| [1] Munshi NV.Gene regulatory networks in cardiac conduction system development. Circ Res. 2012;110(11):1525-1537.[2] Meyers JD,Jay PY,Rentschler S.Reprogramming the conduction system: Onward toward a biological pacemaker. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2016;26(1):14-20.[3] Nam YJ,Lubczyk C,Bhakta M,et al.Induction of diverse cardiac cell types by reprogramming fibroblasts with cardiactranscriptionfactors.Development. 2014;141(22): 4267-4278.[4] Bressan M,Yang PB,Louie JD,et al.Reciprocal myocardial- endocardial interactions pattern the delay in atrioventricular junction conduction.Development. 2014;141(21):4149-4157.[5] Samsa LA,Yang B, Liu J.Embryonic cardiac chamber maturation: Trabeculation, conduction, and cardiomyocyte proliferation.Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2013; 163C(3):157-168.[6] Gassanov N,Er F,Zagidullin N,et al.Endothelin induces differentiation of ANP-EGFP expressing embryonic stem cells towards a pacemaker phenotype. FASEB J.2004; 18(14): 1710-1712.[7] Chen M,LinYQ,Xie SL,et al.Mitogen-activated protein kinase in endothelin-1-induced cardiac differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells.J Cell Biochem. 2010; 111(6): 1619-1628.[8] Zhang X,Zhang CS,Liu YC,et al.Isolation, culture and characterization of cardiac progenitor cells derived from human embryonic heart tubes. Cells Tissues Organs. 2009; 190(4):194-208.[9] Draus JM Jr,Hauck MA,Goetsch M,et al.Investigation of somatic NKX2-5 mutations in congenital heart disease.J Med Genet.2009; 46(2):115-122.[10] George V,Colombo S,Targoff KL.An early requirement for nkx2.5 ensures the first and second heart fieldventricular identity and cardiac function into adulthood.Dev Biol. 2015; 400(1):10-22.[11] Harris BS,Spruill L,Edmonson AM,et al.Differentiation of cardiac Purkinje fibers requires precise spatiotemporal regulation of Nkx2.5 expression. Dev Dyn.2006; 235(1): 38-49.[12] Briggs LE, Takeda M, Cuadra AE,et al.Perinatal loss of Nkx2.5 results in rapid conduction and contraction defects. Circ Res. 2008;103(6):580-590.