中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (12): 1928-1933.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0834
• 组织构建细胞学实验 cytology experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
细胞凋亡和丙二醛在长时间大强度运动模型大鼠骨骼肌中的表达
马 雪,胡亚哲
- 华中师范大学体育学院,湖北省武汉市 430079
Cell apoptosis and expression of malondialdehyde in the skeletal muscle in a model rat undergoing long-term and high-intensity exercise
Ma Xue, Hu Ya-zhe
- School of Physical Education, Central China Normal University, Wuhan 430079, Hubei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
丙二醛(MDA):丙二醛是膜脂过氧化最重要的产物之一,在体外影响线粒体呼吸链复合物及线粒体内关键酶活性。在中性条件下稳定,但在酸性条件下不稳定。在生物体内,自由基作用于脂质发生过氧化反应,氧化终产物为丙二醛,它能加剧膜的损伤,可通过丙二醛了解膜脂过氧化的程度,以间接测定膜系统受损程度。
超氧化物歧化酶(SOD):超氧化物歧化酶是一种源于生命体的活性物质,能消除生物体在新陈代谢过程中产生的有害物质。对人体不断地补充超氧化物歧化酶具有抗衰老的特殊效果。它能催化过氧阴离子发生歧化反应的性质,所以正式将其命名为超氧化物歧化酶。
文题释义:
丙二醛(MDA):丙二醛是膜脂过氧化最重要的产物之一,在体外影响线粒体呼吸链复合物及线粒体内关键酶活性。在中性条件下稳定,但在酸性条件下不稳定。在生物体内,自由基作用于脂质发生过氧化反应,氧化终产物为丙二醛,它能加剧膜的损伤,可通过丙二醛了解膜脂过氧化的程度,以间接测定膜系统受损程度。
超氧化物歧化酶(SOD):超氧化物歧化酶是一种源于生命体的活性物质,能消除生物体在新陈代谢过程中产生的有害物质。对人体不断地补充超氧化物歧化酶具有抗衰老的特殊效果。它能催化过氧阴离子发生歧化反应的性质,所以正式将其命名为超氧化物歧化酶。
.jpg) 文题释义:
丙二醛(MDA):丙二醛是膜脂过氧化最重要的产物之一,在体外影响线粒体呼吸链复合物及线粒体内关键酶活性。在中性条件下稳定,但在酸性条件下不稳定。在生物体内,自由基作用于脂质发生过氧化反应,氧化终产物为丙二醛,它能加剧膜的损伤,可通过丙二醛了解膜脂过氧化的程度,以间接测定膜系统受损程度。
超氧化物歧化酶(SOD):超氧化物歧化酶是一种源于生命体的活性物质,能消除生物体在新陈代谢过程中产生的有害物质。对人体不断地补充超氧化物歧化酶具有抗衰老的特殊效果。它能催化过氧阴离子发生歧化反应的性质,所以正式将其命名为超氧化物歧化酶。
文题释义:
丙二醛(MDA):丙二醛是膜脂过氧化最重要的产物之一,在体外影响线粒体呼吸链复合物及线粒体内关键酶活性。在中性条件下稳定,但在酸性条件下不稳定。在生物体内,自由基作用于脂质发生过氧化反应,氧化终产物为丙二醛,它能加剧膜的损伤,可通过丙二醛了解膜脂过氧化的程度,以间接测定膜系统受损程度。
