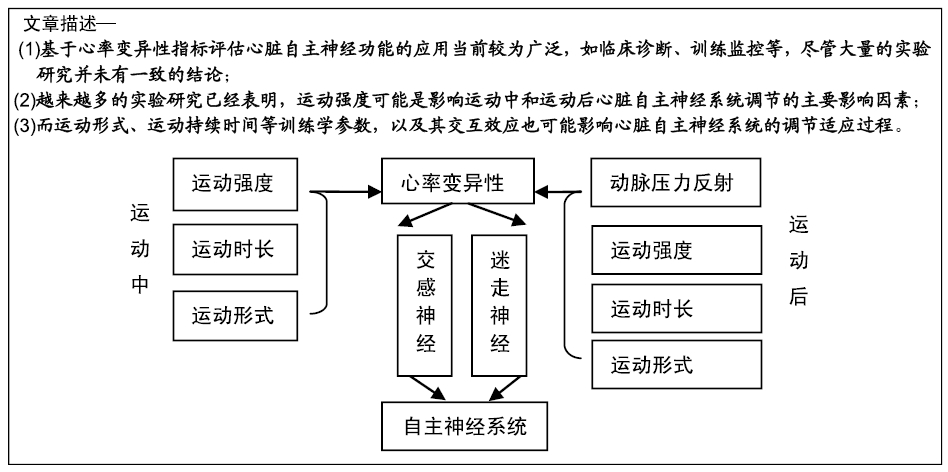
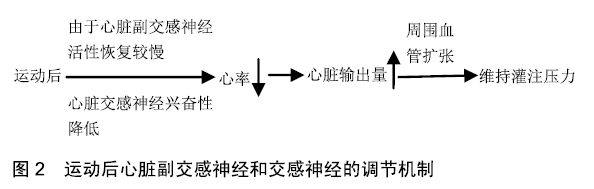
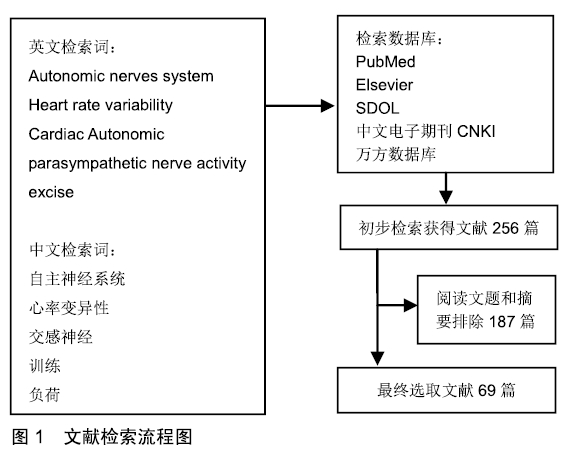
[1] POWELL C, HERRING MP, DOWD KP, et al. The cross-sectional associations between objectively measured sedentary time and cardiometabolic health markers in adults-a systematic review with meta-analysis component. Obesity Reviews. 2017;19(3):381-386.
[2] BERMEJO CA, ÁLVAREZ BC, MARTINEZ VV, et al. Association between physical activity, sedentary behavior, and fitness with health related quality of life in healthy children and adolescents: A protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(12):e6407.
[3] 马继政,孙飙,吕远远.运动性心肌肥大大鼠心肌蛋白差异表达研究[J].西安体育学院学报,2010,27(2):202-205.
[4] 马继政,牛洁.大强度间歇训练心肌细胞分子适应机制[J].体育科技文献通报,2010,18(3):33-34.
[5] 马继政,张仁祥,谷波,等.大强度间歇训练研究与进展[J].南京体育学院学报(自然科学版) ,2013,12(4):8-14.
[6] 马继政. 运动诱导心脏保护机制[J].辽宁体育科技, 2009,31(3):29-31.
[7] 马继政,孙飙,吕远远. IGF-PI3K-Akt信号通路在生理性心肌肥大中的作用研究进展[J].南京体育学院学报(自然科学版) , 2007,6(3):6-10.