[13] Waldron L, Steimle JD, Greco TM,et al.The Cardiac TBX5 Interactome Reveals a Chromatin Remodeling Network Essential for Cardiac Septation. Dev Cell. 2016;36(3): 262-275.[14] Moskowitz IP, Kim JB, Moore ML,et al.A molecular pathway including Id2, Tbx5, and Nkx2-5 required for cardiac conduction system development.Cell. 2007; 129(7): 1365-1376.[15] Patel R,Kos L.Endothelin-1 and Neuregulin-1 convert embryonic cardiomyocytes into cells of the conduction system in the mouse.Dev Dyn. 2005; 233(1):20-28.[16] Mikawa T,Hurtado R.Development of the cardiac conduction system. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2007;18(1):90-100.[17] Han H, Chen Y, Liu G,et al.GATA4 transgenic mice as an in vivo model of congenital heart disease.Int J Mol Med. 2015; 35(6):1545-1553.[18] Luna-Zurita L,Stirnimann CU,Glatt S,et al.Complex Interdependence Regulates Heterotypic Transcription Factor Distributionand Coordinates Cardiogenesis.Cell. 2016;164(5): 999-1014.[19] Wang L,Liu Z,Yin C,etal.Stoichiometry of Gata4, Mef2c, and Tbx5 influences the efficiency and quality of induced cardiac myocyte reprogramming.Circ Res. 2015;116(2):237-244.[20] Linhares VL,Almeida NA,Menezes DC,et al.Transcriptional regulation of the murine Connexin40 promoter by cardiac factors Nkx2-5, GATA4 and Tbx5. Cardiovasc Res. 2004; 64(3):402-411.[21] Hua LL,Vedantham V,Barnes RM,et al.Specification of the mouse cardiac conduction system in the absence of Endothelin signaling.Dev Biol.2014; 393(2):245-254.[22] Asai R,Kurihara Y,Fujisawa K,et al.Endothelin receptor type A expression defines a distinct cardiac subdomain within the heart field and is later implicated in chamber myocardium formation. Development.2010; 137(22):3823-3833.[23] Andrés-Delgado L, Mercader N.Interplay between cardiac function and heart development.BiochimBiophys Acta. 2016; 1863(7 Pt B):1707-1716.[24] Zhang HH, Huang J, DüvelK,etal.Insulin stimulates adipogenesis through the Akt-TSC2-mTORC1 pathway. PLoS One. 2009; 4(7):e6189.[25] Isomoto S,Hattori K,Ohgushi H,et al.Rapamycin as an inhibitor of osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Sci. 2007; 12(1):83-88.