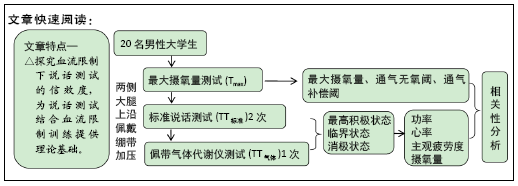
[1] 盛菁菁,魏文哲,沈勇伟.加压运动原理及运用的研究进展[J].体育科研, 2018,39(5):92-99.
[2] 魏佳, 李博, 杨威, 等. 血流限制训练的应用效果与作用机制[J]. 体育科学, 2019,39(4):71-80.
[3] LOPES KG, BOTTINO DA, FARINATTI P, et al. Strength training with blood flow restriction - a novel therapeutic approach for older adults with sarcopenia? A case report. Clin Interv Aging. 2019;14:1461-1469.
[4] Vanwye WR, Weatherholt AM, Mikesky AE. Blood Flow Restriction Training: Implementation into Clinical Practice. Int J Exerc Sci. 2017;10(5):649-654.
[5] 王菲. 有关加压抗阻训练对心血管系统影响的Meta分析及实证研究 [D]. 上海:上海体育学院,2015.
[6] 李志远, 赵之光, 王明波, 等. 4周加压训练对男子手球运动员身体成分和最大力量的影响[J]. 中国体育科技,2019,55(5):37-43.
[7] BENNETT H, SLATTERY F. Effects of Blood Flow Restriction Training on Aerobic Capacity and Performance: A Systematic Review. J Strength Cond Res. 2019; 33(2):572-583.
[8] PARK S, KIM JK, CHOI HM, et al. Increase in maximal oxygen uptake following 2-week walk training with blood flow occlusion in athletes. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010;109(4):591-600.
[9] 盛菁菁, 魏文哲, 孙科, 等. 加压状态下慢速下坡步行的生理负荷与增肌效果研究[J]. 中国体育科技,2019,55(3):13-19.
[10] 魏文哲, 孙科, 赵之光, 等. 不同程度的血流限制对递增速度跑运动中心肺功能的影响[J]. 中国体育科技,2019,55(5):8-13.
[11] PATTERSON SD, HUGHES L, WARMINGTON S, et al. Blood Flow Restriction Exercise:Considerations of Methodology, Application, and Safety. Front Physiol. 2019;10:533.
[12] URSPRUNG WM. The Effects of Blood Flow Restriction Training on VO2Max and 1.5 Mile Run Performance. San Antonio, Texas: Texas A and M University-San Antonio. 2016:29-41.
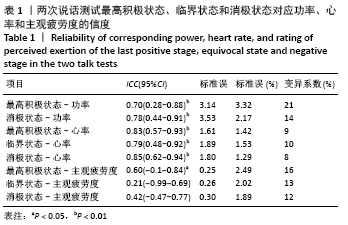
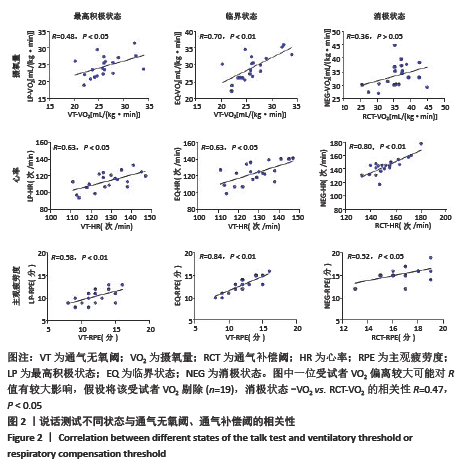
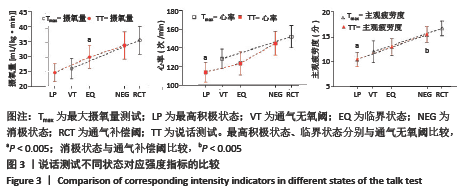
[13] 顾正秋, 徐飞, 魏佳, 等. 说话测试:运动处方强度制定指标的便捷选择[J]. 体育科学,2019,39(12):54-61.
[14] FOSTER C, JOHN PP, SARAH A, et al. Exercise prescription when there is no exercise test: the talk test. Kinesiology. 2018;(Suppl.1):33-48.