超氧化物歧化酶(SOD):超氧化物歧化酶是一种源于生命体的活性物质,能消除生物体在新陈代谢过程中产生的有害物质。对人体不断地补充超氧化物歧化酶具有抗衰老的特殊效果。它能催化过氧阴离子发生歧化反应的性质,所以正式将其命名为超氧化物歧化酶。摘要
背景:骨骼肌细胞凋亡会导致多种骨骼肌疾病的出现,常规疗法效果都不太理想。
目的:分析不同强度运动对大鼠骨骼肌形态结构和细胞凋亡的影响,可以起到预防骨骼肌细胞凋亡的作用。
方法:健康3月龄雄性SD大鼠30只随机分为3组:安静对照组、一般有氧运动组和长时间大强度运动组。安静对照组不进行游泳运动,运动组运用游泳运动制备动物模型,运动组的训练周期都为10周,10周后对大鼠全部实施麻醉后取腓肠肌,用以苏木精-伊红染色观察骨骼肌形态和TUNEL检测细胞凋亡情况;并检测骨骼肌组织超氧化物歧化酶、丙二醛含量,做丙二醛与积分吸光度的相关分析。
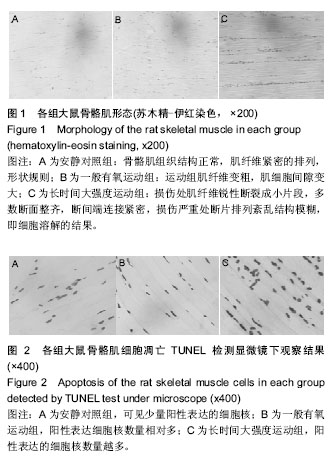
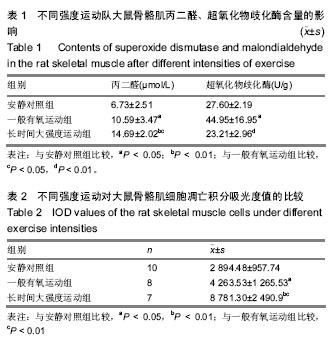
结果与结论:①骨骼肌苏木精-伊红染色结果:长时间大强度运动组肌纤维排列紊乱、结构模糊;②丙二醛和超氧化物歧化酶含量:与安静对照组相比,一般有氧运动组、长时间大强度运动组的丙二醛增加,一般有氧运动组与安静对照组相比较超氧化物歧化酶有显著性增加(P < 0.05),长时间大强度运动组与有氧组相比较超氧化物歧化酶显著性减少(P < 0.05);③TUNEL检测结果:长时间大强度运动组细胞凋亡积分吸光度值显著高于一般有氧运动组和安静对照组(P < 0.01);④相关分析:丙二醛与积分吸光度值之间显著相关,呈正相关关系;⑤结果说明,长时间大强度运动组骨骼肌组织中的长丙二醛增多,机体疲劳程度更为严重。有氧运动使机体骨骼肌逐渐有适应性,而由于过度运动负荷较大,对骨骼肌形态结构有一定损伤,使得细胞凋亡增加。随着运动强度增加导致丙二醛生成增加而清除相对不足,细胞凋亡积分吸光度值增大。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-5279-2423(马雪)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
丙二醛(MDA):丙二醛是膜脂过氧化最重要的产物之一,在体外影响线粒体呼吸链复合物及线粒体内关键酶活性。在中性条件下稳定,但在酸性条件下不稳定。在生物体内,自由基作用于脂质发生过氧化反应,氧化终产物为丙二醛,它能加剧膜的损伤,可通过丙二醛了解膜脂过氧化的程度,以间接测定膜系统受损程度。
超氧化物歧化酶(SOD):超氧化物歧化酶是一种源于生命体的活性物质,能消除生物体在新陈代谢过程中产生的有害物质。对人体不断地补充超氧化物歧化酶具有抗衰老的特殊效果。它能催化过氧阴离子发生歧化反应的性质,所以正式将其命名为超氧化物歧化酶。
文题释义:
丙二醛(MDA):丙二醛是膜脂过氧化最重要的产物之一,在体外影响线粒体呼吸链复合物及线粒体内关键酶活性。在中性条件下稳定,但在酸性条件下不稳定。在生物体内,自由基作用于脂质发生过氧化反应,氧化终产物为丙二醛,它能加剧膜的损伤,可通过丙二醛了解膜脂过氧化的程度,以间接测定膜系统受损程度。
超氧化物歧化酶(SOD):超氧化物歧化酶是一种源于生命体的活性物质,能消除生物体在新陈代谢过程中产生的有害物质。对人体不断地补充超氧化物歧化酶具有抗衰老的特殊效果。它能催化过氧阴离子发生歧化反应的性质,所以正式将其命名为超氧化物歧化酶。