[26] Csibi A, Cornille K, Leibovitch MP,et al.The translation regulatory subunit eIF3f controls the kinase-dependent mTOR signaling required for muscle differentiation and hypertrophy in mouse. PLoS One.2010; 5(2):e8994.[27] Endo M,Antonyak MA,Cerione RA.Cdc42-mTOR signaling pathway controls Hes5 and Pax6 expression in retinoic acid-dependent neural differentiation.J Biol Chem. 2009; 284(8):5107-5118. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
内皮素1:内皮素(endothelin,ET)广泛存在于各种组织和细胞中,心血管系统起主要作用的是内皮素1。内皮素1是调节心血管功能的重要因子,对维持基础血管张力与心血管系统稳态起重要作用。
P19细胞:P19细胞是一类来源于C3H/He小鼠、具有多分化潜能的胚胎癌细胞。P19细胞体外培养条件简便,并且能够被诱导分化为骨骼肌细胞、心肌细胞和神经胶质细胞等多种细胞类型。由于P19细胞易于转染并稳定表达目的基因,因此常借助转基因或基因敲除等操作技术来深入了解细胞增殖和诱导分化的具体调控机制。
文题释义:
内皮素1:内皮素(endothelin,ET)广泛存在于各种组织和细胞中,心血管系统起主要作用的是内皮素1。内皮素1是调节心血管功能的重要因子,对维持基础血管张力与心血管系统稳态起重要作用。
P19细胞:P19细胞是一类来源于C3H/He小鼠、具有多分化潜能的胚胎癌细胞。P19细胞体外培养条件简便,并且能够被诱导分化为骨骼肌细胞、心肌细胞和神经胶质细胞等多种细胞类型。由于P19细胞易于转染并稳定表达目的基因,因此常借助转基因或基因敲除等操作技术来深入了解细胞增殖和诱导分化的具体调控机制。.jpg) 文题释义:
内皮素1:内皮素(endothelin,ET)广泛存在于各种组织和细胞中,心血管系统起主要作用的是内皮素1。内皮素1是调节心血管功能的重要因子,对维持基础血管张力与心血管系统稳态起重要作用。
P19细胞:P19细胞是一类来源于C3H/He小鼠、具有多分化潜能的胚胎癌细胞。P19细胞体外培养条件简便,并且能够被诱导分化为骨骼肌细胞、心肌细胞和神经胶质细胞等多种细胞类型。由于P19细胞易于转染并稳定表达目的基因,因此常借助转基因或基因敲除等操作技术来深入了解细胞增殖和诱导分化的具体调控机制。
文题释义:
内皮素1:内皮素(endothelin,ET)广泛存在于各种组织和细胞中,心血管系统起主要作用的是内皮素1。内皮素1是调节心血管功能的重要因子,对维持基础血管张力与心血管系统稳态起重要作用。
P19细胞:P19细胞是一类来源于C3H/He小鼠、具有多分化潜能的胚胎癌细胞。P19细胞体外培养条件简便,并且能够被诱导分化为骨骼肌细胞、心肌细胞和神经胶质细胞等多种细胞类型。由于P19细胞易于转染并稳定表达目的基因,因此常借助转基因或基因敲除等操作技术来深入了解细胞增殖和诱导分化的具体调控机制。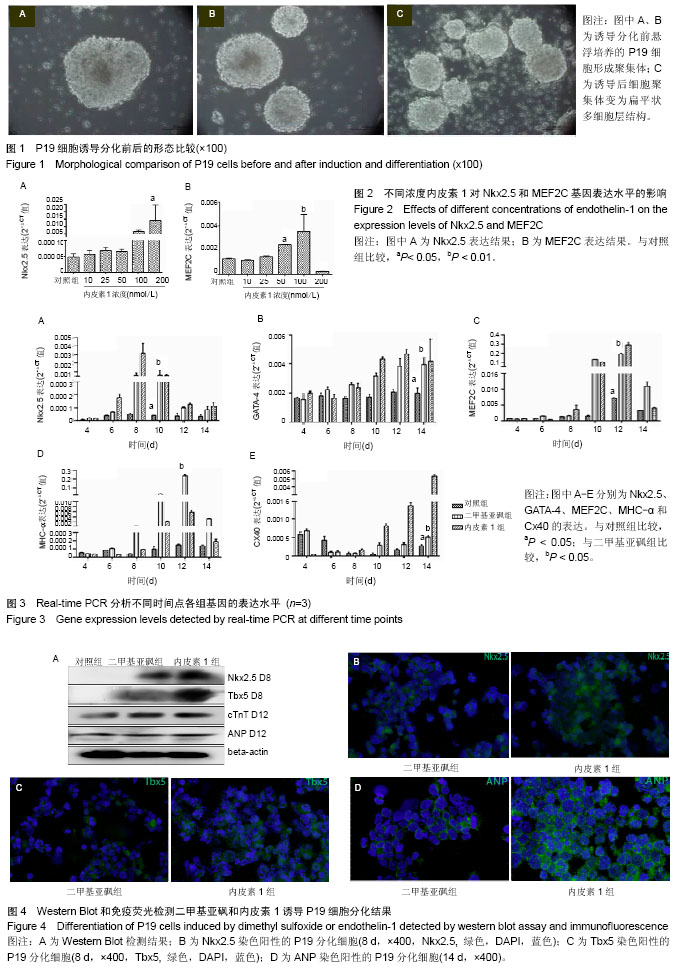
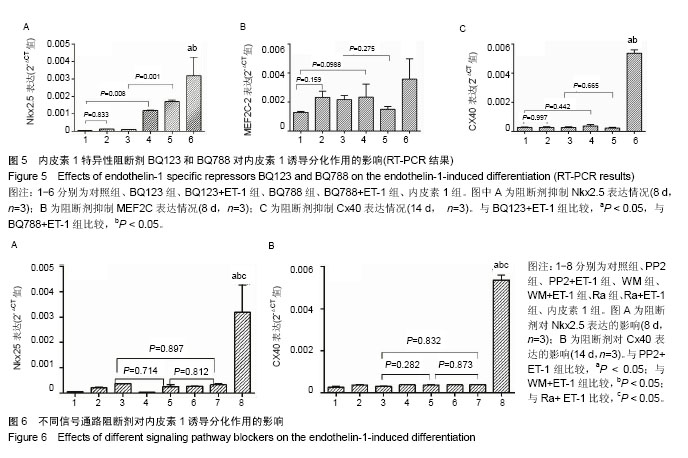
.jpg) 文题释义:
内皮素1:内皮素(endothelin,ET)广泛存在于各种组织和细胞中,心血管系统起主要作用的是内皮素1。内皮素1是调节心血管功能的重要因子,对维持基础血管张力与心血管系统稳态起重要作用。
P19细胞:P19细胞是一类来源于C3H/He小鼠、具有多分化潜能的胚胎癌细胞。P19细胞体外培养条件简便,并且能够被诱导分化为骨骼肌细胞、心肌细胞和神经胶质细胞等多种细胞类型。由于P19细胞易于转染并稳定表达目的基因,因此常借助转基因或基因敲除等操作技术来深入了解细胞增殖和诱导分化的具体调控机制。
文题释义:
内皮素1:内皮素(endothelin,ET)广泛存在于各种组织和细胞中,心血管系统起主要作用的是内皮素1。内皮素1是调节心血管功能的重要因子,对维持基础血管张力与心血管系统稳态起重要作用。
P19细胞:P19细胞是一类来源于C3H/He小鼠、具有多分化潜能的胚胎癌细胞。P19细胞体外培养条件简便,并且能够被诱导分化为骨骼肌细胞、心肌细胞和神经胶质细胞等多种细胞类型。由于P19细胞易于转染并稳定表达目的基因,因此常借助转基因或基因敲除等操作技术来深入了解细胞增殖和诱导分化的具体调控机制。