| [1] Shi Y, Hu G, Su J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: a new strategy for immunosuppression and tissue repair.Cell Res. 2010;20(5):510-518.[2] El Agha E, Kramann R, Schneider RK, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Fibrotic Disease.Cell Stem Cell. 2017;21(2): 166-177.[3] Prabhu SD, Frangogiannis NG.The Biological Basis for Cardiac Repair After Myocardial Infarction: From Inflammation to Fibrosis.Circ Res. 2016;119(1):91-112.[4] HaiderHKh, Ashraf M.Bone marrow cell transplantation in clinical perspective.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2005;38(2):225-235.[5] Ali EHA, Ahmed-Farid OA, Osman AAE.Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate sodium nitrite-induced hypoxic brain injury in a rat model.Neural Regen Res. 2017; 12(12):1990-1999.[6] Teng X, Chen L, Chen W, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Improve the Microenvironment of Infarcted Myocardium Contributing to Angiogenesis and Anti-Inflammation.Cell PhysiolBiochem. 2015;37(6): 2415-2424.[7] Han D, Huang W, Li X, et al. Melatonin facilitates adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells to repair the murine infarcted heart via the SIRT1 signaling pathway.J Pineal Res. 2016;60(2):178-192.[8] Huang W, Fan W, Wang Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells in alleviating sepsis-induced mice cardiac dysfunction via inhibition of mTORC1-p70S6K signal pathway.Cell Death Discov. 2017;3:16097.[9] Joggerst SJ, Hatzopoulos AK.Stem cell therapy for cardiac repair: benefits and barriers.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2009;11: e20.[10] Gnecchi M, He H, Liang OD, et al. Paracrine action accounts for marked protection of ischemic heart by Akt-modified mesenchymal stem cells.Nat Med. 2005;11(4):367-368.[11] Pers YM, Ruiz M, Noël D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells for the management of inflammation in osteoarthritis: state of the art and perspectives.