[8] CIPRYAN L.The effect of fitness level on cardiac autonomic regulation, IL-6, total antioxidant capacity, and muscle damage responses to a single bout of high-intensity interval training.J Sport Health Sci.2018; 7(3):363-371.
[9] 孙飙,马继政.直立位递增运动负荷时左室收缩期血流动力学变化[J].中国康复医学杂志,2003,18(12):44-47.
[10] 马继政,孙飙,牛洁.有氧运动和左室的舒张功能[J].中国临床康复, 2004, 5(6):1138-1139.
[11] MICHAEL S, GRAHAM KS, DAVIS GM OAM. Cardiac Autonomic Responses during Exercise and Post-exercise Recovery Using Heart Rate Variability and Systolic Time Intervals-A Review.Front Physiol, 2017,29(8):301-307.
[12] HANSEN J, SANDER M, HALD CF, et al. Metabolic modulation of sympathetic vasoconstriction in human skeletal muscle: role of tissue hypoxia. Jour Physio.2010; 527(2):387-396.
[13] MICHELINI LC, O'LEARY DS, RAVEN PB, et al.Neural control of circulation and exercise: a translational approach disclosing interactions between central command, arterial baroreflex, and muscle metaboreflex[J]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015; 309(3): H381-392.
[14] MUELLER PJ, CLIFFORD PS, CRANDALL CG, et al. Integration of Central and Peripheral Regulation of the Circulation during Exercise: Acute and Chronic Adaptations. Compr Physiol. 2017;8(1):103-151.
[15] FISHER JP, YOUNG CN, FADEL PJ. Autonomic adjustments to exercise in humans.Compre Physiol, 2015; 5:475-512.
[16] TSUCHIMOCHI H, MATSUKAWA K, KOMINE H, et al. Direct measurement of cardiac sympathetic efferent nerve activity during dynamic exercise. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2002;283(5): H1896-1906.
[17] 孙飙,马继政.递增运动负荷时男性青年左室舒张期血流动力学变化[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2003,22(6):548-552.
[18] 马继政,孙飙,张爱军,等. 运动负荷递增时优秀运动员心输出量和摄氧量之间关系的研究[J].南京体育学院学报(自然科学版), 2007, 6(2):7-10.
[19] VESTERINEN V, NUMMELA A, LAINE T, et al.A Sub-maximal Running Test With Post-exercise Cardiac Autonomic and Neuromuscular Function in Monitoring Endurance Training Adaptation.J Strength Cond Res.2017; 31(1):233-243.
[20] TAKAHASHI M, MATSUKAWA K, NAKAMOTO T, et al. Control of heart rate variability by cardiac parasympathetic nerve activity during voluntary static exercise in humans with tetraplegia.J Appl Physiol. 2007;103(5): 1669-1677.
[21] 胡斐,王金之,黄佩玲,等.不同负重量站立30 min对健康青年心脏自主神经功能产生的影响[J].中国应用生理学杂志, 2017,33(2):193-196.
[22] 王增刚,胡斐,徐盛嘉,等. 18 km中等强度负重行军对心脏自主神经功能产生的影响[J].军事体育学报, 2018,37(1):118-121.
[23] 于文兵,高丽丽,李天义,等. 三种力量训练方案对健康青年心脏自主神经功能的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2017,32(5):548-553.
[24] 胡斐,徐盛嘉,王晓磊,等.力量和耐力组合训练对青年男性心脏自主神经功能影响的研究[J].辽宁体育科技,2018,40(2):48-53.
[25] 胡斐,徐盛嘉,沈铭彬,等. 大强度的无氧间歇练习、有氧耐力练习及其组合练习的次序对恢复期心脏自主神经功能的影响[J].体育科研, 2017,38(6): 87-92.
[26] FU Q, LEVINE BD.Exercise and the autonomic nervous system[M]. Handb Clin Neurol.2013;117(117C):147-160.
[27] ROSENWINKEL ET, BLOOMFIELD DM, ARWADY MA, et al. Exercise and autonomic function in health and cardiovascular disease. Cardiol Clin.2001;19(3):369-87.
