available devices.AJR.1991; 156:813-821.[20] Neuerburg J,Gtinther RW.Developments in inferior vena cava filters: A European viewpoint.Semin lntervent Radiol. 1994; 11(4):349-357.[21] Kinney TB.Update on inferior vena cava filters.J Vasc Interv Radiol.2003;14:425-440.[22] Joels CS,Sing RF,Heniford BT.Complications of inferior vena cava filters.Am Surg.2003;69:654–659.[23] Ju NR,Conlon LW.Inferior Vena Cava Filter Migration.J Emerg Med.2015;50(3):e151-e153.[24] Streiff MB.Vena caval filers: a comprehensive review.Blood. 2000;95:3669-3677.[25] Shelgikar C,Mohebali J,Sarfati MR,et al.A design modification to minimize tilting of an inferior vena cava filter does not deliver a clinical benefit.J Vas Surg.2010;52(4):920.[26] Matsui Y,Horikawa M,Ohta K,et al.Mechanisms of Günther Tulip filter tilting during transfemoral placement.Diagn Interv Imaging.2017;98(7-8):543.[27] Kuyumcu G,Walker TG.Inferior vena cava filter retrievals, standard and novel techniques.Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2016; 6(6):642.[28] Owens CA,Bui JT,Knuttinen MG,et al.Intracardiac migration of inferior vena cava filters: review of published data. Chest. 2009;136:877-887.[29] Hideo T,Keiji I,Eisho K,et al.Initial and 6-Month Results of Biodegradable Poly-l-Lactic Acid Coronary Stents in Humans. Circulation.2000;102:399-403.[30] Piskin E.Biodegradable polymers as biomaterials.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.1994;6:775-795.[31] Valimaa T,Laaksovirta S.Degradation behaviour of self-reinforced 80L/20G PLGA devices in vitro. Biomaterials. 2004;25(7-8):1225-1232.[32] Wong YS,Xiong Y,Venkatraman SS,et al.Shape memory in un-cross-linked biodegradable polymers. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2008;19(2):175-191.[33] Pego APGM.Biodegradable polymers based on trimethylene carbonate for tissue engineering applications.2017.[34] Kozlovskiy R,Shvets V,Kuznetsov A.Technological aspects of the production of biodegradable polymers and other chemicals from renewable sources using lactic acid.J Clean Prod.2017.DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.08.092[35] Fuf? O,Fuf O,Vl?sceanu GM,et al.Nanostructurated Composites Based on Biodegradable Polymers and Silver Nanoparticles[M]//Handbook of Composites from Renewable Materials,2017. |
.jpg)
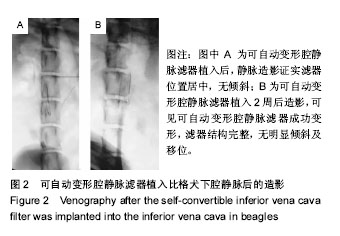
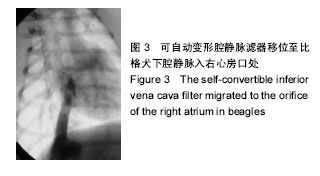
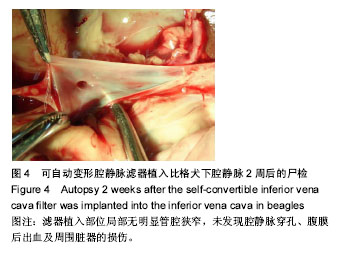
.jpg)
.jpg)