| [1] Pop DM, Sori??u O, ?u?man S, et al. Potential of placental-derived human mesenchymal stem cells for osteogenesis and neurogenesis. Rom J MorpholEmbryol. 2015;56(3):989-996.[2] Nitkin CR, Bonfield TL.Concise Review: Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Pediatric Disease: Perspectives on Success and Potential Improvements.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(2):539-565.[3] Caplan AI.All MSCs are pericytes?Cell Stem Cell. 2008;3(3):229-230.[4] Parekkadan B, Milwid JM.Mesenchymal stem cells as therapeutics. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2010;12:87-117.[5] Wegmeyer H, Bröske AM, Leddin M, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell characteristics vary depending on their origin.Stem Cells Dev. 2013; 22(19):2606-2618.[6] Gucciardo L, Ochsenbein-Kölble N, Ozog Y, et al. A comparative study on culture conditions and routine expansion of amniotic fluid-derived mesenchymal progenitor cells.Fetal DiagnTher. 2013;34(4):225-235.[7] Sun B, Meng XH, Liu R, et al. Mechanism study for hypoxia induced differentiation of insulin-producing cells from umbilical cord blood- derived mesenchymal stem cells.BiochemBiophys Res Commun. 2015;466(3):444-4449.[8] 牛婷,李爱斌,曹景云,等.胎盘间充质干细胞的应用研究[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(32):5236-5242.[9] 郝白露,杨瑞峰,彭祥炽,等.改良的人脐带间充质干细胞培养方法[J].中国计划生育学杂志,2013,21(1):44-49.[10] 庞荣清,何洁,李福兵,等.一种简单的人脐带间充质干细胞分离培养方法[J].中华细胞与干细胞杂志(电子版),2011, 1(2):30-33.[11] 刘巨超,张兰,张博峰. 新生大鼠肝细胞分离及体外培养方法[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(53):10465-10468.[12] 王绮雯,吴启端,陈奕芝.温胰蛋白酶消化法和冷消化法培养乳鼠心肌细胞的比较[J].中国医药指南,2013,11(20):401-403.[13] 张飞,王一雄,武忠炎,等.人脐带间充质干细胞生物特性比较:胰酶冷消化和组织块法体外培养[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(41):6614-6619.[14] 刘芳,杨辉,汪兆艳.自体骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗唐氏综合征临床观察[J].转化医学杂志,2016,5(5):288-290.[15] Li J, Wei Y, Yan L, et al. Multiplacenta derived stem cell/cytokine treatment increases survival time in a mouse model with radiation- induced bone marrow damage. Cytotechnology. 2016; 68(6): 2677-2686.[16] 高舒平,曲春辉,周瑞. 干细胞与转化医学研究进展浅析[J].中国实验动物学报,2016,24(4):440-442.[17] Du WJ, Chi Y, Yang ZX, et al. Heterogeneity of proangiogenic features in mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue, umbilical cord, and placenta.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):163.[18] Wegmeyer H, Bröske AM, Leddin M, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell characteristics vary depending on their origin.Stem Cells Dev. 2013; 22(19):2606-2618.[19] Gucciardo L, Ochsenbein-Kölble N, Ozog Y, et al. A comparative study on culture conditions and routine expansion of amniotic fluid-derived mesenchymal progenitor cells.Fetal DiagnTher. 2013;34(4):225-235.[20] Beane OS, Fonseca VC, Cooper LL, et al. Impact of aging on the regenerative properties of bone marrow-, muscle-, and adipose- derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells.PLoS One. 2014;9(12): e115963.[21] Bryzek A, Czekaj P, Plewka D, et al. Expression and co-expression of surface markers of pluripotency on human amniotic cells cultured in different growth media.Ginekol Pol. 2013;84(12):1012-1024.[22] 姚旺祥,裴国献,刘勇,等.兔胎盘源性间充质干祖细胞的分离方法比较[J]. 生物医学工程与临床,2007,11(2):85-87. [23] 马树立,李芳,徐彪,等.胎盘各组织来源间充质干细胞生物学特性比较[J].国际免疫学杂志,2013,36(5):397-401. |
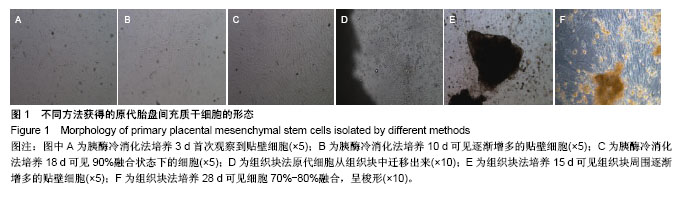
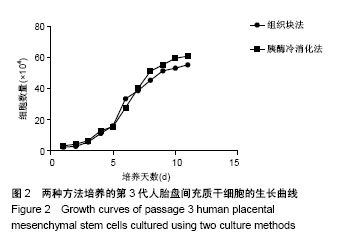
.jpg)
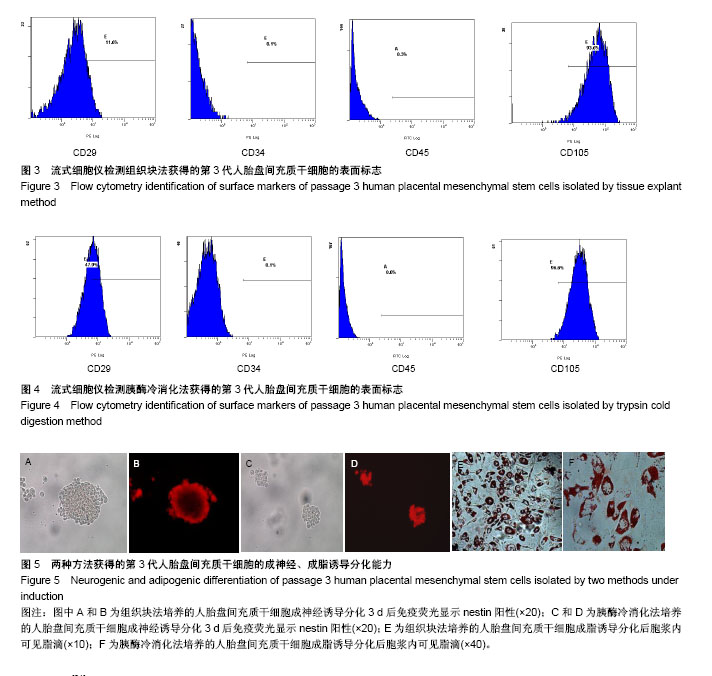
.jpg)