[28] KAIKKONEN P, NUMMELA A, RUSKO H. Heart rate variability dynamics during early recovery after different endurance exercises. Eur J Appl Physiol.2007;102(1):79-86.
[29] PICHON AP, DE BISSCHOP C, ROULAUD M, et al. Spectral analysis of heart rate variability during exercise in trained subjects. Med Sci Sports Exerc.2004;36(10):1702-1708.
[30] RANADIVE SM, FAHS CA, YAN H, et al. Heart rate recovery following maximal arm and leg-ergometry. Clin Auton Res. 2011;21(2):117-120.
[31] LEICHT AS, SINCLAIR WH, SPINKS WL. Effect of exercise mode on heart rate variability during steady state exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2008; 102(2):195-204.
[32] TULPPO MP, MÄKIKALLIO TH, LAUKKANEN RT, et al. Differences in autonomic modulation of heart rate during arm and leg exercise. Clin Physiol.1999;19(4):294-299.
[33] COTTIN F, DURBIN F, PAPELIER Y. Heart rate variability during cycloergometric exercise or judo wrestling eliciting the same heart rate level. Eur J Appl Physiol.2004;91(2-3):177-184.
[34] GONZÁLEZ-CAMARENA R, CARRASCO-SOSA S, ROMÁN-RAMOS R, et al. Effect of static and dynamic exercise on heart rate and blood pressure variabilities. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2000;32(10):1719-1728.
[35] WEIPPERT M, BEHRENS M, GONSCHOREK R, et al. Muscular contraction mode differently affects autonomic control during heart rate matched exercise. Front Physiol. 2015;19(6):156-167.
[36] BUCHHEIT M. Monitoring training status with HR measures: do all roads lead to Rome. Front Physiol.2014; 27(5):73-80.
[37] BLAIN G, MESTE O, BOUCHARD T, et al. Assessment of ventilatory thresholds during graded and maximal exercise test using time varying analysis of respiratory sinus arrhythmia.Br J Sports Med.2005;39(7): 448-452.
[38] FADEL PJ. Reflex control of the circulation during exercise. Scand J Med Sci Sports.2015;4(25):74-82.
[39] COOTE JH. Recovery of heart rate following intense dynamic exercise. Exp Physiol.2010;95(3):431-440.
[40] PEÇANHA T, SILVA-JÚNIOR ND, FORJAZ CL. Heart rate recovery: autonomic determinants, methods of assessment and association with mortality and cardiovascular diseases. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2014; 34(5):327-339.
[41] MICHAEL S, JAY O, HALAKI M, et al. Submaximal exercise intensity modulates acute post-exercise heart rate variability. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2016;116(4):697-706.
[42] HAUTALA A,TULPPO MP,MÄKIKALLIO TH,et al.Changes in cardiac autonomic regulation after prolonged maximal exercise. Clin Physiol. 2001;21(2):238-45.
[43] FISHER JP, SEIFERT T, HARTWICH D, et al. Autonomic control of heart rate by metabolically sensitive skeletal muscle afferents in humans. J Physiol.2010; 588(7):1117-1127.
[44] VIVEKANANTHAN DP, BLACKSTONE EH, POTHIER CE, et al. Heart rate recovery after exercise is a predictor of mortality, independent of the angiographic severity of coronary disease.J Am Coll Cardiol.2003; 42(5):831-838.
[45] ROMERO SA , MINSON CT, HALLIWILL JR. The cardiovascular system after exercise. J Appl Physiol.2017;122(4):925-932.
[46] 马继政,孙飙,牛洁,等. 恒定负荷运动中和运动后左室舒张功能的变化[J].体育学刊, 2004,11(2):132-135.
[47] PEÇANHA T, BARTELS R, BRITO L C, et al. Methods of assessment of the post-exercise cardiac autonomic recovery: A methodological review. Int J Cardiol.2017;227(15):795-802.
[48] CASONATTO J, GOESSLER KF, CORNELISSEN VA, et al. The blood pressure-lowering effect of a single bout of resistance exercise: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2016, 23(16):1700-1714.