[15] FOSTER C, PORCARI JP, ANDERSON J, et al. The talk test as a marker of exercise training intensity. J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev. 2008;28(1):24-30.
[16] VOELKER SA, FOSTER C, JOHN PP, et al. Relationship between the talk test and ventilatory threshold in cardiac patients. Clinical exercise physiology. 2002;(4): 120-123.
[17] GILLESPIE BD, MCCORMICK JJ, MERMIER CM, et al. Talk test as a practical method to estimate exercise intensity in highly trained competitive male cyclists. J Strength Cond Res. 2015;29(4):894-898.
[18] NIELSEN SG, BUUS L, HAGE T, et al. The graded cycling test combined with the talk test is reliable for patients with ischemic heart disease. J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev. 2014;34(4):276-280.
[19] KRAWCYK RS, ANDERS V, PETERSEN NC, et al. “Graded Cycling Test with Talk Test” Is a Reliable Test to Monitor Cardiovascular Fitness in Patients with Minor Stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017;26(3):494-499.
[20] WOLTMANN ML, FOSTER C, PORCARI JP, et al. Evidence that the talk test can be used to regulate exercise intensity. J Strength Cond Res. 2015;29(5):1248-1254.
[21] LOENNEKE JP, FAHS CA, ROSSOW LM, et al. Effects of cuff width on arterial occlusion: implications for blood flow restricted exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2012;112(8):2903-2912.
[22] GREEN JM, CREWS TR, BOSAK AM, et al. Overall and differentiated ratings of perceived exertion at the respiratory compensation threshold: effects of gender and mode. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2003;89(5):445-450.
[23] VILLAMIL CJ, CAMBLOR PM, VALLE DM. Validity of the modified conconi test for determining ventilatory threshold during on-water rowing. J Sports Sci Med. 2011;10(4):616-623.
[24] 中华人民共和国中央人民政府. 中华人民共和国宪法 [EB/OL]. http://wenku.cyjzzd.com/a/130035##wk-more
[25] Marín PJ, Lozano AS, Medeiros FS, et al. Reliability and validity of the OMNI-vibration exercise scale of perceived exertion.J Sports Sci Med. 2012;11(3):438-443.
[26] CASAMICHANA D, CASTELLANO J, GONZALEZ JC, et al. Relationship between indicators of training load in soccer players.J Strength Cond Res. 2013;27(2):369-374.
[27] NIELSEN SG, VINTHER A. Graded cycling test combined with the talk test is responsive in cardiac rehabilitation. J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev. 2016;36(5): 368-374.
[28] JEANES EM, JEANS EA, FOSTER C, et al. Translation of exercise testing to exercise prescription using the talk test. J Strength Cond Res. 2011;25(3):590-596.
[29] BALLWEG J, FOSTER C, JOHN P, et al. Reliability of the talk test as a surrogate of ventilatory and respiratory compensation thresholds .J Sports Sci Med. 2013;12(3):610-611.
[30] MARROYO RJ, VILLA JG, GARC AJ, et al. Relationship between the talk test and ventilatory thresholds in well-trained cyclists. J Strength Cond Res. 2013; 27(7):1942-1949.
[31] EMANUEL IH A. Rating of Perceived Effort: Methodological Concerns and Future Directions.Sports Med. 2020;50(4):679-687.
[32] ASSA T, GEVA N, ZARKH Y, et al. The type of sport matters: Pain perception of endurance athletes versus strength athletes. Eur J Pain. 2019;23(4):686-696.
[33] PERSINGER R, FOSTER C, GIBSON M, et al. Consistency of the Talk Test for Exercise Prescription. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2004;36(9):1632-1636.
[34] BEVERLEY MD, FOSTER C, PORCARI JP, et al. Relationship between the talk test and ventilatory threshold. Journal of Cardiopulmonary Rehabilitation and Prevention.1999;19(5): 287.
[35] RECALDE JP, PEDRO T, FOSTER C, et al. The talk test as a simple marker of ventilatory threshold. South African J Sports Med. 2002;9(2):5-8.
[36] CREEMERS N, FOSTER C, PORCARI JP, et al. The physiological mechanism behind the talk test. Kinesiology. 2017;(1):3-8.
[37] Yasuda T, Abe T, Brechue WF, et al. Venous blood gas and metabolite response to low-intensity muscle contractions with external limb compression. Metabolism. 2010;59(10):1510-1519. |