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(11): 2027-2035.[12] Enomoto M.The future of bone marrow stromal cell transplantation for the treatment of spinal cord injury.Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(3):383-384.[13] HaiderHKh, Ashraf M.Implantation of genetically manipulated BM cells for cardiac repair.Cytotherapy. 2005;7(1):74-75.[14] Kim SW, Houge M, Brown M, et al. Cultured human bone marrow-derived CD31(+) cells are effective for cardiac and vascular repair through enhanced angiogenic, adhesion, and anti-inflammatory effects.J Am CollCardiol. 2014;64(16): 1681-1694.[15] Chen L, Zhang Y, Tao L, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells with eNOS Over-Expression Enhance Cardiac Repair in Rats with Myocardial Infarction.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2017;31(1): 9-18.[16] Toma C, Pittenger MF, Cahill KS, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells differentiate to a cardiomyocyte phenotype in the adult murine heart.Circulation. 2002;105(1):93-98.[17] Westman PC, Lipinski MJ, Luger D, et al. Inflammation as a Driver of Adverse Left Ventricular Remodeling After Acute Myocardial Infarction.J Am CollCardiol. 2016;67(17): 2050-2060.[18] Prabhu SD, Frangogiannis NG.The Biological Basis for Cardiac Repair After Myocardial Infarction: From Inflammation to Fibrosis.Circ Res. 2016;119(1):91-112.[19] Reesink HL, Sutton RM, Shurer CR, et al. Galectin-1 and galectin-3 expression in equine mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs), synovial fibroblasts and chondrocytes, and the effect of inflammation on MSC motility.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017; 8(1):243.[20] Chen Z, Eadie AL, Hall SR, et al. Assessment of hypoxia and TNF-alpha response by a vector with HRE and NF-kappaB response elements.Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2017;9:46-54. |
.jpg)
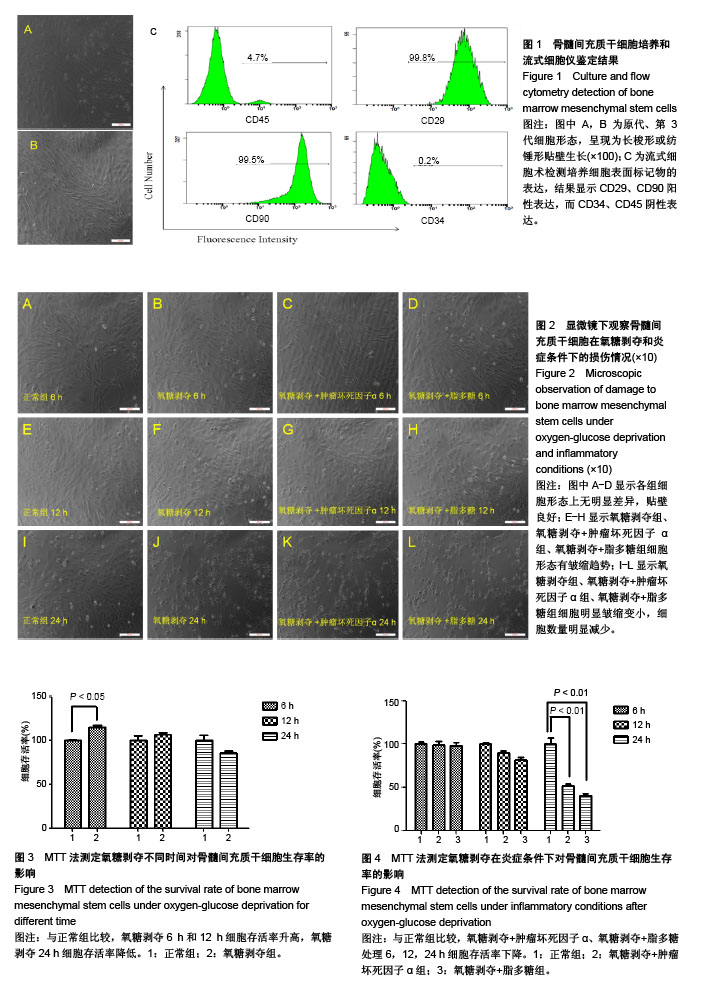

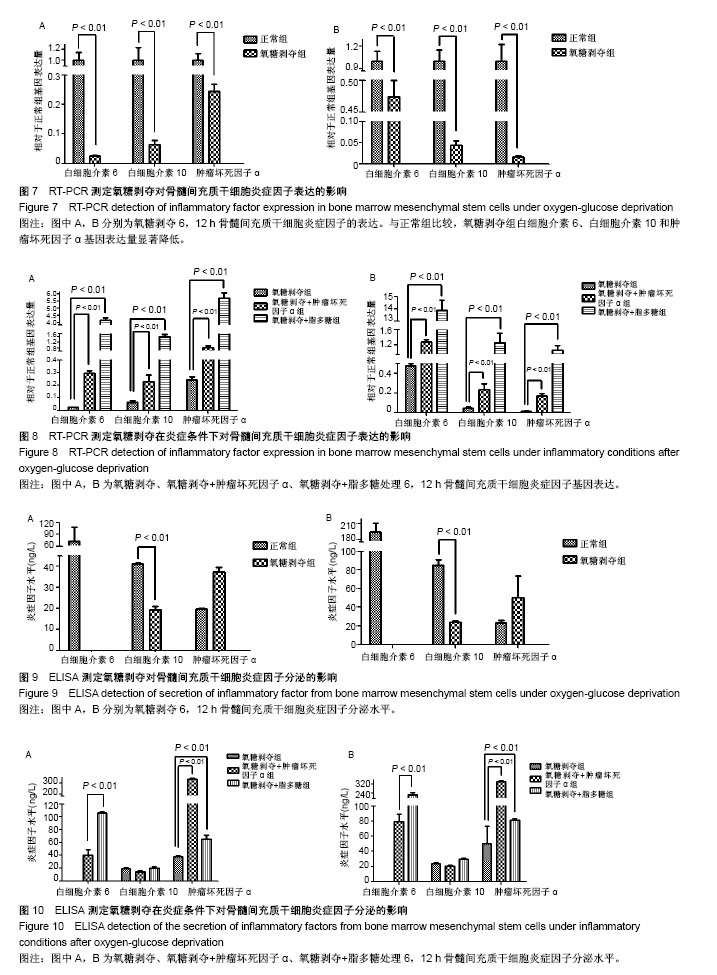
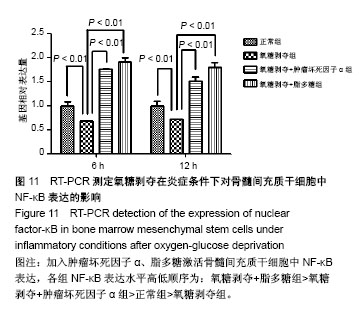
.jpg)
.jpg)