[49] CASONATTO J,TINUCCI T, DOURADO AC, et al. Cardiovascular and autonomic responses after exercise sessions with different intensities and durations. Clinics.2011;66(3):453-458.
[50] NIEMELÄ TH, KIVINIEMI AM, HAUTALA AJ, et al. Recovery pattern of baroreflex sensitivity after exercise. Med Sci Sport Exerc. 2008;40(5): 864-870.
[51] 马继政. PGC-1α、运动与心肌能量代谢[J].贵州体育科技, 2009,(4):42-46.
[52] AHMADIAN M, ROSHAN VD, HOSSEINZADEH M. Parasympathetic reactivation in children: influence of two various modes of exercise. Clin Auton Res.2015;25(4):207-212.
[53] STANLEY J, PEAKE JM, BUCHHEIT M . Cardiac Parasympathetic Reactivation Following Exercise: Implications for Training Prescription. Sports Med.2013;43(12):1259-1277.
[54] MICHAEL S, JAY O, HALAKI M, et al. Submaximal exercise intensity modulates acute post-exercise heart rate variability. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2016;116(4):697-706.
[55] 巩绪伟,王增刚,胡斐,等. 两种运动形式对健康青年心脏自主神经系统功能产生的运动效果[R].杭州:中华人民共和国第十三届学生运动会科学论文报告会,2017,9.
[56] SEILER S, HAUGEN O, KUFFEL E. Autonomic recovery after exercise in trained athletes: intensity and duration effects. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007;39(8):1366-1373.
[57] CASONATTO J, TINUCCI T, DOURADO AC, et al. Cardiovascular and autonomic responses after exercise sessions with different intensities and durations. Clinics.2011;66(3):453-458.
[58] KAIKKONEN P, NUMMELA A, RUSKO H. Heart rate variability dynamics during early recovery after different endurance exercises. Eur J Appl Physiol.2007;102(1):79-86.
[59] KAIKKONEN P, HYNYNEN E, MANN T, et al. Can HRV be used to evaluate training load in constant load exercises. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010; 108(3):435-342.
[60] CUNHA FA, MIDGLEY AW, GONÇALVES T, et al. Parasympathetic reactivation after maximal CPET depends on exercise modality and resting vagal activity in healthy men. Springerplus.2015;27(4):100-110.
[61] 马继政,徐盛嘉,丁明超,等.基本运动训练原则在促进新入校大学生基础运动技能方面的实践研究[J].体育科技, 2018(2):136-142.
[62] BELLENGER CR, FULLER JT, THOMSON RL, et al. Monitoring Athletic Training Status Through Autonomic Heart Rate Regulation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med.2016;46(10): 1461-1486
[63] NELSON MJ, THOMSON RL, ROGERS DK, et al. Maximal rate of increase in heart rate during the rest-exercise transition tracks reductions in exercise performance when training load is increased. J Sci Med Sport.2014; 17:129–133.
[64] PANISSA VL, CAL ABAD CC, JULIO UF, et al. High-Intensity Intermittent Exercise and its Effects on Heart Rate Variability and Subsequent Strength Performance. Front Physiol. 2016;7:81-91.
[65] BUCHHEIT M. Monitoring training status with HR measures: do all roads lead to Rome?.Front Physiol.2014;5:73-82.
[66] 马继政,丁明超,黄强年. 现役人员人类能力最佳化——训练负荷的监控策略[J].湖北体育科技,2018,37(5):426-429.
[67] STANLEY J, PEAKE JM, BUCHHEIT M. Cardiac parasympathetic reactivation following exercise: implications for training prescription. Sports Med.2013;43(12):1259-1277.
[68] BUCHHEIT M, LAURSEN PB, AHMAIDI S. Parasympathetic reactivation after repeated sprint exercise. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007;293(1):H133-141
[69] LA GERCHE A, GEWILLIG M. What Limits Cardiac Performance during Exercise in Normal Subjects and in Healthy Fontan Patients. Int J Pediatr.2010;331(5):1-7.
|